Impairments found in neurons derived from people with schizophrenia and genetic mutation
UMass Amherst molecular neuroscientist continues research with $2.25 million grant
2021-07-14
(Press-News.org) A scientific team has shown that the release of neurotransmitters in the brain is impaired in patients with schizophrenia who have a rare, single-gene mutation known to predispose people to a range of neurodevelopmental disorders.
Significantly, the results from the research with human-derived neurons validated previous and new experiments that found the same major decrease in neurotransmitter release and synaptic signaling in genetically engineered human neurons with the same genetic variant - the deletion of neurexin 1 (NRXN1). NRXN1 is a protein-coding gene at the synapse, a cellular junction that connects two nerve cells to communicate efficiently.
Both the research with human-derived and engineered human neurons also found an increase in the levels of CASK, an NRXN1-binding protein, which were associated with changes in gene expression.
"Losing one copy of this neurexin 1 gene somehow contributes to the etiology or the disease mechanism in these schizophrenia patients," says molecular neuroscientist ChangHui Pak, assistant professor of biochemistry and molecular biology at the University of Massachusetts Amherst and lead author of the research published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. "It causes a deficit in neural communication."
Pak is quick to add that although this single-gene mutation puts people at risk for schizophrenia, autism, Tourette syndrome and other neuropsychiatric disorders, "at the end of the day, we don't know what causes schizophrenia. This variant gives us insight into what cellular pathways would be perturbed among people with schizophrenia and a lead to study this biology."
When she conducted most of the research, Pak was working in the Stanford University lab of Thomas Südhof, a neuroscientist who shared the 2013 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for helping to lay the molecular basis for brain chemistry, including neurotransmitter release.
The research team obtained cell specimens from schizophrenia patients with an NRXN1 deletion who donated samples to a national biorepository for genetic studies of psychiatric disorders. Pak and colleagues converted the participants' specimens into stem cells and then turned them into functional neurons to study. "We're rewinding these cells back, almost like a time machine - what did these patients' brains look like early on," Pak explains.
Labs at Stanford, Rutgers University and FUJIFILM Cellular Dynamics were independently involved in the generation and analysis of neurons. For comparison with the human-derived neurons, Pak and team also created human neurons from embryonic stem cells, engineering them to have one less copy of the NRXN1 gene. With engineered human neurons, they had previously noted the neurotransmitter impairment and were interested in whether they would have the same findings with patient-derived neurons.
"It was good to see the consistent biological finding that indeed the neurexin 1 deletion in these patients actually does mess up their neuronal synaptic communication, and secondly that this is reproducible across different sites whoever does the experiment," Pak says.
Notably, the researchers did not see the same decrease in neurotransmitter release and other effects in engineered mouse neurons with analogous NRXN1 deletion. "What this suggests is there is a human-specific component to this phenotype. The human neurons are particularly vulnerable to this genetic insult, compared to other organisms, adding to the value of studying human mutations in human cellular systems," Pak says.
Being able to reproduce the results is key to the development of drugs that can better treat schizophrenia. "Everything was done blindly and at different sites. We wanted to not only learn about the biology but also be at the top of our game to ensure rigor and reproducibility of these findings," Pak says. "We showed the field how this can be done."
Pak and her team are now continuing the research in the Pak Lab, supported by a five-year, $2.25 million grant from the National Institute of Mental Health. The scientists are using the latest stem cell and neuroscience methodologies to explore the molecular basis of synaptic dysfunction in schizophrenia and other neuropsychiatric disorders.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-14
WACO, Texas (July 13, 2021) - Climate change mitigation efforts have led to shifts from fossil-fuel dependence to large-scale renewable energy. However, renewable energy sources require significant land and could come at a cost to ecosystems. A new study led by Ryan McManamay, Ph.D., assistant professor of environmental science at Baylor University, evaluates potential conflicts between alternative energy strategies and biodiversity conservation.
The study, published in Biological Conservation, evaluates potential tradeoffs between climate benefits ...
2021-07-13
Cancer survivors ages 18 to 64 faced fewer financial barriers to health care after the Affordable Care Act was implemented than they did before the landmark law took effect, University of Michigan researchers found.
In fact, they believe the ACA helped the financial burden (problems related to the cost of medical care) for younger cancer survivors fall to its lowest estimated levels in 20 years.
"There has been a lot of talk about the ACA affecting people who don't have the Medicare safety net," said Christopher Su, M.D., a clinical fellow in the division of hematology and oncology at Michigan Medicine and the first author of the paper. "We were able to drill down to that and show that it did make a difference to younger cancer ...
2021-07-13
The COVID-19 pandemic and the situations of stress and sadness associated with it have not significantly increased the prevalence of depression and anxiety among participants in the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brazil) who live in the city of São Paulo.
ELSA-Brazil has been monitoring the overall health of 15,000 civil servants at six public universities and research centers in Brazil since 2008. The survey on mental health during the pandemic was conducted in São Paulo and involved 2,117 members of the staff of the University of São Paulo (USP) - in active service or retired - who are participants in the nationwide study and aged 50-80.
The survey is supported by São Paulo Research Foundation ...
2021-07-13
In early March 2020, the University of Washington became the first four-year U.S. university to transition to online-only classes due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Many researchers predicted severe consequences of these physical distancing measures. To understand how this change affected college students' mental health, UW researchers surveyed 147 UW students over the 2020 spring quarter, which began shortly after the university transitioned to online-only classes. The team compared the students' responses to a previous survey of 253 students in spring quarter 2019.
The researchers didn't see much change in average levels of students' depressive symptoms, anxiety, stress or loneliness between 2019 and 2020 or between the beginning and the end of spring quarter ...
2021-07-13
Magnetars are bizarre objects -- massive, spinning neutron stars with magnetic fields among the most powerful known, capable of shooting off brief bursts of radio waves so bright they're visible across the universe.
A team of astrophysicists has now found another peculiarity of magnetars: They can emit bursts of low energy gamma rays in a pattern never before seen in any other astronomical object.
It's unclear why this should be, but magnetars themselves are poorly understood, with dozens of theories about how they produce radio and gamma ray bursts. The recognition of this unusual pattern of gamma ray activity ...
2021-07-13
Bacterial vaginosis is the most common and recurrent gynecological condition affecting nearly 30% of women between the ages of 15 and 44, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. A University of Arizona Health Sciences-led study recently identified a specific bacteria family and uncovered how it contributes to bacterial vaginosis, paving the way for new insights into disease prevention and treatment.
Led by Melissa Herbst-Kralovetz, PhD, a member of the BIO5 Institute and associate professor of basic medical sciences at the College of Medicine - Phoenix, researchers found that members of the Veillonellaceae bacteria family contribute to an increase in inflammation and cell death, and alter the acidity of the cervical microenvironment. These changes support bacterial ...
2021-07-13
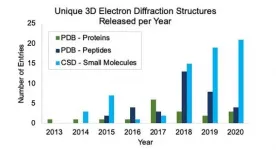
CAMBRIDGE July 13, 2021 - To date, solving structures of potential therapeutics using X-ray diffraction (XRD) has been an assumed, pivotal step in the drug development process. But a recent paper by a team of researchers led by NanoImaging Services shows how microcrystal electron diffraction (MicroED) is growing to obtain the structures of potential pharmaceuticals.
Three-dimensional crystal structures that show the relative positions of atoms, bonds and intramolecular interactions are needed to understand stability, reactivity, solubility and, ultimately, suitability ...
2021-07-13
New Rochelle, NY, July 13, 2021--Males with COVID-19 had significantly higher rates of hospitalization and of transfer to the intensive care unit (ICU) according to a new study. A higher percentage of males died of COVID-19 compared to females, as reported in the study published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Women's Health. Click here to read the article now.
Joanne Michelle Gomez, MD, Rush University Medical Center, and coauthors, studied the first 8,108 positive COVID-19 patients that presented to the Rush University System from March 1-June 21, 2020. Nineteen percent of males required hospitalization, compared to 13% of females. ...
2021-07-13
In a new study of adults from the general population who were infected with COVID-19 in 2020, more than a quarter report not having fully recovered after six to eight months. Those findings are described this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Milo Puhan and colleagues at the University of Zurich, Switzerland.
While initial public health responses to the SARS-CoV-2 virus focused on reducing the acute burden of COVID-19, a growing body of evidence indicates that the infection can also result in longer-term physical and mental health consequences. These long-term consequences, currently referred to as "post-COVID-19 syndrome" or "Long Covid" are ...
2021-07-13
COVID-19 vaccination strategies in the United States are informed by individual characteristics such as age and occupation. A study published in the open access journal PLOS Medicine by Sasikiran Kandula and Jeffrey Shaman of Columbia University, New York, United States suggests that including socioeconomic indicators as prioritization criteria for vaccination may help minimize severe outcomes, particularly deaths.
Efforts to reduce COVID-19 mortality rates in the US have focused on prioritizing vaccination initially for those at a higher risk of severe outcomes. The effectiveness of population-level ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Impairments found in neurons derived from people with schizophrenia and genetic mutation
UMass Amherst molecular neuroscientist continues research with $2.25 million grant