Quantum physics helps destroy cancer cells
Researchers have found a way to enhance radiation therapy using novel iodine nanoparticles
2021-07-14
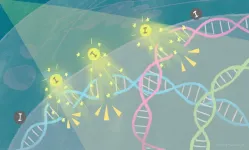
(Press-News.org) Cancer cell death is triggered within three days when X-rays are shone onto tumor tissue containing iodine-carrying nanoparticles. The iodine releases electrons that break the tumor's DNA, leading to cell death. The findings, by scientists at Kyoto University's Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS) and colleagues in Japan and the US, were published in the journal Scientific Reports.
"Exposing a metal to light leads to the release of electrons, a phenomenon called the photoelectric effect. An explanation of this phenomenon by Albert Einstein in 1905 heralded the birth of quantum physics," says iCeMS molecular biologist Fuyuhiko Tamanoi, who led the study. "Our research provides evidence that suggests it is possible to reproduce this effect inside cancer cells."
A long-standing problem with cancer radiation therapy is that it is not effective at the center of tumors where oxygen levels are low due to the lack of blood vessels penetrating deeply into the tissue. X-ray irradiation needs oxygen to generate DNA-damaging reactive oxygen when the rays hit molecules inside the cell.
Tamanoi, together with Kotaro Matsumoto and colleagues have been trying to overcome this issue by finding more direct ways to damage cancer DNA. In earlier work, they showed that gadolinium-loaded nanoparticles could kill cancer cells when irradiated with 50.25 kiloelectron volts of synchrotron-generated X-rays.
In the current study, they designed porous, iodine-carrying organosilica nanoparticles. Iodine is cheaper than gadolinium and releases electrons at lower energy levels.
The researchers dispersed their nanoparticles through tumor spheroids, 3D tissue containing multiple cancer cells. Irradiating the spheroids for 30 minutes with 33.2 keV of X-rays led to their complete destruction within three days. By systematically changing energy levels, they were able to demonstrate that the optimum effect of tumor destruction occurs with 33.2 keV X-ray.
Further analyses showed that the nanoparticles were taken up by the tumor cells, localizing just outside their nuclei. Shining just the right amount of X-ray energy onto the tissue prompted iodine to release electrons, which then caused double-strand breaks in the nuclear DNA, triggering cell death.
"Our study represents an important example of employing a quantum physics phenomenon inside a cancer cell," says Matsumoto. "It appears that a cloud of low-energy electrons is generated close to DNA, causing double strand breaks that are difficult to repair, eventually leading to programmed cell death."
The team next wants to understand how electrons are released from iodine atoms when they are exposed to X-rays. They are also working on placing iodine on DNA rather than near it to increase efficacy, and to test the nanoparticles on mouse models of cancer.
Key contributors to this work are Yuya Higashi (iCeMS), Hiroyuki Saitoh (QST) and Toshiki Tajima (UC Irvine, Dept. of Physics & Astronomy) in addition to Tamanoi and Matsumoto.
INFORMATION:
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-93429-9
About Kyoto University's Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS):
At iCeMS, our mission is to explore the secrets of life by creating compounds to control cells, and further down the road to create life-inspired materials.
https://www.icems.kyoto-u.ac.jp/
For more information, contact:
I. Mindy Takamiya/Christopher Monahan
cd@mail2.adm.kyoto-u.ac.jp
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-14
July 14, 2021 (Toronto) A new study from the World Health Organization's (WHO) International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), published in the journal Lancet Oncology, has found an association between alcohol and a substantially higher risk of several forms of cancer, including breast, colon, and oral cancers. Increased risk was evident even among light to moderate drinkers (up to two drinks a day), who represented 1 in 7 of all new cancers in 2020 and more than 100,000 cases worldwide.
In Canada, alcohol use was linked to 7,000 new cases of cancer in 2020, including 24 per cent of breast cancer cases, 20 per cent of colon cancers, 15 per cent of rectal cancers, and 13 per cent of oral and liver cancers.
"All ...
2021-07-14
As the Parker Solar Probe ventures closer to the sun, we are learning new things about our home star.
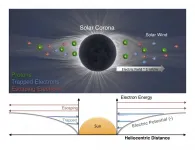
In a new study, physicists led by the University of Iowa report the first definitive measurements of the sun's electric field, and how the electric field interacts with the solar wind, the fast-flowing current of charged particles that can affect activities on Earth, from satellites to telecommunications.
The physicists calculated the distribution of electrons within the sun's electric field, a feat made possible by the fact that the Parker Solar Probe jetted within 0.1 astronomical units (AU), or a mere 9 million miles, from the sun--closer than any spacecraft has approached. From the electrons' distribution, the physicists ...
2021-07-14
For the first time, scientists have seen stony coral cells engulf dinoflagellates - single-celled, photosynthetic algae that are crucial for keeping coral alive
The researchers used a cell line called IVB5, which contains endoderm-like cells cultured from the stony coral, Acropora tenuis
Around 40% of coral cells incorporated the algae in around 30 minutes and remained healthy for one month
The research is a step towards understanding the partnership between coral and dinoflagellates and could shed light on how coral bleaching occurs
In a world-first, scientists in Japan have observed individual stony coral cells engulfing single-celled, photosynthetic algae.
The microscopic algae, known as dinoflagellates, were ...
2021-07-14
A new paper in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, published by Oxford University Press, indicates that disruptions in health care due to the COVID 19 pandemic may increase breast cancer deaths.
In March 2020 public health measures prohibited most elective procedures, including mammography, due to hospital capacity and limited personal protective equipment. This reduced mammograms up to 80%. Breast cancer patients also experienced treatment delays and reductions in planned or expected chemotherapy treatments.
Researchers here used three independently-developed breast cancer simulation models from the National Cancer Institute's Cancer Intervention and Surveillance Modeling Network to ...
2021-07-14
Washington/Philadelphia, July 14, 2021--New research finds that high school students who attended school remotely during the COVID-19 pandemic suffered socially, emotionally, and academically compared with those who attended in person.
The study was published today in Educational Researcher (ER) by researchers Angela L. Duckworth, Tim Kautz, Amy Defnet, Emma Satlof-Bedrick, Sean Talamas, Benjamin Lira, and Laurence Steinberg. ER is a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association.
"Many news stories have reported on individual stories of teenagers who have suffered from anxiety, depression, and other mental health challenges during the pandemic," said lead author Duckworth, ...
2021-07-14
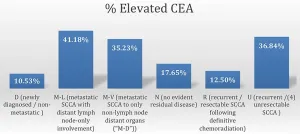
Oncotarget published "CEA as a blood-based biomarker in anal cancer" which reported that the mean Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) among subgroups by clinical status at the time of presentation to our institution was highest among those patients with metastatic Squamous cell carcinoma of the anal canal (SCCA) to visceral organs, however this finding was not statistically significant by ANOVA .
By clinical subgroup, the percentage of patients with an abnormally elevated CEA was highest in those patients with metastatic disease to lymph nodes followed by recurrent/unresectable SCCA , and metastatic SCCA ...
2021-07-14
New research published online in the International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction found that Canadians with a history of drug dependence are much less likely to have flourishing mental health and are more likely to have mental illness.
Researchers compared a nationally representative sample of 460 Canadians with a history of illicit drug dependence (excluding cannabis) to 20,305 Canadians with no history of illicit drug dependence using data drawn from Statistic Canada's Canadian Community Health Survey-Mental Health.
While 80% of those with a history of drug dependence were in remission, more than half (52.1%) were still experiencing mental illness. Further, only 37.9% were in excellent mental health, which is markedly lower than the 74.1% of ...
2021-07-14
Unlike other population-level stressful events such as natural disasters, COVID-19 has not resulted in a net increase in smoking, according to a new study from the International Tobacco Control (ITC) Project, at the University of Waterloo.
The researchers also found that although nearly half of smokers reported that COVID-19 made them think about quitting, the vast majority of smokers did not change their smoking habits during the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Led by Shannon Gravely, research assistant professor with the ITC Project, the study ...
2021-07-14
Before Millennials were over laugh-cry emojis, they were the most used emojis across the world, according to researchers at USC. The emoji was more popular than smiley faces say researchers who categorized millions of tweets across 30 countries and evaluated over 1700 emojis. Their study, "An empirical study of emoji usage on Twitter in linguistic and national contexts" was published in Online Social Networks and Media.
Mayank Kejriwal, a research assistant professor in the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering, and a research lead at the USC Information Sciences Institute who is the lead author on the paper, says approximately 100 emojis are used most often.
The most important take away? Emojis represent ...
2021-07-14
A new study by researchers at Queen Mary University of London, University of Oxford, Institute for Advanced Studies, Vienna, and the Medical University of Graz, has found that lateral flow tests detect Covid-19 with similar accuracy to laboratory-based PCR tests, providing they are used at the onset of infection and soon after symptoms start.
Lateral flow tests are cheaper and produce a result in just 30 minutes - much faster than the time it takes to receive a PCR test result, which can take 1-3 days. The finding could be pivotal to national strategies ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Quantum physics helps destroy cancer cells
Researchers have found a way to enhance radiation therapy using novel iodine nanoparticles