Researchers improve lab constraint on exotic spin interaction
2021-07-14
(Press-News.org) Prof. DU Jiangfeng, Prof. RONG Xing, and their colleagues from the Key Laboratory of Micromagnetic Resonance, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), set the most stringent laboratory constraint on the exotic spin- and velocity-dependent interaction at the micrometer scale. This study was published in Physical Review Letters.
The search for dark matter, dark energy, and extra forces is important for the understanding of the existence of the matter that accounts for about a quarter of the universe, but little progress has been made. It is necessary to theoretically and experimentally find particles outside the Standard Model, a tradition model for microscopic particles excluding dark matter, as candidates for dark matter.
The exotic spin interaction can be induced by new bosons outside the Standard Model, such as axons, axon-like bosons, dark photons and Z-bosons. Since its proposition in 1984, a series of sophisticated experiments have been made to explore these exotic spin interactions.
In this study, the researchers carried out an experimental exploration of the velocity-dependent exotic spin interactions. They used the quartz tuning fork to drive the mass source to make simple harmonic motion in the direction perpendicular to the diamond surface.
Then, they designed the experimental sequence to convert the exotic interaction to be explored into the quantum phase information of the single-spin quantum sensor. This experiment gave the laboratory limit on a type of velocity-dependent spin interaction at the micrometer scale. The limit at 200 microns is four orders of magnitude stricter than the bound established in the previous results based on the atomic spectra of Cesium, Ytterbium, and Thallium.
This study, as an interesting marriage of quantum sensing techniques and the test of fundamental interactions (traditionally in particle physics), is appealing to general physicists, and it provides an approach to probing new physics beyond the Standard Model.
Prof. DU's team has focused on research of the static exotic spin interaction. In 2018, it for the first time used nitrogen-vacancy defects in diamond as a single-spin sensor to search for exotic spin interactions (Nature Communications), and later set the most optimized constraint at the time on the micrometer scale on the spin-dependent exotic interaction with the single-spin sensor (Physical Review Letters), demonstrating the ability of the single-spin quantum sensor made from the single nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamond to explore new physical phenomena at the micro-nano scale.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-14
Shells of tamarind, a tropical fruit consumed worldwide, are discarded during food production. As they are bulky, tamarind shells take up a considerable amount of space in landfills where they are disposed as agricultural waste.
However, a team of international scientists led by Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has found a way to deal with the problem. By processing the tamarind shells which are rich in carbon, the scientists converted the waste material into carbon nanosheets, which are a key component of supercapacitors - energy storage devices that are used in automobiles, buses, electric vehicles, trains, and elevators.
The study reflects ...
2021-07-14
Osaka, Japan - When things get too much, we're often advised to "take a load off," but when it comes to bone maintenance, doing the opposite can be a good thing. Researchers from Japan have discovered some key mechanisms of how physical load stimulates bone growth.
In a study published July 13, 2021 at 11 a.m. ET in Cell Reports, researchers from the National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center Research Institute have revealed that the expression of the peptide osteocrin (OSTN) is influenced by load - decreasing when load is reduced, and increasing when it is added.
Bones and skeletal muscles are strengthened by the load associated with exercise, preventing bone and muscle atrophy, and maintaining bone and muscle strength is important for maintaining physical activity. ...
2021-07-14
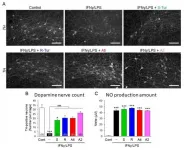
Researchers from Kumamoto University, Japan have found that a component derived from turmeric essential oil, aromatic turmerone (ar-turmerone), and its derivatives act directly on dopaminergic nerves to create a neuroprotective effect on tissue cultures of a Parkinson's disease model. This appears to be due to enhanced cellular antioxidant potency from the activation of Nrf2. The researchers believe that the ar-turmerone derivatives identified in this study can be used as new therapeutic agents for Parkinson's disease.
Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative disease caused by the ...
2021-07-14
When it comes to the medicinal and therapeutic properties of Cannabis sativa, an unsolved mystery is whether there exists an "entourage effect," whereby the pain-relieving effects of the plant as a whole are greater than any of its individual parts. New research from the University of Arizona Health Sciences has found evidence that favors the entourage effect theory and positions Cannabis terpenes, the part of the plant that provides flavor and aroma, as a promising new target for pain therapies that would require lower doses and produce fewer side effects.
"A lot of people are taking cannabis and cannabinoids for pain," said lead researcher John Streicher, PhD, a member ...
2021-07-14
An associate professor of marketing at The University of Texas at Arlington says digital avatars can replace a sales force and customer service employees at a fraction of the cost.
In this context, avatars are typically computer-generated representations of people. UTA Associate Professor Fred Miao says they can fill the void in interactive assistance that a majority of shoppers says they want.
"An Accenture survey of online shoppers shows that 62% never completed their purchases because there was no real-time customer service or support. That Accenture survey also shows that 90% of those shoppers wanted some sort of interactive assistance during the shopping process," said Miao, faculty fellow of the John Merrill Endowed Professorship ...
2021-07-14
Sea-level rise threatens to produce more frequent and severe flooding in coastal regions and is expected to cause trillions of dollars in damages globally if no action is taken to mitigate the issue. However, communities trying to fight sea-level rise could inadvertently make flooding worse for their neighbors, according to a new study from researchers at The University of Texas at Arlington and the Stanford Natural Capital Project published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Michelle Hummel, an assistant professor of civil engineering at UTA, was lead author of the report, which shows how seawalls constructed along the San Francisco Bay shoreline ...
2021-07-14
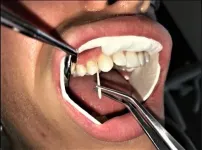
UW researchers reveal new aspects of gum disease and body's protective response
SEATTLE - A team led by University of Washington researchers has, for the first time, identified and classified how different people respond to the accumulation of dental plaque, the sticky biofilm that gathers on teeth. Their work, recently published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS), sheds important new light on why some people may be more prone to serious conditions that lead to tooth loss and other problems.
Left unchecked, plaque buildup can induce gingivitis, or gum inflammation. Gingivitis, ...
2021-07-14
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Oregon State University scientists are beginning to unravel the key microorganisms that contribute to the fermentation of kombucha, research that is already aiding large-scale kombucha producers in the fast-growing industry.
Kombucha is a fermented tea drink that has been homebrewed around the world for centuries, but in recent years has become widely popular with a global market size expected to grow from $1.3 billion in 2019 to $8.1 billion by 2027, according to an industry report. Several large producers, including Humm and Brew Dr., are based in Oregon.
Kombucha is produced by fermenting sugared tea using a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast, commonly referred to as SCOBY, and adding flavorings to enhance the taste. But ...
2021-07-14
Vaccine skepticism among young adults may stall efforts to achieve herd immunity - a threshold in which approximately 80 percent of a population is vaccinated against the coronavirus.
A study by UC San Francisco researchers found that about one in four unvaccinated people aged 18 to 25 said that they "probably will not" or "definitely will not" get the COVID-19 vaccination, despite the fact that this demographic has been found to be more likely than other age-groups to transmit coronavirus, jeopardizing the health of older unvaccinated adults and facilitating ...
2021-07-14
Each fingertip has more than 3,000 touch receptors, which largely respond to pressure. Humans rely heavily on sensation in their fingertips when manipulating an object. The lack of this sensation presents a unique challenge for individuals with upper limb amputations. While there are several high-tech, dexterous prosthetics available today - they all lack the sensation of "touch." The absence of this sensory feedback results in objects inadvertently being dropped or crushed by a prosthetic hand.
To enable a more natural feeling prosthetic hand interface, researchers from Florida Atlantic University's ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers improve lab constraint on exotic spin interaction