(Press-News.org) COLUMBUS, Ohio - Facebook posts by members of the U.S. Congress reveal the depth of the partisan divide over the COVID-19 pandemic, new research shows.
A study of all 12,031 Facebook posts concerning the pandemic by members of Congress between March and October 2020 showed that Democrats generally took a more negative or neutral tone on the issue, while Republicans were more likely to have a positive tone in their posts.
Public crises, like the pandemic, highlight how central social media is to messaging and how important it is to understand how rhetoric impacts engagement and sharing of messages said Laura Moses, co-author of the study and a doctoral student in political science at The Ohio State University.
"When members of Congress communicate with the public about the pandemic, there is not a 'rally around the flag' effect, suggesting a shift toward partisan politics," Moses said.
The study also found that Democrats posted more on COVID-19 than did Republicans, negative posts were shared more often than positive ones, and Republicans' posts attracted more engagement, such as "likes" and comments, than did Democrats' messages.
Moses conducted the study with Janet Box-Steffensmeier, professor of political science at Ohio State. Their results were published today (July 14, 2021) in the journal Science Advances.
These findings reflect the overall fractured nature of politics in the country today, Box-Steffensmeier said.
"We find partisan tone differences in messaging, even at the outset of the crisis" she said.
The researchers measured the tone in members' Facebook messages using a state-of-the-art machine learning tool that analyzed the text in each message. The tool looked for the use of words that are positive or negative to give an overall "sentiment" score for each message.
For example, a post offering a resource guide to staying safe and healthy was labeled positive. A message that criticized a Trump administration official for comparing lockdowns to slavery was labeled negative. A post that urged readers to wear a mask was marked as neutral.
Results showed that Democratic members posted an average of 26 times about COVID-19 during the period of the study, compared to 18 times for Republicans. The only pandemic-related issue that Republicans posted more about than Democrats was social distancing.
While Democrats tended to have a more negative tone than did Republicans, they were still slightly on the positive side overall. The one issue about which Democrats were more negative than positive was the postal service: Trump admitted to blocking funding for the postal service, and some Democrats tied this to delayed delivery of medicines, as well as interference with mail-in voting.
Many of the more negative posts by Democrats were critical of the Trump administration's response to the pandemic.
Republicans were most positive when discussing resources and sharing information related to the pandemic.
"For example, Democrats use a more negative tone when discussing the pandemic and the Trump administration than Republicans discussing the same topic," Moses said.
Democrats' tone shifted drastically relative to Republicans' after milestones that marked the severity of the pandemic, such as when COVID-19 deaths in the United States exceeded 100,000, the study found.
Overall, negative posts were more likely to be spread by Facebook users, meaning that Democrats saw an increase in their messages being shared. But Republicans saw an increase in engagement, meaning users commented on their posts or responded with one of the reaction emojis such as "like" or "love."
There was an increase in "sad" emoji reactions to the more negatively toned posts and to posts by more liberal members, results showed.
Negative tone also increased the use of the "haha" emoji, suggesting that users were replying with sarcasm or distaste.
The researchers noted that the study did not account for images or videos used in the posts, which may also affect the tone that Facebook users take away from a message.
Even with just the text, the study showed that tone impacts engagement with messaging from members of Congress. This has important implications for understanding how government can connect individuals with crucial information in emergent or pivotal moments, Box-Steffensmeier said.
"Facebook messages about COVID-19 suggest that members of Congress were not amplifying the public health or medical professional information about the global health emergency," she said.
"The divergence in tone between Democrats and Republicans suggests that members of are crafting messaging to represent their opinions or political identity, rather than sending a unified government response."
INFORMATION:
Contact: Janet Box-Steffensmeier, Box-Steffensmeier.1@osu.edu
Laura Moses, Moses.96@osu.edu
Written by Jeff Grabmeier, Grabmeier.1@osu.edu
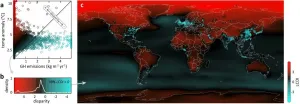
New research, led by the Monterey Bay Aquarium, illustrates the disparity between the narrow origins and far-reaching impacts of greenhouse emissions responsible for disrupting the global climate system. Published in Science Advances today, the study was built upon the most comprehensive accounting of global emissions from the burning of fossil fuels. It reveals that the regions generating the most emissions are different from those expected to suffer the most severe warming. The result of this comparison shows the fundamental disparities - quite literally putting them on the map - associated with where, and who, will experience the greatest impacts of climate change.
"One of the dirty tricks of climate change is that local pollution has far-reaching consequences," ...
An analysis of the tone used in pandemic-related social media posts from U.S. Congress members over an 8-month period in 2020 finds clear partisan differences, with Democrats using a slightly negative tone compared with Republicans, who appeared to use more strongly positive language in their COVID-19 messaging. Democrats were also far more likely than Republicans to use neutral language. The study also indicates that tone plays a critical role in elite communications, finding that the public engages more with content that has a negative tone. The study authors note that messaging from political elites during a crisis such ...
A new study on the effects of Airbnb listings on Boston neighborhoods suggests that the prevalence of listings may hamper local social dynamics that prevent crime. However, tourists themselves do not appear to generate or attract higher levels of crime. Babak Heydari, Daniel T. O'Brien, and Laiyang Ke of Northeastern University in Boston, MA, USA present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on July 14, 2021.
Widespread sentiment holds that Airbnb listings cause increased crime in residential neighborhoods. However, there has been limited research to explore and clarify this link.
To better understand the relationship ...
A team of international researchers, led by the University of Bologna, has discovered the fossilised remains of methane-cycling microbes that lived in a hydrothermal system beneath the seafloor 3.42 billion years ago.
The microfossils are the oldest evidence for this type of life and expand the frontiers of potentially habitable environments on the early Earth, as well as other planets such as Mars.
The study, published in the journal Science Advances, analysed microfossil specimens in two thin layers within a rock collected from the Barberton Greenstone Belt in South Africa. This region, near the border with Eswatini and Mozambique, contains some of the oldest and best-preserved sedimentary rocks ...
GALVESTON, TEXAS - A new study published in Science Translational Medicine reports on the Ebola vaccine-mediated protection of five mucosal vaccine vectors based on the human and avian paramyxoviruses. The study comprehensively characterized the antibody response to each vaccine, identifying features and functions that were elevated in survivors and that could serve as vaccine correlates of protection.
The multi-year study, led by Alexander Bukreyev, PhD, of the University of Texas Medical Branch (UTMB) Galveston National Laboratory looked at whether all the vaccines conferred protection and produced ...
BUFFALO, N.Y. - Write down the benefits of obtaining a college degree and, more than likely, all the items on the completed list will relate to graduates: higher salaries, autonomous jobs and better access to health care, for instance. All of those factors, supported by extensive research, help draw a direct line connecting higher education and health. Similar research suggests how the education of parents affects their children.
Now, two University at Buffalo sociologists have used a new wave of data from a survey launched in 1994 to further extend the geometry linking educational attainment and health that demonstrates another dimension of the intergenerational effects ...
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- A new study from the University of Missouri found the unanticipated transitions to virtual schooling due to COVID-19 exposed the lack of digital resources among Black families in the United States, including access to Wi-Fi and technological savviness. As two-thirds of the country's Black children are born into single-parent households, the findings help explain the extensive stress virtual schooling caused for many Black families trying to keep their children learning and engaged online while at home during the pandemic.
"What we found was parents and caregivers often felt disempowered in the rapidly changing environment, as they did not necessarily feel equipped with the tools or technological savviness to effectively engage in their children's ...
T lymphocytes, or T cells, are immune cells with diverse roles in building the body's immunity. How does one particular cell type fight against a host of different pathogens? The key to this adaptability is in alternative splicing, wherein the cell produces multiple forms of proteins for identifying different types of invading viruses and microbes, as well as destroying cancer cells. So, it is not surprising that finding ways to improve the production of T cells with enhanced pathogen recognition capacity is an actively researched area of modern science.
In 2011, scientists from the Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) in Korea discovered a protein called NSrp70, which ...
Urea is a critical element found in everything from fertilizers to skin care products. Large-scale production of urea, which is naturally a product of human urine, is a massive undertaking, making up about 2% of global energy use and emissions today.
For decades, scientists and engineers have sought to make this process more energy efficient as demand for fertilizer grows with increased population. An international research team that includes scientists and engineers from The University of Texas at Austin has devised a new method for making urea that is more environmentally friendly than today's process ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Roadless national forests in the American West burn more often and at a slightly higher severity than national forests with roads, but the end result for the roadless forests is greater fire resilience, Oregon State University researchers say.
The findings, published today in Environmental Research Letters, provide a key piece of the puzzle for a region trying to develop better approaches to living with fire in the wake of a 2020 fire season that brought historically disastrous blazes.
Limiting smoke exposure and reducing risk to water supplies, habitat and human infrastructure from huge, uncontrolled fires are important goals of policymakers, said James Johnston, a researcher in the OSU College of Forestry and the ...