A genome of photosynthetic animals decoded
Genome analysis reveals chloroplast acquisition without gene transfer in photosynthetic sea slugs
2021-07-15
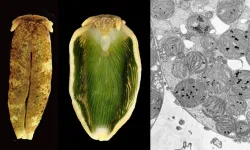
(Press-News.org) Plants, algae and some bacteria are able to perform photosynthesis, which is the process of transforming sunlight energy into sugar. Animals are generally unable to use this process to acquire energy, but there are a few known exceptions to this. Some sea slugs take up chloroplasts from the algae that they consume into their cells. These chloroplasts retain their ability to perform photosynthetic activity within the animal cells for several months, and thus provide them with photosynthesis-derived nutrition. This process is called "kleptoplasty", and it has attracted much attention due to its amazing uniqueness in making animals photosynthetic for over 50 years.
A pressing question is how these sequestered chloroplasts retains their photosynthetic capability without algal nuclei. Since the genome of the algal nucleus encodes most of the proteins required for photosynthesis, chloroplasts isolated from algal cells instantly lose their photosynthetic capability. Nevertheless, algae-eating sea slugs retain this photosynthetic capability for months. There have been numerous debates about the mechanisms underlying the phenomenon of sequestered chloroplasts retaining photosynthetic capabilities over the long term. A widely accepted hypothesis accounting for kleptoplasty is the horizontal gene transfer of the photosynthesis genes from algae to sea slug.
A team of researchers at the National Institute for Basic Biology (NIBB), in addition to collaborators from seven other Japanese institutions, have published the genome of the sea slug, Plakobranchus ocellatus type black, in eLife. "Since the sea slug is a non-model organism, its genome analysis was very tough in comparison to model organisms such as the mouse and the fruitfly. Furthermore, there was no high-quality genetic information for them. This situation consequently hindered the verification of the hypothesis of algae-derived horizontal gene transfer," said Shuji Shigenobu, a genome scientist and professor at NIBB who is the corresponding author of the paper, "But we succeeded in accurately revealing the genome information of the sea slug". Scientists are ready to settle the arguments concerning the horizontal transfer of algal genes to the animal nucleus based on newly unveiled genome data. "We looked at the genome very carefully, but we found no evidence of photosynthetic genes encoded on the sea slug genome, " he said.
"We are embarking upon a new challenge to answer the question: how does the sea slug retains this function without horizontal gene transfer?", said Taro Maeda, the first and co-corresponding author of the paper. "Our genome data also provides clues to this. We have found several candidate genes related to the long-term maintenance of photosynthetic activity. These genes related to protein metabolism, oxidative stress tolerance, and innate immunity should be subsequently highlighted in future studies."
The mechanisms underlying kleptoplasty are still elusive. Further understanding of this phenomenon may lead us to innovative biotechnologies, which, for example, could bestow photosynthetic abilities to other various animal cells in the future.
INFORMATION:
eLife
"Chloroplast acquisition without the gene transfer in kleptoplastic sea slugs, Plakobranchus ocellatus" by Taro Maeda, Shunichi Takahashi, Takao Yoshida, Shigeru Shimamura, Yoshihiro Takaki, Yukiko Nagai, Atsushi Toyoda, Yutaka Suzuki, Asuka Arimoto, Hisaki Ishii, Nori Satoh, Tomoaki Nishiyama, Mitsuyasu Hasebe, Tadashi Maruyama, Jun Minagawa, Junichi Obokata, Shuji Shigenobu
DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.60176
Contact:
Prof. Shuji Shigenobu
National Institute for Basic Biology
E-mail:
shige@nibb.ac.jp
Dr. Taro Maeda
E-mail:
taromaedaj@gmail.com
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-15
Since the Paris Climate Agreement that took effect in 2016, 121 countries have pledged to become carbon neutral by 2050 as the world tries to reduce its fuel consumption. The Korean government also unveiled its 2050 Carbon Neutral Strategy on December 7, 2020 and declared Carbon Zero, making transition to new and renewable energy a topic of conversation. Recently, a joint research team from POSTECH and Korea University has developed a radiative cooling material that can reduce energy consumption by selectively reflecting or transmitting sunlight.
A research team led by Professor Junsuk Rho, Ph.D. candidate Minkyung Kim, and Dr. Dasol Lee of POSTECH's departments of mechanical engineering and chemical engineering, and a team led by Professor Heon Lee and Soomin of the Department of Materials ...
2021-07-15
Combined perceptions of the risk and availability of cannabis influence the risk of cannabis use more than perceived risk and perceived availability alone, according to a new study at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. Researchers observed that those who perceived cannabis as low-risk and available were more likely to report using the drug in the past year and almost daily compared to those individuals who perceived cannabis as high-risk and unavailable. This is the first study to consider the joint effects of perceived risk and perceived availability. The results are published in the journal Drug and Alcohol Dependence.
"Our study described the evolution of joint perceptions of cannabis risk and availability from 2002-2018 and estimated the relationship between combined ...
2021-07-15
Adolescent girls and young women can and will use HIV prevention products with consistency, according to interim results of a study of two different methods: daily use of the antiretroviral (ARV) tablet Truvada® as oral pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) and the monthly END ...
2021-07-15
Shining a beam of light into potentially contaminated water samples may hold the key to real-time detection of hydrocarbons and pesticides in water.
UBC Okanagan researchers are testing the use of fluorescence to monitor water quality. The results, they say, show great promise.
When a beam of light is shone into the water, it excites the electrons in molecules of certain compounds and causes them to emit light. The characteristics of the emitted light are like a fingerprint and can be used to identify certain contaminants, explains Nicolas Peleato, an assistant professor at UBCO's School of Engineering.
"The challenge with using this fluorescence approach is that ...
2021-07-15
Repairing complex electrical appliances is time consuming and rarely cost-effective. The working group led by Prof. Dr. Karl Mandel, Professorship of Inorganic Chemistry at Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU), has now developed a smart microparticle that enables defective components in these appliances to be identified more quickly and easily by using light signals. In the long-term, this could make repairs easier and extend the operating life of devices. The results have been published in the journal Advanced Functional Materials.
To identify defective components in a device, particles known as supraparticles are applied to the individual parts. These particles measure between one and ten micrometres and under black light they provide information ...
2021-07-15
Fukuoka, Japan--At this very moment, the billions of neurons in your brain are using their trillions of connections to enable you to read and comprehend this sentence.
Now, by studying the neurons involved in the sense of smell, researchers from Kyushu University's Faculty of Medical Sciences report a new mechanism behind the biomolecular bonsai that selectively strengthens these connections.
How neuronal circuits remodel themselves over time, especially during early development, is an open question in neurobiology. At the start of neuronal development, neurons form excessive amounts of connections ...
2021-07-15
The cryosphere, a term used to describe the areas of the Earth's surface where water exists in solid form, plays an important role in regulating the Earth's climate. Due to cryospheric retreat; for example, the melting Greenland ice sheet in the Arctic, greenhouse gases that were formerly in "frozen storage" are now being released. High Mountain Asia, also known as the Tibetan Plateau, hosts the largest volume of glaciers outside the polar regions. However, Tibetan glaciers are currently excluded from global greenhouse gas budgets.
According to Shichang Kang, leader of a group of researchers who recently became the first team to measure the flux variations of greenhouse gases (CO2 and CH4) in typical glacial basins in High Mountain Asia, it's important that Tibetan glaciers are not ...
2021-07-15
New research will help doctors identify, treat and prevent potentially dangerous irregular heartbeats in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), a common heart condition in which the heart thickens and strains to pump blood.
These chaotic heart rhythms are known as atrial fibrillation. Atrial fibrillation can be asymptomatic, but it can lead to blood clots, stroke or even heart failure. The new research, from an international team of doctors and scientists, identifies risk factors for major atrial fibrillation outcomes, such as the need for procedures or hospitalization for more than 24 ...
2021-07-15
Scientists have developed a rapid, highly accurate test to detect antibodies against the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 in human serum, opening a new avenue for understanding the full extent of the pandemic and evaluating the effectiveness of vaccines.
In the 18 months since the emergence of Covid-19 pandemic, great strides have been made in discovering and inventing various approaches to track and control the spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Rapid and accurate diagnosis has always been vital in this regard. The gold standard since the beginning of the pandemic has been the RT-PCR method; however, it is time-consuming, labor-intensive, and requires sophisticated ...
2021-07-15
Single-cell RNA sequencing has revealed a subset of cells that could provide protection from a rare, but severely debilitating and fatal, lung disease. The findings were published by Nagoya University researchers and colleagues in the European Respiratory Journal. Further research could lead to new therapeutic strategies for the disease, called idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).
Approximately 15 in every 100,000 people worldwide develop IPF. Its prognosis and five-year survival rate can be worse than many types of cancer. It involves the development of scar tissue on the lung, impairing gas exchange and making ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A genome of photosynthetic animals decoded
Genome analysis reveals chloroplast acquisition without gene transfer in photosynthetic sea slugs