Words matter: Language can reduce mental health and addiction stigma, NIH leaders say
2021-07-19
(Press-News.org) WHAT:
In a perspective published in Neuropsychopharmacology, leaders from the National Institutes of Health address how using appropriate language to describe mental illness and addiction can help to reduce stigma and improve how people with these conditions are treated in health care settings and throughout society. The authors define stigma as negative attitudes toward people that are based on certain distinguishing characteristics. More than a decade of research has shown that stigma contributes significantly to negative health outcomes and can pose a barrier to seeking treatment for mental illness or substance use disorders.
Thirty five?percent of people with serious mental illness in the U.S., and nearly 90% of people with substance use disorders,?do not receive?treatment. The perspective authors point to evidence that stigma-related bias among clinicians can contribute to a treatment-averse mindset and to flawed clinical care, including failure to implement proven methods of treatment. Further, when a person with a mental illness or substance use disorder continues to experience stigma, they may begin to internalize it. This "self-stigma" can lead to lower self-esteem and feelings of self-worth and can become an ongoing source of distress that may exacerbate symptoms and create barriers to successful treatment.
Conversely, efforts to reduce stigma may reduce the psychological burden it places on individuals and can be an important component of removing barriers to care. The authors highlight numerous studies showing that using?scientifically accurate language?and terms?that?centralize the experience of patients?with mental illness and substance use disorders is one key component to reducing stigma. They argue that a shift in language is?crucial for mobilizing resources toward mental health and addiction services and eroding the prejudices that keep people who need?those services from seeking or receiving them. Though stigma is difficult to eliminate, they contend that changing the language we use to describe these conditions can make a significant and immediate difference for the people experiencing them.
INFORMATION:
ARTICLE:
ND Volkow, JA Gordon, and GF Koob. Choosing Appropriate Language to Reduce the Stigma Around Mental Illness and Substance Use Disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology. DOI: 10.1038/s41386-021-01069-4 (2021).
WHO:
- Nora D. Volkow, M.D., director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)
- George F. Koob, Ph.D., director of the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA)
About the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA): NIDA is a component of the National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIDA supports most of the world's research on the health aspects of drug use and addiction. The Institute carries out a large variety of programs to inform policy, improve practice, and advance addiction science. For more information about NIDA and its programs, visit http://www.nida.nih.gov.
About the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA): The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA), part of the National Institutes of Health, is the primary U.S. agency for conducting and supporting research on the causes, consequences, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of alcohol use disorder. NIAAA also disseminates research findings to general, professional, and academic audiences. Additional alcohol research information and publications are available at http://www.niaaa.nih.gov.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.nih.gov.
Contacts:
NIDA Press Office
301-443-6245
media@nida.nih.gov
NIAAA Press Office
301-443-2857
NIAAAPressOffice@mail.nih.gov
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-19
New models of neutron stars show that their tallest mountains may be only fractions of millimetres high, due to the huge gravity on the ultra-dense objects. The research is presented today at the National Astronomy Meeting 2021.
Neutron stars are some of the densest objects in the Universe: they weigh about as much as the Sun, yet measure only around 10km across, similar in size to a large city.
Because of their compactness, neutron stars have an enormous gravitational pull around a billion times stronger than the Earth. This squashes every feature on the ...
2021-07-17
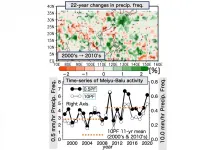
Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have analyzed long-term precipitation radar data from satellites and found significantly enhanced rainfall over the most recent decade during the annual Meiyu-Baiu rainy season in East Asia. The data spans 23 years and gives unprecedented insight into how rainfall patterns have changed. They showed that the increased rainfall was driven by the decadal increased transport of moisture from the tropics and frequent occurrence of the upper tropospheric trough over the front.
From the second ...
2021-07-17
Highlights
The results of a new study support the validity of a score that considers various patient-reported outcome measures and preferences for assessing health-related quality of life in individuals with kidney failure.
The score is calculated from assessments of cognitive function, depression, fatigue, pain interference, physical functioning, sleep disturbance, and ability to participate in social roles.
Washington, DC (July 16, 2021) -- Results from a new study support the validity of a score that considers various patient-reported measures and preferences for assessing health-related quality of life and promoting patient-centered care in individuals with kidney failure. The study appears in an upcoming issue of CJASN.
The ...
2021-07-17
Highlights
The sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor dapagliflozin reduced kidney, cardiovascular, and mortality risks in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease, similar to benefits seen in individuals with normal or moderately impaired kidney function.
Rates of serious side effects were similar in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease who received dapagliflozin or placebo.
Washington, DC (July 16, 2021) -- Studies have shown that diabetes drugs called sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors can provide kidney- and cardiovascular-related ...
2021-07-16
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine and Rady Children's Institute for Genomic Medicine have produced a stem cell model that demonstrates a potential route of entry of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, into the human brain.
The findings are published in the July 9, 2021 online issue of Nature Medicine.
"Clinical and epidemiological observations suggest that the brain can become involved in SARS-CoV-2 infection," said senior author Joseph Gleeson, MD, Rady Professor of Neuroscience at UC San Diego School of Medicine and ...
2021-07-16
PITTSBURGH, July 16, 2021 - For the first time ever, researchers from the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine discovered that phages--tiny viruses that attack bacteria--are key to initiating rapid bacterial evolution leading to the emergence of treatment-resistant "superbugs." The findings were published today in Science Advances.
The researchers showed that, contrary to a dominant theory in the field of evolutionary microbiology, the process of adaptation and diversification in bacterial colonies doesn't start from a homogenous clonal population. They were shocked to discover that the cause of much of the early adaptation wasn't random ...
2021-07-16
Researchers at UC San Francisco are zeroing in on how the immune system may play a role in miscarriage, which affects about a quarter of pregnancies.
Working in mice, the researchers have found that a recently discovered subset of cells in the immune system may prevent the mother's immune system from attacking the placenta and fetus. If the research is confirmed in further animal studies, and the cells play a similar role in people, they could point the way toward new therapies for pregnancies that are threatened by defects in immune tolerance.
The researchers showed that pregnant mice who did not have this subset of cells, known as extrathymic Aire-expressing cells, were twice as likely to miscarry, and in many ...
2021-07-16
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- From biochemical reactions that produce cancers, to the latest memes virally spreading across social media, simple actions can generate complex behaviors. For researchers trying to understand these emergent behaviors, however, the complexity can tax current computational methods.
Now, a team of researchers has developed a new algorithm that can serve as a more effective way to analyze models of biological systems, which in turn allows a new path to understanding the decision-making circuits that make up these systems. The researchers add that the algorithm will help scientists study how relatively ...
2021-07-16
For thousands of years, people looked into the night sky with their naked eyes -- and told stories about the few visible stars. Then we invented telescopes. In 1840, the philosopher Thomas Carlyle claimed that "the history of the world is but the biography of great men." Then we started posting on Twitter.
Now scientists have invented an instrument to peer deeply into the billions and billions of posts made on Twitter since 2008 -- and have begun to uncover the vast galaxy of stories that they contain.
"We call it the Storywrangler," says Thayer Alshaabi, a doctoral student at the University of Vermont who co-led the new research. "It's like a telescope to look -- in real time -- at all this data that people ...
2021-07-16
A new method developed by Institute for Systems Biology (ISB) and University of California, Riverside provides new insights into cancer biology by allowing researchers to show how fatty acids are absorbed by single cells.
Fatty acids, along with glucose and amino acids, are a major energy source for cellular growth and proliferation, and abnormal fatty acid metabolism is often seen in cancer. Dr. Wei Wei's lab at ISB and Dr. Min Xue's lab at UC Riverside have been collaborating for years to develop a series of chemical probes and analytical approaches for quantifying cellular glucose uptake, lactate production, amino acid ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Words matter: Language can reduce mental health and addiction stigma, NIH leaders say