Improving access to mental health services in low-income communities
UH researcher: Communication, coordination, collaboration are key
2021-07-20
(Press-News.org) When it comes to improving access to mental health services for children and families in low-income communities, a University of Houston researcher found having a warm handoff, which is a transfer of care between a primary care physician and mental health provider, will help build trust with the patient and lead to successful outcomes.
"Underserved populations face certain obstacles such as shortage of providers, family beliefs that cause stigma around mental health care, language barriers, lack of transportation and lack of insurance. A warm handoff, someone who serves as a go-between for experts and patients, can ensure connections are made," said Quenette L. Walton, assistant professor at the UH Graduate College of Social Work.
In the United States, as much as 14% of children experience emotional problems from birth to five years of age, and 75% of children with diagnosed mental health disorders are seen by pediatric primary care physicians. But in many under-resourced communities, integrated behavioral health interventions are not readily available.
Walton, principal investigator and lead author of a study published in Child & Youth Care Forum, identified and evaluated strategies used by pediatricians, psychiatrists, psychologists, licensed medical health counselors, program managers and coordinators to improve the referral system and access to pediatric mental health care for low-income, minority families in Los Angeles County, where the research was conducted.
"This group developed a patient-centered, telehealth-based intervention to streamline the process from referral to actual treatment," Walton explained. "That included updating their systems to give specialty mental health providers access to information they need - basically closing the loophole so services can be consistent."
Three major themes emerged from the research to inform how pediatric primary care physicians and mental health providers assist their low-income children and families with accessing mental health care: communication, coordination and collaboration.
Effective communication including phone calls, emails or written reports improved access to mental health services for this population.
Coordination of services required knowing how to make the referral process more efficient and effective so providers, working together, could more quickly discuss a shared treatment plan and implementation.
Collaboration of services entailed a warm handoff between pediatric primary care physicians and mental health providers. This person helped with navigating the system and worked with providers to develop a shared and agreed-upon plan of care.
"It takes several times for people to really buy into the need for mental health care. So, if we can be more intentional in our efforts to get people access to resources they need, despite their challenges, then they will feel valued and more likely to come in for services," Walton added. "Just an additional five or 10 minutes makes a difference for a patient."
Co-authors of the study include Elizabeth Bromley, University of California, Los Angeles Geffen School of Medicine; Lorena Porras-Javier, UCLA Children's Discovery & Innovation Institute; and Tumaini R. Coker, University of Washington School of Medicine and Seattle Children's Hospital.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-20
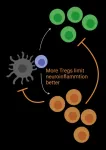
Irvine, CA - July 20, 2021 - In a new University of California, Irvine-led study, researchers found that a certain protein prevented regulatory T cells (Tregs) from effectively doing their job in controlling the damaging effects of inflammation in a model of multiple sclerosis (MS), a devastating autoimmune disease of the nervous system.
Published this month in Science Advances, the new study illuminates the important role of Piezo1, a specialized protein called an ion channel, in immunity and T cell function related to autoimmune neuroinflammatory disorders.
"We found that Piezo1 selectively restrains Treg cells, limiting their potential to mitigate ...
2021-07-20
Newborns at risk for Type 1 diabetes because they were given antibiotics may have their gut microorganisms restored with a maternal fecal transplant, according to a Rutgers study.
The study, which involved genetic analysis of mice, appears in the journal Cell Host & Microbe.
The findings suggest that newborns at risk for Type 1 diabetes because their microbiome - the trillions of beneficial microorganisms in and on our bodies - were disturbed can have the condition reversed by transplanting fecal microbiota from their mother into their gastrointestinal tract after the antibiotic course has been completed.
Type 1 diabetes is the most ...
2021-07-20
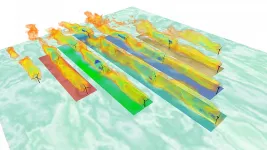
WASHINGTON, July 20, 2021 -- In the wind power industry, optimization of yaw, the alignment of a wind turbine's angle relative to the horizonal plane, has long shown promise for mitigating wake effects that cause a downstream turbine to produce less power than its upstream partner. However, a critical missing puzzle piece in the application of this knowledge has recently been added -- how to automate the identification of which turbines are experiencing wake effects amid changing wind conditions.
In the Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, by AIP Publishing, ...
2021-07-20
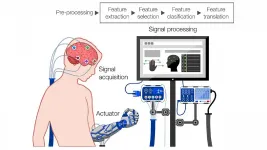
WASHINGTON, July 20, 2021 -- Surpassing the biological limitations of the brain and using one's mind to interact with and control external electronic devices may sound like the distant cyborg future, but it could come sooner than we think.
Researchers from Imperial College London conducted a review of modern commercial brain-computer interface (BCI) devices, and they discuss the primary technological limitations and humanitarian concerns of these devices in APL Bioengineering, from AIP Publishing.
The most promising method to achieve real-world BCI applications is through electroencephalography (EEG), a method ...
2021-07-20
Millions of people in countries around the world could face an increased risk of malnutrition as climate change threatens their local fisheries.
New projections examining more than 800 fish species in more than 157 countries have revealed how two major, and growing, pressures - climate change and over-fishing - could impact the availability of vital micronutrients from our oceans.
As well as omega-3 fatty acids, fish are an important source of iron, zinc, calcium, and vitamin A. A lack of these vital micronutrients is linked to conditions such as maternal mortality, stunted growth, and pre-eclampsia.
Analyses by an international team from the UK and Canada and led by scientists from Lancaster ...
2021-07-20
PHILADELPHIA -- (July 20, 2021) -- Alternative polyadenylation (APA) is an RNA processing mechanism that regulates gene expression by generating different ends on RNA transcripts of the same gene. Though it affects more than half of human genes, the significance of APA was poorly understood. Now a new study by The Wistar Institute describes an important function of APA in allowing certain mRNAs to reach specific sites of protein synthesis and reveals that length, sequence and structural properties can determine the destination (and fate) of mRNAs within the cell. These findings, published online in the journal Cell Reports, shed light on the consequences of APA that may represent a paradigm shift in the mRNA metabolism field.
The ...
2021-07-20
What The Study Did: Credit reports were analyzed to estimate the amount of medical debt in collections nationally and by geographic region and income group and its association with Medicaid expansion under the Affordable Care Act.
Authors: Neale Mahoney, Ph.D., of Stanford University in Stanford, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2021.8694)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional ...
2021-07-20
New Rochelle, NY, July 19, 2021--Duct tape and items retrieved from the water are common pieces of evidence in forensic cases. A new study evaluates the recovery of DNA from folded duct tape that has been submerged in ocean water for up to 2 weeks. The study is published in the peer-reviewed journal Forensic Genomics. Click here to read the article now.
Joseph Donfack, PhD, from the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) Laboratory Division, and coauthors showed that it is possible to recover enough DNA to yield a complete short tandem repeat (STR) profile from folded duct tape that has been submerged in ocean water for up to 2 weeks if the initial ...
2021-07-20
On 23 July 2012, humanity escaped technological and economic disaster. A diffuse cloud of magnetized plasma in the shape of a slinky toy tens of thousands of kilometers across was hurled from the Sun at a speed of hundreds of kilometers per second.
This coronal mass ejection (CME) just missed the Earth because its origin on the Sun was facing away from our planet at the time. Had it hit the Earth, satellites might have been disabled, power grids around the globe knocked out, GPS systems, self-driving cars, and electronics jammed, and railway tracks ...
2021-07-20
Retail traders often fear that reducing the amount of urban space made available for parking private vehicles would have a negative effect on their businesses. A survey conducted by researchers from the Institute for Advanced Sustainability Studies (IASS) on two shopping streets in Berlin shows that traders have a skewed perception of their customers' mobility habits. The findings of this research will facilitate better-informed decision-making around urban land-use planning.
The researchers surveyed around 2,000 customers and 145 retailers on Kottbusser Damm (Friedrichshain-Kreuzberg district) and Hermannstraße (Neukölln district). The vast majority of shoppers - 93 per cent - had not travelled to their ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Improving access to mental health services in low-income communities
UH researcher: Communication, coordination, collaboration are key