Study uncovers factors linked to radical attitudes and intentions
2021-07-21
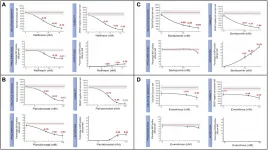
(Press-News.org) A systematic review and meta-analysis published in Campbell Systematic Reviews identified and examined more than 100 risk and protective factors for radical attitudes, intentions, and behaviors (including terrorism) in democratic countries.
The factors can be grouped into five domains:
socio-demographic and background factors,
psychological and personality trait factors,
attitudinal and subjective belief related factors,
experiential factors, and
traditional criminogenic factors
While there is great variation, the most significant factors are traditional criminogenic and social-psychological factors.
"Our results suggest that some of the factors most commonly targeted by counter violent extremism interventions, such as social integration, have only small relationships with radicalization. On the other hand, traditional criminogenic factors, such as low self-control, have far more robust relationships," said lead author Michael Wolfowicz, PhD, of The Hebrew University of Jerusalem. He noted that the findings suggest that interventions commonly used to combat criminological outcomes may also be useful for fighting radicalization.
"Additionally, our results suggest a need to revamp the way that risk assessment tools are constructed, as not all factors included in such tools should be given the same weight," said Dr. Wolfowicz. "We hope that our results will contribute to the development of more evidence-based practice in this field."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-21
It's important to communicate about hard-to-see and complex environmental topics and issues with young people. In an article published in People and Nature, an international team reflects on the group's creation of the Shout Trout Workout, a lyric poem, comic, and music video for children aged 8-14 years old designed to entertain, engage, and enrich learning about migratory fishes and aquatic environments.
The authors hope that sharing their experiences and reflections will be useful and inspiring for those who aim to create learning enrichment and engagement materials about ecological ...
2021-07-21
Results from a study published in Ibis show that how close Golden Eagles will fly to wind turbines depends on habitat suitability inside and outside of a wind farm. Also, the largest impact of wind farms was a loss of Golden Eagle habitat, which could be mitigated by including the study's findings in wind farm planning.
The study included data from 59 GPS-tagged Golden Eagles before and after turbine operation at 80 wind farms across Scotland.
"Previous research on Golden Eagles, notably in the United States, has tended towards collision with turbine blades as the main consequence of their interaction with wind farms. Our study shows that across numerous wind farms in Scotland, this was not the case, but that deleterious habitat loss through avoidance of turbines was ...
2021-07-21
Researchers led by the Garvan Institute of Medical Research have discovered a link between cognitive decline and a faster rate of bone loss, and found that cognitive decline over five years increased future fracture risk in women. The association between cognitive decline and bone loss was weaker in men.
The study of individuals aged 65 and older was carried out over 16 years and has revealed a potential new approach to help identify older people who may be at risk of fracture.
"Bone loss and cognitive decline are major public health issues, but both are 'silent diseases' that can go undetected and untreated for long periods, often ...
2021-07-21
WASHINGTON (July 21, 2021) - Twenty-nine percent of Americans are taking more supplements today than they were before the COVID-19 pandemic, bringing the percentage of U.S. supplement-takers to 76%, according to a new survey conducted by The Harris Poll on behalf of Samueli Foundation. Nearly two-thirds of those who increased supplement use (65%) cited a desire to enhance their overall immunity (57%) or protection from COVID-19 (36%) as reasons for the increase. Other common reasons for increasing supplement use were to take their health into their own hands (42%), improve their sleep (41%), and improve their mental health (34%).
"The COVID-19 pandemic is a catalyst for increased supplement use," said Wayne Jonas, MD, executive director ...
2021-07-21
Oncotarget published "Genomic clustering analysis identifies molecular subtypes of thymic epithelial tumors independent of World Health Organization histologic type" which reported that genomic information from 102 evaluable TETs from The Cancer Genome Atlas dataset and from the IU-TAB-1 cell line underwent clustering analysis to identify molecular subtypes of TETs.
Six novel molecular subtypes of TETs from the TCGA were identified, and there was no association with WHO histologic subtype.
The IU-TAB-1 cell line clustered into the TH4 molecular subtype and in vitro testing of candidate therapeutics was performed.
Sensitivity to nelfinavir ...
2021-07-21
New research from Bocconi University in Milan highlights that, contrary to received wisdom, connections to organized crime harm a company's financial performance and increase by 25.5% its likelihood to go bust.
Using a novel dataset from AISI, the Italian Internal Intelligence and Security agency, Bocconi professors Antonio Marra, Donato Masciandaro, and Nicola Pecchiari in a paper co-authored with Pietro Bianchi (Florida International University) published online in The Accounting Review, identify 1,840 criminally connected firms headquartered in Italy's Lombardy region.
Lombardy, the Northern Italian region around Milan, is not ...
2021-07-21
A relaxing vacation on the beach frees us from many of the worries of everyday life. But the sand not only cleans the head and soul of vacationers - it also cleans the seawater.
Coastal sands are so-called biocatalytic filters. Hundreds of thousands of bacteria live on each grain of sand, and they process, for example, nitrogen and carbon from the seawater that flows through the sands. In this way, the sands act like giant, purifying filters. Much of what the seawater washes into the ground does not come out again.
A study by researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology in Bremen, Germany, published in the journal ISME Communications, now shows that the bacteria living on the sand are very different from the ones in seawater. And while the bacterial ...
2021-07-21
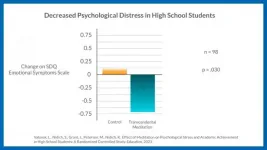
Students who participated in a meditation-based Quiet Time program utilizing the Transcendental Meditation (TM) technique for four months had significant improvements in overall emotional stress symptoms, quality of sleep, and English Language Arts (ELA) academic achievement according to a new randomized controlled trial published last month in Education. The study was conducted by researchers from the Center for Wellness and Achievement in Education and Stanford University. This was the first randomized control trial to investigate the effects of TM on standardized academic tests.
"Students have been experiencing increased levels ...
2021-07-21
An adhesive tape patented by Staffordshire University researchers to recover trace evidence from crimes scenes is being adopted to analyse microplastics more efficiently.
Man-made polymer particles or ‘microplastics’ are proven to be present in land, air and water environments. However, despite extensive global studies, there is no standardised approach for their collection and analysis.
Currently, studies regularly involve retrieving microplastic samples from water using a filtration method. Samples are commonly analysed in situ on the filter or after removal from it by ...
2021-07-21
Smartphone gaming can be harmful to players who game to escape their negative mood and feelings of boredom, a new study has found.
Researchers at the University of Waterloo found that bored "escape players"--those who have difficulty engaging with the real environment and sustaining attention--may seek "flow," which is a deep and effortless state of concentration in an activity linked to loss of awareness of time and space.
"We found that people who experience intense boredom frequently in everyday life reported playing smartphone games to escape or alleviate these feelings ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study uncovers factors linked to radical attitudes and intentions