(Press-News.org) A new quantitative study suggests people seeking asylum are more likely to experience mental health deterioration as they spend more time living in refugee camps, backing up qualitative evidence from aid organisations.
The research, co-authored by Dr Francisco Urzua from the Business School (formerly Cass) alongside practitioners from Moria Medical Support (MMS) and academics from Universidad del Desarrollo, Chile and University of Amsterdam, the Netherlands measured incidences of acute mental health crises arising from extended stays in the Moria refugee camp on the western Greek Island of Lesbos.
Key findings from the study include:
Acute mental health crises were significantly linked with the length of time somebody stayed in the Moria refugee camp: the longer a refugee stayed in the camp, the more likely they were to suffer a mental health crisis.
A 10 per cent increase in the number of days spent in the camp led to a 3.3 per cent increase in the chances of a refugee suffering a mental health crisis - a significant factor given an average length of stay of 70.6 days.
Refugees of Iranian, Iraqi and Syrian ethnicity were most significantly affected by longer stays in the refugee camps, with male refugees more likely to experience incidences of acute mental health crises than women as time spent in the refugee camp increased.
The study used three months of anonymised data from MMS, a transitory clinic that offered night-time medical services to the island at the time, between January and April 2018. This included Psychological First Aid (PFA) and psychiatric crisis management, with patient data on age, gender, ethnicity and length of stay in the camp.
An acute mental health crisis is defined as a case of somebody either harming themselves through a non-accidental implemented wound, a suicide attempt requiring hospital care, or a state of unease constituted by anxiety, nervous agitation or undirected aggression.
Dr Urzua said that results supported prior claims about the quality of life in refugee camps, and that actions should be taken to safeguard inhabitants throughout the asylum process.
"The EU-Turkey deal of 2016 has seen camp populations multiply in size, but adequate mental health care provisions have not been expanded or improved in equal measure," Dr Urzua said.
"Our study expands upon existing qualitative evidence that the prolonged system of asylum has detrimental effects on mental health, brought on by poor living conditions of refugee camps.
"This mental health deterioration not only affects the individuals themselves but also has significant repercussions for fellow refugees with increased physical violence and the destabilisation of an often close-knit social environment, which in turn affects the mental wellbeing of others. Furthermore, the implications of deteriorating mental health most likely continue even after release, which makes it harder for refugees to integrate into a new society.
"It is clear to see from our study and prior anecdotal evidence that mental health in these camps is a serious problem, and it is imperative that policymakers from across Europe take action and uphold the 1951 Geneva Refugee Convention to protect the rights and wellbeing those awaiting and granted asylum."
Dr Willemine van de Wiel, doctor and coordinator at Moria Medical Support said more needed to be done to support conditions at the Moria camp and others in the northern hemisphere.
"During our time on the Island of Lesbos, my overwhelming feeling was frustration at the conditions in the camp - a sentiment shared by many seasoned NGO-workers.
"In our experience, refugees are better off in many camps in the global south in terms of safety, housing, access to food, sanitation and medical services.
"I hope this research adds to public awareness about the psychological impact of life in these camps and inspires the development of a more humane asylum process."
INFORMATION:
'Mental health consequences of long-term stays in refugee camps: preliminary evidence from Moria' is published in BMC Public Health. The co-authors of the paper are:
Dr Willemine van de Wiel, Moria Medical Support
Carla Castillo-Laborde, Universidad del Desarrollo, Chile
Dr Francisco Urzua, The Business School (formerly Cass)
Michelle Fish, Moria Medical Support
Willem F. Scholte, University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Researchers from the School of Biomedical Engineering & Imaging Sciences at King's College London have automated brain MRI image labelling, needed to teach machine learning image recognition models, by deriving important labels from radiology reports and accurately assigning them to the corresponding MRI examinations. Now, more than 100,00 MRI examinations can be labelled in less than half an hour.
Published in European Radiology, this is the first study allowing researchers to label complex MRI image datasets at scale.
The researchers say it would take years to manually perform labelling of more than 100,000 MRI examinations.
Deep learning typically requires tens of thousands of labelled images to ...
Scientists have developed a 'nanobody' - a small fragment of a llama antibody - that is capable of chasing out human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) as it hides away from the immune system. This then enables immune cells to seek out and destroy this potentially deadly virus.
Around four out of five people in the UK are thought to be infected with HCMV, and in developing countries this can be as high as 95%. For the majority of people, the virus remains dormant, hidden away inside white blood cells, where it can remain undisturbed and undetected for decades. ...
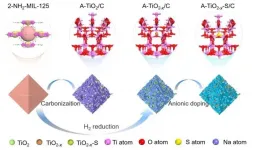
The research team of Prof. Xiaobo Ji and associate Prof. Guoqiang Zou has proposed an ingenious oxygen vacancy (OV)-engineering strategy to realize high content anionic doping in TiO2 and offered valuable insights into devise electrode materials with fast charge transfer kinetics in the bulk phase. The article titled "High content anion (S/Se/P) doping assisted by defect engineering with fast charge transfer kinetics for high-performance sodium ion capacitors" is published in Science Bulletin. Xinglan Deng is listed as first author and Prof. Guoqiang Zou as corresponding author.
The ...
An international research team has come up with an innovative method for metal recovery from industrial waste. The new method allows the simultaneous recovery of multiple metals from waste oxides in a single process. This novel route will lower the burden on waste storage facilities with significant contributions to the economic and environmental sustainability of industrial waste management. The study was published in Journal of Environmental Management. This work is the first in a series of studies aimed at developing cost-effective and environmentally sustainable solutions for industrial waste recycling.
Some of the major industries ...
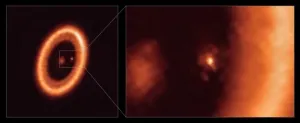
Using the Atacama Large Millimetre/submillimeter Array (ALMA), in which the European Southern Observatory (ESO) is a partner, astronomers have unambiguously detected the presence of a disc around a planet outside our Solar System for the first time. The observations will shed new light on how moons and planets form in young stellar systems.
"Our work presents a clear detection of a disc in which satellites could be forming," says Myriam Benisty, a researcher at the University of Grenoble, France, and at the University of Chile, who led the new research published today in The Astrophysical Journal Letters. "Our ALMA observations were obtained at such exquisite resolution that we could clearly identify ...
Cambridge, MA ¬- Astronomers at the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian have helped detect the clear presence of a moon-forming region around an exoplanet -- a planet outside of our Solar System. The new observations, published Thursday in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, may shed light on how moons and planets form in young stellar systems.
The detected region is known as a circumplanetary disk, a ring-shaped area surrounding a planet where moons and other satellites may form. The observed disk surrounds exoplanet PDS 70c, one of two giant, Jupiter-like planets orbiting a star nearly 400 light-years away. Astronomers had found hints of a "moon-forming" disk around this exoplanet before but since ...
Participation in elite adult rugby may be associated with changes in brain structure.
This is the finding of a study of 44 elite rugby players, almost half of whom had recently sustained a mild head injury while playing.
The study, part of the Drake Rugby Biomarker Study, was led by Imperial College London and published in the journal Brain Communications.
The research found a significant proportion of the rugby players had signs of abnormalities to the white matter, in addition to abnormal changes in white matter volume over time.
White matter is the 'wiring' of the brain, and helps brain cells communicate with each other. The research team say more work is now needed to investigate the long-term effects of professional rugby on brain health.
Professor David Sharp, senior author ...
Adults and children with COVID-19 who have a history of malnutrition may have an increased likelihood of death and the need for mechanical ventilation, according to a study published in Scientific Reports.
Malnutrition hampers the proper functioning of the immune system and is known to increase the risk of severe infections for other viruses, but the potential long-term effects of malnutrition on COVID-19 outcomes are less clear.
Louis Ehwerhemuepha and colleagues investigated associations between malnutrition diagnoses and subsequent COVID-19 severity, using medical records for 8,604 children and 94,495 adults (older than 18 years) who were hospitalised with COVID-19 in the United States between March and June 2020. Patients with a diagnosis ...
A new study published online today in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute reports that one third of the most popular cancer treatment articles on social media contain misinformation. Further, the vast majority of that misinformation has the potential to harm cancer patients by supporting approaches that could negatively impact the quality of their treatment and chances for survival. The study also showed that articles containing misinformation garner more attention and engagement than articles with evidence-based information.
The internet is a major source for health information, and misinformation is growing among many types of health conditions. This is an urgent challenge because it can result in patients making ...
Levels of omega-3 fatty acids in the blood are as good a predictor of mortality from any cause as smoking, according to a study involving the Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute (IMIM), in collaboration with The Fatty Acid Research Institute in the United States and several universities in the United States and Canada. The study, published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, used data from a long-term study group, the Framingham Offspring Cohort, which has been monitoring residents of this Massachusetts town, in the United States, since 1971.
Researchers have found that omega-3 levels in blood erythrocytes (the so-called red blood cells) are very good mortality risk predictors. The study concludes that "Having higher levels of these ...