Improving air quality reduces dementia risk, multiple studies suggest
2021-07-26
(Press-News.org) DENVER, JULY 26, 2021 -- Improving air quality may improve cognitive function and reduce dementia risk, according to several studies reported today at the END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Misplaced trust: When trust in science fosters pseudoscience
2021-07-26
The Covid-19 pandemic and the politicization of health-prevention measures such as vaccination and mask-wearing have highlighted the need for people to accept and trust science.
But trusting science isn't enough.
A new study finds that people who trust science are more likely to believe and disseminate false claims containing scientific references than people who do not trust science. Reminding people of the value of critical evaluation reduces belief in false claims, but reminding them of the value of trusting science does not.
"We conclude that ...
Two types of blood pressure meds prevent heart events equally, but side effects differ
2021-07-26
DALLAS, July 26, 2021 -- People who are just beginning treatment for high blood pressure can benefit equally from two different classes of medicine - angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) - yet ARBs may be less likely to cause medication side effects, according to an analysis of real-world data published today in Hypertension, an American Heart Association journal.
While the class of blood pressure-lowering medicines called angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors may be prescribed more commonly, angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) work just as well and may cause fewer side effects. Currently, ACE inhibitors are prescribed more commonly than ARBs as a first-time blood pressure ...
New statement provides path to include ethnicity, ancestry, race in genomic research
2021-07-26
DALLAS, July 26, 2021 -- Genomic studies have produced advances in how to calculate and reduce heart-disease risk, however, the benefits don't necessarily apply to people from historically marginalized racial and ethnic groups and Indigenous populations. Efforts must be made to eliminate barriers to increase their participation in genomic research, according to a new scientific statement from the American Heart Association, published today in the Association's journal Circulation: Genomic and Precision Medicine.
"Profound breakthroughs in genetic and genomic science are rapidly improving our ability to prevent, detect and treat cardiovascular ...
Among effective antihypertensive drugs, less popular choice is slightly safer
2021-07-26
NEW YORK, NY (July 26, 2021)--Two types of drugs that are recommended as a first treatment for patients with high blood pressure were found equally effective in improving cardiovascular outcomes, but the more popular type causes slightly more side effects, finds a multinational observational study led by researchers at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons.
The study, which analyzed claims and electronic health data from millions of patients worldwide, is the largest to compare the safety and efficacy of angiotensin-converting ...
Juicy past of favorite Okinawan fruit revealed
2021-07-26
Citrus fruits from the mandarin family have important commercial value but how their diversity arose has been something of a mystery
Researchers analyzed the genomes of the East Asian varieties and found a second center of diversity in the Ryukyu Islands along with the previously known center in the mountains of southern China
They discovered a new citrus species native to Okinawa that arose about two million years ago when the Ryukyu archipelago became disconnected from mainland Asia
Other citrus from Okinawa and mainland Japan, including shiikuwasha and tachibana, are hybrids of this newly discovered wild species with different mainland Asian varieties
This research may have commercial implications and ...
Anticipate a resurgence of respiratory viruses in young children
2021-07-26
Canada should anticipate a resurgence of a childhood respiratory virus as COVID-19 physical distancing measures are relaxed, authors warn in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
Cases of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) have risen sharply in Australia and, more recently, the United States as COVID-19 case counts have waned and pandemic public health measures have been relaxed. Respiratory syncytial virus affects the lower respiratory tract and can cause serious illness and death. Before the COVID-19 pandemic, about 2.7 million children worldwide were infected with RSV each year, and it was the fourth most common cause of death in young children.
"The off-season resurgence in seasonal respiratory viruses now potentially poses a threat to vulnerable infants," ...
Anxiety, depression, burnout rising as college students prepare to return to campus
2021-07-26
A new "return to campus" survey led by The Ohio State University's Office of the Chief Wellness Officer finds rising rates of anxiety, depression, burnout and the use of unhealthy coping mechanisms among students navigating through a year affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, similar to other data on college students throughout the U.S.
Ohio State conducted surveys in August 2020 and April 2021 of randomly-selected students to assess changes in mental health, coping strategies, healthy lifestyle behaviors and needs over time. Among the 1,072 Ohio State students who responded:
Students who screened positive for anxiety:
August 2020: 39%
April 2021: 42.6%
Students who screened positive for depression:
August 2020: 24.1%
April 2021: 28.3%
Students who screened ...
Goal-setting and positive parent-child relationships reduce risk of youth vaping
2021-07-26
PITTSBURGH, July 26, 2021 - Adolescents who set goals for their future and those with strong parental support are less likely to use e-cigarettes and other tobacco products, according to a study by UPMC Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh and University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine physician-scientists.
The research, published today in the journal Pediatrics, suggests that strategies to prevent youth vaping may be different from what works to dissuade youth from smoking cigarettes.
"The use of e-cigarettes by young people is at epidemic proportions, with 27% of youth ...
New research identifies cancer types with little survival improvements in adolescents and young adul
2021-07-26
Survival rates for adolescents and young adults diagnosed with cancer have varied considerably depending on cancer type. A new study indicates that survival for multiple cancer types in such patients has improved in recent years, but some patients diagnosed with common cancer types still show limited survival improvements. The results are published by Wiley early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
For the study, investigators at the National Cancer Institute analyzed survival trends related to cancers with the highest mortality rates in adolescents and young adults. Relying on information from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) cancer ...
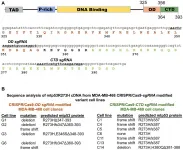
Oncotarget: Replication-stress sensitivity in breast cancer cells
2021-07-26
Oncotarget published "Frame-shift mediated reduction of gain-of-function p53 R273H and deletion of the R273H C-terminus in breast cancer cells result in replication-stress sensitivity" which reported that these authors recently documented that gain-of-function mutant p53 R273H in triple negative breast cancer cells interacts with replicating DNA and PARP1. The missense R273H GOF mtp53 has a mutated central DNA binding domain that renders it unable to bind specifically to DNA, but maintains the capacity to interact tightly with chromatin.
Both the C-terminal domain ...