(Press-News.org) Infants outperform artificial intelligence in detecting what motivates other people’s actions, finds a new study by a team of psychology and data science researchers. Its results, which highlight fundamental differences between cognition and computation, point to shortcomings in today’s technologies and where improvements are needed for AI to more fully replicate human behavior.
“Adults and even infants can easily make reliable inferences about what drives other people’s actions,” explains Moira Dillon, an assistant professor in New York University’s Department of Psychology and the senior author of the paper, which appears in the journal Cognition. “Current AI finds these inferences challenging to make.”
“The novel idea of putting infants and AI head-to-head on the same tasks is allowing researchers to better describe infants’ intuitive knowledge about other people and suggest ways of integrating that knowledge into AI,” she adds.
“If AI aims to build flexible, commonsense thinkers like human adults become, then machines should draw upon the same core abilities infants possess in detecting goals and preferences,” says Brenden Lake, an assistant professor in NYU’s Center for Data Science and Department of Psychology and one of the paper’s authors.
It’s been well-established that infants are fascinated by other people—as evidenced by how long they look at others to observe their actions and to engage with them socially. In addition, previous studies focused on infants’ “commonsense psychology”—their understanding of the intentions, goals, preferences, and rationality underlying others’ actions—have indicated that infants are able to attribute goals to others and expect others to pursue goals rationally and efficiently. The ability to make these predictions is foundational to human social intelligence.
Conversely, “commonsense AI”—driven by machine-learning algorithms—predicts actions directly. This is why, for example, an ad touting San Francisco as a travel destination pops up on your computer screen after you read a news story on a newly elected city official. However, what AI lacks is flexibility in recognizing different contexts and situations that guide human behavior.
To develop a foundational understanding of the differences between humans’ and AI’s abilities, the researchers conducted a series of experiments with 11-month-old infants and compared their responses to those yielded by state-of-the-art learning-driven neural-network models.
To do so, they deployed the previously established “Baby Intuitions Benchmark” (BIB)—six tasks probing commonsense psychology. BIB was designed to allow for testing both infant and machine intelligence, allowing for a comparison of performance between infants and machines and, significantly, providing an empirical foundation for building human-like AI.
Specifically, infants on Zoom watched a series of videos of simple animated shapes moving around the screen—similar to a video game. The shapes’ actions simulated human behavior and decision-making through the retrieval of objects on the screen and other movements. Similarly, the researchers built and trained learning-driven neural-network models—AI tools that help computers recognize patterns and simulate human intelligence—and tested the models’ responses to the exact same videos.
Their results showed that infants recognize human-like motivations even in the simplified actions of animated shapes. Infants predict that these actions are driven by hidden but consistent goals—for example, the on-screen retrieval of the same object no matter what location it’s in and the movement of that shape efficiently even when the surrounding environment changes. Infants demonstrate such predictions through their longer looking to such events that violate their predictions—a common and decades-old measurement for gauging the nature of infants’ knowledge. Adopting this “surprise paradigm” to study machine intelligence allows for direct comparisons between an algorithm’s quantitative measure of surprise and a well-established human psychological measure of surprise—infants’ looking time. The models showed no such evidence of understanding the motivations underlying such actions, revealing that they are missing key foundational principles of commonsense psychology that infants possess.
“A human infant’s foundational knowledge is limited, abstract, and reflects our evolutionary inheritance, yet it can accommodate any context or culture in which that infant might live and learn,” observes Dillon.
The paper’s other authors are Gala Stojnić, an NYU postdoctoral fellow at the time of the study, Kanishk Gandhi, an NYU research assistant at the time of the study, and Shannon Yasuda, an NYU doctoral student.
The research was supported by grants from the National Science Foundation (DRL1845924) and the Defense Advanced Projects Research Agency (HR001119S0005).
# # #
END
Infants outperform AI in “commonsense psychology”
New study shows how infants are more adept at spotting motivations that drive human behavior
2023-02-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
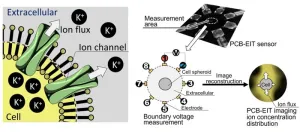
Non-invasive imaging of spatiotemporal ion distribution across cell membranes
2023-02-21
The cell membrane has numerous channels for the transport of various substances, including ions, between the cell and its environment. Ion transport determines the ion exchange rate (or the transmembrane transport coefficient), which, in turn, controls biological functions, such as nerve excitation, heartbeat, muscle contraction, and hormone secretion. It can also be anisotropic, wherein a non-uniform distribution of ions causes different ion exchange rates in different directions. This effect is quite pronounced in heterogeneous tissues. Therefore, the boundaries and overlap of tissues can be detected by measuring the associated anisotropic transmembrane transport.
Fluorescence ...
Investigating land subsidence in Japan through consecutive DInSAR and law of material conservation
2023-02-21
Land subsidence is a phenomenon wherein the Earth’s surface sinks downwards. It occurs mainly due to human activities, such as excessive groundwater extraction. It is a major global concern, affecting 19% of the world’s population. In Japan, some parts of the Tokyo metropolitan region are already sinking. This process can accelerate the flooding of coastal areas and cause damage to buildings and infrastructure. Therefore, monitoring land subsidence is crucial.
In Japan, observation wells are utilized to measure changes in the land surface and groundwater levels every few months. Additionally, the global navigation satellite system (GNSS) is also popular. However, ...
Study provides roadmap for using convalescent plasma as an effective COVID-19 treatment
2023-02-21
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Three years into the COVID-19 pandemic, new variant outbreaks continue to fuel economic disruptions and hospitalizations across the globe. Effective therapies remain unavailable in much of the world, and circulating variants have rendered monoclonal antibody treatments ineffective. But a new analysis shows how convalescent plasma can be used as an effective and low-cost treatment both during the COVID-19 pandemic and in the inevitable pandemics of the future.
In a study published in Clinical Infectious Diseases, an international ...
Improving access to reproductive health services among youth with intellectual and developmental disabilities
2023-02-21
New York, NY | February 21, 2023 — The National Institutes of Health (NIH) will award $3,906,026 over five years to researchers from the Institute for Implementation Science in Population Health (ISPH) at the CUNY Graduate School of Public Health and Health Policy (CUNY SPH) to test the efficacy of a new socialization and sex education curriculum for young people with intellectual and developmental disabilities.
CUNY SPH Professor Suzanne McDermott and Associate Professor Heidi Jones will test the curriculum in a randomized controlled trial among 856 adolescents ...
Working a four-day week boosts employee wellbeing while preserving productivity, major six-month trial finds
2023-02-21
Sixty-one organisations in the UK committed to a 20% reduction in working hours for all staff, with no fall in wages, for a six-month period starting in June 2022. The vast majority of companies also retained full-time productivity targets.
Now, results from the world’s largest trial of a four-day working week reveal significantly reduced rates of stress and illness in the workforce – with 71% of employees self-reporting lower levels of “burnout”, and 39% saying they were less ...
Prisons and Probation Ombudsman should improve transparency in death investigations to improve prison safety, report finds
2023-02-21
The UK Prisons and Probation Ombudsman (PPO) must improve transparency when investigating prisoner deaths, according to a new report and policy brief by prison safety experts at the University of Nottingham.
The report, written by Dr Sharon Shalev, draws on research led by Dr Philippa Tomczak in the Faculty of Social Sciences, which offers recommendations to the PPO and policymakers for improving prisoner death investigations and promoting change.
Every year, hundreds of prisoners die in England and Wales — in the 12 months to September 2022, there were 307 deaths in prison custody1. These deaths will almost always be ...
How do parents decide if they should vaccinate their kids against SARS-CoV-2?
2023-02-21
For parents, the decision to vaccinate their kids against SARS-CoV-2 is complex, influenced by scientific evidence, political and social pressures, and views about individual versus collective benefits of vaccination, according to a new study published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.221401.
Researchers conducted a qualitative study with in-depth interviews of 20 parents to understand their views about SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, with a goal to support future vaccination initiatives.
“Given the ...
Advocacy by LGBTQ+ school clubs may help combat student depression
2023-02-21
Advocacy by student-led Gender-Sexuality Alliance (GSA) clubs could help to reduce school-wide disparities in depressive symptoms between LGBTQ+ and heterosexual students, according to a new study.
The findings, published today in the Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, suggest that schools with GSAs (also known as Gay-Straight Alliances) that engage in more advocacy to highlight issues affecting LGBTQ+ students can help to promote well-being among LGBTQ+ youth across the wider school population.
“Discrimination ...
Does living along the US-Mexico border affect the chances of survival among children with leukemia?
2023-02-21
Residing in border regions was linked with a higher risk of dying within five years among children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the most common type of pediatric cancer.
In an analysis of cancer registry data from Texas, children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) who lived along the border with Mexico were more likely to die within five years than those living in other areas of the state. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
The ...
New way to predict the damage and aging of bridges by using DNA. technologies
2023-02-21
The Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Kim Byung-Suk) announced that it has developed the D.N.A. (Data, Network, and AI) technologies to predict the levels of damage and aging of bridges for preventive maintenance.
As of 2021, the percentage of Korean bridges aged 30 years or more stands at a relatively low 12.5%. However, this ratio is expected to increase in the next decade to 39.3% by 2031 and rapidly spike up to 76.1% in 20 years. For the preemptive management of these aging bridges, the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
[Press-News.org] Infants outperform AI in “commonsense psychology”New study shows how infants are more adept at spotting motivations that drive human behavior