(Press-News.org) Researchers from Oregon Health & Science University and institutions across the country have identified a pill used to treat a common skin disease as an “incredibly promising” treatment for alcohol use disorder.
The study was recently published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
On average, the people who received the medication, called apremilast, reduced their alcohol intake by more than half — from five drinks per day to two.
“I’ve never seen anything like that before,” said co-senior author Angela Ozburn, Ph.D., associate professor of behavioral neuroscience in the OHSU School of Medicine and a research biologist with the Portland VA Health Care System.
The lead author is Kolter Grigsby, Ph.D., a postdoctoral fellow in the Ozburn laboratory at OHSU.
Beginning in 2015, Ozburn and collaborators searched a genetic database looking for compounds likely to counteract the expression of genes known to be linked to heavy alcohol use. Apremilast, an FDA-approved anti-inflammatory medication used to treat psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, appeared to be a promising candidate.
They then tested it in two unique animal models that have a genetic of risk for excessive drinking, as well as in other strains of mice at laboratories across the country. In each case, apremilast reduced drinking among a variety of models predisposed to mild to heavy alcohol use. They found that apremilast triggered an increase in activity in the nucleus accumbens, the region of the brain involved in controlling alcohol intake.
Researchers at the Scripps Research Institute in La Jolla, California, then tested apremilast in people.
The Scripps team conducted a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical proof-of-concept study involving 51 people who were assessed over 11 days of treatment.
“Apremilast’s large effect size on reducing drinking, combined with its good tolerability in our participants, suggests it is an excellent candidate for further evaluation as a novel treatment for people with alcohol use disorder,” said co-senior author Barbara Mason, Ph.D., Pearson Family professor in the Department of Molecular Medicine at Scripps.
The clinical study involved people with alcohol use disorder who weren’t seeking any form of treatment, and Mason predicts that apremilast may be even more effective among people who are motivated to reduce their alcohol consumption.
“It’s imperative for more clinical trials to be done on people seeking treatment,” Ozburn said. “In this study, we saw that apremilast worked in mice. It worked in different labs, and it worked in people. This is incredibly promising for treatment of addiction in general.”
An estimated 95,000 people in the United States die every year from alcohol-related deaths, according to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism.
Currently, there are three medications approved for alcohol use disorder in the United States: Antabuse, which produces an acute sensitivity akin to a hangover when alcohol is consumed; acamprosate, a medication thought to stabilize chemical signaling in the brain that is associated with relapse; and naltrexone, a medication that blocks the euphoric effects of both alcohol and opioids.
The research reported here was supported by the National Institutes of Health awards AA016651, AA013519, AA010760, AA07468, AA027692, U01 AA013498, DA013429, P60AA06420 and U01AA025476; the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs awards BX000313, BX004699 and IK2 BX002488; and a gift from the John R. Andrews Family. The content is solely the responsibility of the researchers and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH or the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs.
END
Pill for skin disease also curbs excessive drinking
Study from OHSU, research institutions nationwide lands on promising treatment for alcohol use disorder
2023-02-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
University of Ottawa physician is first Canadian winner of new award focused on health workforce wellness
2023-02-21
The University of Ottawa's Dr. Mamta Gautam is the first awardee of the AFMC Wellness Award, a new national honour that recognizes an individual in Canada who has shown dedication to the promotion and advancement of the wellness of physicians, medical students, and others.
“I am truly humbled and honoured. Promoting physician wellbeing is an area that I have been passionate about for over 30 years. To have the AFMC create an award to recognize contributions in this area lends further credibility to the importance of this topic,” ...
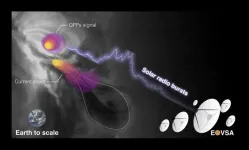
Researchers discover mysterious source of 'heartbeat-like' radio bursts in a solar fare
2023-02-21
A solar radio burst with a signal pattern, akin to that of a heartbeat, has been pinpointed in the Sun’s atmosphere, according to a new study.
In findings published in the journal Nature Communications, an international team of researchers has reported uncovering the source location of a radio signal coming from within a C-class solar flare more than 5,000 kilometers above the Sun’s surface.
Researchers say the study’s findings could help scientists better understand the physical processes behind the energy release of solar flares — the solar system’s most powerful explosions.
“The ...
Three talented researchers recognized as endowed chairs
2023-02-21
Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah (The U) is pleased to congratulate three of our newest endowed chairs. A chair appointment recognizes excellence, while providing academic distinction and funding for future research. Alana Welm, PhD, received a five-year extension in her current role as Ralph E. and Willia T. Main Presidential Endowed Chair in Cancer Research, Aik Choon Tan, PhD, was named the Jon and Karen Huntsman Presidential Professor in Cancer Research, and Brad Cairns, PhD, was named ...
New transmitter design for small satellite constellations improves signal transmission
2023-02-21
Today, there are many emerging applications for small satellite constellations, ranging from space-borne networks to environmental monitoring. However, small satellites have special needs when it comes to transmitter (TX) technology. For one, they have stringent limitations on power consumption as they draw energy from solar panels and cannot easily dissipate generated heat. Moreover, small satellites need to communicate with fast-moving targets that can be over a thousand kilometers away. Thus, they require efficient and precise beam steering capabilities to direct most of the transmitted power ...
Improving the performance of satellites in low Earth orbit
2023-02-21
A database updated in 2022 reported around 4,852 active satellites orbiting the earth. These satellites serve many different purposes in space, from GPS and weather tracking to military reconnaissance and early warning systems. Given the wide array of uses for satellites, especially in low Earth orbit (LEO), researchers are constantly trying to develop better ones. In this regard, small satellites have a lot of potential. They can reduce launch costs and increase the number of satellites in orbit, providing a better network with wider coverage. ...
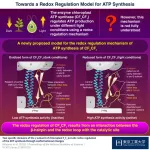
Researchers uncover how photosynthetic organisms regulate and synthesize ATP
2023-02-21
ATP, the compound essential for the functioning of photosynthetic organisms such as plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, is produced by an enzyme called “chloroplast ATP synthase” (CFoCF1). To control ATP production under varying light conditions, the enzyme uses a redox regulatory mechanism that modifies the ATP synthesis activity in response to changes in the redox state of cysteine (Cys) residues, which exist as dithiols under reducing (light) conditions, but forms a disulfide bond under oxidizing (dark) conditions. ...
Sheep can benefit urban lawn landscapes and people
2023-02-21
Bicycles whirr by, students rush to class, staff and faculty are grabbing lunch or coffee on the go — and sheep graze the grassy knolls among the traffic, bleating every now and then. The grazing is their job.
The 25 wooly sheep who seasonally — for the past two years — leave their University of California, Davis, barns to nibble on lawns at various central campus locations, are doing much more than mowing, fertilizing and improving the ecosystem. The sheep also are improving people’s mental health.
The sheep — four breeds of Suffolk, Hampshire, Southdown and Dorset — first took on this role in 2021, when COVID-19 ...
UCLA Health tip sheet: Pesticides & Parkinson’s symptoms; Gender-affirming hormones tied to mental health for transgender youth; Body composition, not BMI, may signal risk for cardiovascular disease
2023-02-21
UCLA Health Tip Sheet Feb. 21, 2023
Below is a brief roundup of news and story ideas from the experts at UCLA Health. For more information on these stories or for help on other stories, please contact us at uclahealthnews@mednet.ucla.edu.
Body composition, not BMI, may signal risk for cardiovascular disease Body mass index has long been a measure of a person’s risk of developing cardiovascular disease, but body composition and its role in the disease have not been well studied. In a new study, ...
Better tools needed to determine ancient life on Mars
2023-02-21
ITHACA, N.Y. – Current state-of-the-art instrumentation being sent to Mars to collect and analyze evidence of life might not be sensitive enough to make accurate assessments, according to a research team co-led by a Cornell University astronomer.
In a paper published in Nature Communications, visiting planetary scientist Alberto Fairén, and an international team of researchers, claim that ancient organic material in Martian rocks could be difficult, if not impossible, to detect with current instruments and techniques.
Fairén – also a research professor at the Center ...
Rewiring blood cells to give rise to precursors of sperm
2023-02-21
Different cell types—say, heart, liver, blood, and sperm cells—possess characteristics that help them carry out their unique jobs in the body. In general, those characteristics are hard-wired. Without intervention, a heart cell won’t spontaneously transform into a liver cell.
Yet researchers from the University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine, working with collaborators from the University of Texas at San Antonio and Texas Biomedical Research Institute, have prompted marmoset blood cells to acquire the flexibility of stem cells. Then they directed those stem cells to take on the characteristics of sperm ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
[Press-News.org] Pill for skin disease also curbs excessive drinkingStudy from OHSU, research institutions nationwide lands on promising treatment for alcohol use disorder