Public voting now open for the 2023 Morgridge Ethics Cartooning Competition
2023-02-21
(Press-News.org)
Eighteen cartoons have been selected as finalists in the 2023 Ethics Cartooning Competition, an annual contest sponsored by the Morgridge Institute for Research.
Participants from the University of Wisconsin-Madison and affiliated biomedical centers or institutes submitted their work, then a panel of judges selected the final cartoons for display to the public, who is invited to vote and help determine the 2023 winners.
This year’s cartoons depict a variety of research ethics topics, such as the ethics of scientific publishing, research funding and environments, questionable research practices, drug pricing, the ethics of experimenting on animals, social impacts of scientific research, and scientists as responsible members of society.
The Morgridge Ethics Cartooning Competition, developed by Morgridge Bioethics Scholar in Residence Pilar Ossorio, encourages scientists to shed light on timely or recurring issues that arise in scientific research.
“Ethical issues are all around us,” says Ossorio. “An event like the competition encourages people to identify some of those issues, perhaps talk about them with friends and colleagues, and think about how to communicate about those issues with a broader community of people.”
Public voting is open until March 10, 2023: https://morgridge.org/story/ethics-cartooning-contest-vote-2023/
###
As an independent research organization, the Morgridge Institute for Research explores uncharted scientific territory to discover tomorrow’s cures. In affiliation with the University of Wisconsin-Madison, we support researchers who take a fearless approach to advancing human health in emerging fields such as regenerative biology, metabolism, virology and biomedical imaging. Through public programming, we work to inspire scientific curiosity in everyday life. Learn more at: morgridge.org
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-02-21
The Boyce Thompson Institute (BTI) is delighted to announce that faculty member Fay-Wei Li has been promoted to Associate Professor on January 13. Li was evaluated on his achievements to date and likelihood of continued success in the future.
Since joining BTI in 2017, Li has developed an internationally-recognized program on seed-free plants, both in terms of genome sequencing and in making biological discoveries. He also is an excellent science communicator, with a knack for explaining the importance of scientific discoveries to a wide range of audiences.
The ...
2023-02-21
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. – So much of modern life is spent on screens: Zoom meetings and websites, smartphones and videogames, televisions and social media. How are all those pixels and rectangles affecting how we see?
Binghamton University, State University of New York Professor of Psychology Peter Gerhardstein and doctoral candidate Nicholas Duggan explore the phenomenon in “Levels of Orientation Bias Differ Across Digital Content Categories: Implications for Visual Perception,” recently published in the journal Perception. Their paper covers the extent to which online content ...
2023-02-21
CLEVELAND: Supported by a new $3.14 million grant from the National Institutes of Health to Cleveland Clinic, researchers are using an emerging technology known as “digital twins” to better understand healthcare disparities based on where someone lives. Researchers from Cleveland Clinic and MetroHealth aim to use this information to develop strategies designed to reduce these disparities in health outcomes.
The research team, led by Jarrod Dalton, Ph.D., of Cleveland Clinic, and Adam Perzynski, Ph.D., of MetroHealth, ...
2023-02-21
(MIAMI, FL, FEB. 21, 2023) – To create the most effective, personalized treatment plans for patients with Hodgkin lymphoma or other cancers, scientists and clinicians need the clearest picture of the genetic changes leading to the cancer’s development. That picture, say scientists at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center in the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, comes into much better focus when whole genome sequencing – rather than the current standard, exome sequencing – is used to identify changes driving the cancer.
Exome sequencing, which reads only protein-coding genes, can detect some specific mutations and other variants that propel cancers, ...
2023-02-21
Written by Kay Ledbetter, 806-547-0002, skledbetter@ag.tamu.edu
Imagine your favorite cured meat like beef jerky, pepperoni or bacon without any added sodium nitrite from any source currently necessary for color and shelf life. Wes Osburn, Ph.D., is doing exactly that.
At center, Wes Osburn, Ph.D., Texas A&M University meat scientist, is working in his lab with students Tanner Wright and Arlie Reeves on a new no nitrite-added cured meat system. (Texas A&M AgriLife photo ...
2023-02-21
Eurasian spruce bark beetles (Ips typographus) burrow into the bark of Norway spruce (Picea abies) trees where they mate and lay their eggs. Major outbreaks in Europe have decimated millions of hectares of conifer forests. The beetles preferentially attack trees that are already infected with symbiotic fungi (such as Grosmannia penicillata), which is thought to weaken host trees and break down their chemical defenses, allowing the beetles to successfully develop in the bark.
To investigate the chemical signals ...
2023-02-21
The mass outbreaks of bark beetles observed in recent years have caused shocking amounts of forest damage throughout Germany. As reported by the Federal Statistical Office in July 2022, more than 80% of the trees that had to be felled in the previous year were damaged by insects. The damaged timber felled due to insect damage amounted to more than 40 million cubic meters. One of the main pests is the European spruce beetle Ips typographus. In the Thuringian Forest and the Harz Mountains, for example, the beetle, which is only a few millimeters long, encountered spruce monocultures that had already been weakened by high temperatures and extended ...
2023-02-21
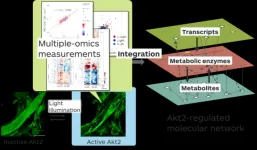
Takeaki Ozawa and his team from the University of Tokyo reveal the metabolic reactions upon activating an enzyme called Akt2. In doing so, they reveal the inner workings of insulin-regulated metabolism. The findings lead the way for Akt2-targeting therapeutics for diabetes and metabolic disorders.
It takes energy to do anything—even to exist. You can metabolize food to convert glucose into energy: thanks to many cascades of molecular reactions within your cells. As soon as you eat, your pancreas secretes insulin hormone, which starts ...
2023-02-21
SAN FRANCISCO, CA—February 21, 2023—Of all the known genetic risk factors for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease, the strongest is a gene for the protein called ApoE4. People with one copy of this gene are 3.5 times more likely, on average, to develop Alzheimer’s than others, and those with two copies face a 12-fold increased risk. However, exactly how ApoE4 boosts the risk of Alzheimer’s remains unclear.
Multiple types of cells in the brain make ApoE4—some of it is produced by neurons, but other brain cells called glia make it in higher quantities. For that reason, most prior research on this protein has focused on ...
2023-02-21
University Professor Douglas Rhoads has been named a Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science, the world’s largest general scientific society and publisher of the journal Science.
As one of only 20 fellows representing the Section on Agriculture, Food & Renewable Resources, Rhoads was chosen by his peers and colleagues for advancing science and its applications in service to society. The organization elected a total of 505 fellows across 24 scientific sections.
Rhoads is director of the Interdisciplinary ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Public voting now open for the 2023 Morgridge Ethics Cartooning Competition