(Press-News.org) WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – Feb. 23, 2023 – Wake Forest University and Wake Forest University School of Medicine will receive $3 million over five years from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to help researchers take the next steps in nearly a decade of research that indicates dance can promote cognitive health.
The grant funds a new study called IGROOVE that will help researchers determine what kinds of dance, the frequency of the dance classes and what aspects of the dance class – music, social interaction, cognitive challenge – affect fitness, memory and brain health.
The research will be co-led by Christina E. Hugenschmidt, Ph.D., associate professor of gerontology and geriatric medicine at Wake Forest University School of Medicine, and Christina T. Soriano, M.F.A., dance professor and vice provost of the arts and interdisciplinary initiatives at Wake Forest University.
The study is highly innovative in its research techniques and methodology. The team will test outcomes for different “doses” of dance. Participants will attend classes one, two or three days a week for six months and either learn four different styles of dance or be randomized to a music appreciation class control group.
Research on physical activity and its effects on older adults has traditionally focused on gym-based activities like treadmill walking or fitness classes. While cardiorespiratory fitness has proven to be important for brain health in aging, it is not the only factor.
Dancing raises heart rate and also encourages social connections. Formal dances like the tango or classical dance are also cognitively challenging.
“We are thrilled that the NIH continues to support Wake Forest’s research on dance and how movement benefits brain health,” Soriano said. “Because dance is a fun and social activity, older adults may be more likely to keep dancing as they age.”
A history of research on dance and dementia
Hugenschmidt and Soriano have collaborated on past studies that looked at the effects of improvisational dance on the brain. Their previous work used dance to test the effects of social engagement and movement on well-being in older adults with early-stage dementia.
Preliminary results from these past studies suggest that improvisational dance can improve secondary symptoms of dementia that affect quality of life – including gait and balance challenges, mood changes, apathy and depression.
“In spite of all the promising findings about dance, very basic information is lacking that is available for other forms of exercise, Hugenschmidt said. “How often do you need to dance to see improvements in fitness and brain function? What about dance affects improvements - is it improved fitness, the music, social connections or cognitive challenges? This new study will help us answer these questions.”
Want to groove? Adults aged 65 and older who are interested in joining the new IGROOVE study are encouraged to call 336-713-MOVE (6683) or email igroove@wakehealth.edu.
END
$3M NIH grant will fund next steps of research on dance and brain health
2023-02-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UC Irvine researchers create E. coli-based water monitoring technology
2023-02-23
Irvine, Calif., Feb. 23, 2023 – People often associate Escherichia coli with contaminated food, but E. coli has long been a workhorse in biotechnology. Scientists at the University of California, Irvine have demonstrated that the bacterium has further value as part of a system to detect heavy metal contamination in water.
E. coli exhibit a biochemical response in the presence of metal ions, a slight change that researchers were able to observe with chemically assembled gold nanoparticle optical sensors. Through a machine-learning ...
New $2.9 million grant helps researchers address food insecurity for Hoosiers
2023-02-23
INDIANAPOLIS—With a $2.9 million grant from the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities, researchers from Indiana University School of Medicine are working to improve food insecurity in Indiana and ultimately improve the health of people in Indiana.
Individuals who experience food insecurity–inconsistent access to affordable and nutritious food–are more susceptible to a variety of health conditions, including hypertension and Type 2 Diabetes. The FoRKS: Food Resources ...
On the road to better solid-state batteries
2023-02-23
A team from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and Florida State University has designed a new blueprint for solid-state batteries that are less dependent on specific chemical elements, particularly critical metals that are challenging to source due to supply chain issues. Their work, reported recently in the journal Science, could advance solid-state batteries that are efficient and affordable.
Touted for their high energy density and superior safety, solid-state batteries could be a game-changer for the electric car industry. ...
National Center to Reframe Aging welcomes 16 to new advisory board
2023-02-23
The National Center to Reframe Aging — the nation’s leading organization dedicated to reshaping the conversation about older people — has established a new advisory board with 16 members from such diverse professional backgrounds as communications and public relations, research, policy, and law.
These board members were tapped to bring knowledge, strategic thinking, and interpersonal attributes to their role; to identify key organizations and decision-makers who can help advance the initiative; and support activities aligning with National Center project goals.
“We look forward to working with this talented group of advisors to grow ...
Heterostructures developed at Purdue support predictions of counterpropagating charged edge modes at the v=2/3 fractional quantum Hall state
2023-02-23
In 2018, a team of physicists at Purdue University invented a device which experimentally showed quasiparticles interfering for the first time in the fractional quantum Hall effect at filling factor v=1/3. Further development of these heterostructures has allowed the Manfra Group to expand their research to experiments that explore counterflowing charged edge modes at the 2/3 fractional quantum Hall state.
They have recently published their findings, “Half-Integer Conductance Plateau at the ν = 2/3 Fractional Quantum Hall State in a Quantum Point Contact,” in Physical Review Letters on February 17, 2023. This ...
Fungi that causes pine ghost canker detected in southern California trees
2023-02-23
Fungal pathogens that cause die-back in grape, avocado, citrus, nut and other crops has found a new host and is infecting conifer trees causing Pine Ghost Canker in urban forest areas of Southern California.
The canker can be deadly to trees.
Scientists from University of California, Davis, first spotted evidence that the pathogens had moved to pines during a routine examination of trees in Orange County in 2018. Over four years, they found that more than 30 mature pines had been infected in an area of nearly 100 acres, according ...
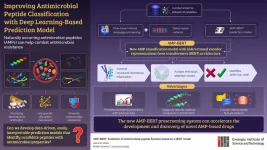
GIST researchers develop “AMP-BERT”: A new AI-based “finder” of antimicrobial peptides
2023-02-23
Over the last few decades, antimicrobial resistance has become a major public health concern globally. This has led to a search for alternative methods of treating microbial infections. One such innovation is the discovery of antimicrobial properties of certain peptides. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are short peptides found in most animals, plants, and microorganisms as a natural defense against infections. AMPs combat harmful bacteria via a nonspecific mechanism that prevents them from developing antimicrobial resistance. Despite these exceptional abilities, research on AMPs is being hindered because the existing systems for identifying candidate ...
Alternate framework for distributed computing tames Big Data’s ever growing costs
2023-02-23
The sheer volume of ‘Big Data’ produced today by various sectors is beginning to overwhelm even the extremely efficient computational techniques developed to sift through all that information. But a new computational framework based on random sampling looks set to finally tame Big Data’s ever-growing communication, memory and energy costs into something more manageable.
A paper describing the framework was published in the journal Big Data Mining and Analytics on Jan. 26.
The amount of data being produced from social networks, business transactions, the ‘Internet of Things’, finance, healthcare and beyond has exploded ...
Insilico Medicine sends first generative AI-designed drug for COVID-19 and variants to clinic
2023-02-23
Insilico Medicine, a clinical-stage biotech company powered by generative AI, today announces that China National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) has approved the Investigational New Drug (IND) application for ISM3312, an orally available 3CLpro inhibitor generated and designed with the support of Insilico’s proprietary generative chemistry platform Chemistry42 for the treatment of COVID-19.
ISM3312 is a highly selective small molecule inhibitor with a novel molecular structure optimized from compounds which were generated and designed by Chemistry42 based on the structure of 3CL protease. It binds to ...
Children’s lung capacity improved in cleaner air
2023-02-23
As air pollution in Stockholm has decreased, so has the lung capacity of children and adolescents has improved, a new study published in the European Respiratory Journal reports. The researchers from Karolinska Institutet consider the results important, since the lung health of the young greatly affects the risk of their developing chronic lung diseases later in life.
“Fortunately, we’ve seen a decrease in air pollutants and therefore an increase in air quality in Stockholm over the past 20 years,” says the study’s last author ...