(Press-News.org) Astronomers from the University of Texas and the University of Arizona have discovered a rapidly growing black hole in one of the most extreme galaxies known in the very early Universe. The discovery of the galaxy and the black hole at its centre provides new clues on the formation of the very first supermassive black holes. The new work is published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
Using observations taken with the Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA), a radio observatory sited in Chile, the team have determined that the galaxy, named COS-87259, containing this new supermassive black hole is very extreme, forming stars at a rate 1000 times that of our own Milky Way and containing over a billion solar masses worth of interstellar dust. The galaxy shines bright from both this intense burst of star formation and the growing supermassive black hole at its centre.
The black hole is considered to be a new type of primordial black hole – one heavily enshrouded by cosmic “dust”, causing nearly all of its light to be emitted in the mid-infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum. The researchers have also found that this growing supermassive black hole (frequently referred to as an active galactic nucleus) is generating a strong jet of material moving at near light speed through the host galaxy.
Today, black holes with masses millions to billions of times greater than that of our own Sun sit at the centre of nearly every galaxy. How these supermassive black holes first formed remains a mystery for scientists, particularly because several of these objects have been found when the Universe was very young. Because the light from these sources takes so long to reach us, we see them as they existed in the past; in this case, just 750 million years after the Big Bang, which is approximately 5% of the current age of the Universe.
What is particularly astonishing about this new object is that it was identified over a relatively small patch of the sky typically used to detect similar objects – less than 10 times the size of the full moon – suggesting there could be thousands of similar sources in the very early Universe. This was completely unexpected from previous data.
The only other class of supermassive black holes we knew about in the very early Universe are quasars, which are active black holes that are relatively unobscured by cosmic dust. These quasars are extremely rare at distances similar to COS-87259, with only a few tens located over the full sky. The surprising discovery of COS-87259 and its black hole raises several questions about the abundance of very early supermassive black holes, as well as the types of galaxies in which they typically form.
Ryan Endsley, the lead author of the paper and now a Postdoctoral Fellow at The University of Texas at Austin, says “These results suggest that very early supermassive black holes were often heavily obscured by dust, perhaps as a consequence of the intense star formation activity in their host galaxies. This is something others have been predicting for a few years now, and it’s really nice to see the first direct observational evidence supporting this scenario.”
Similar types of objects have been found in the more local, present-day Universe, such as Arp 299 shown here. In this system, two galaxies are crashing together generating an intense starburst as well as heavy obscuration of the growing supermassive black hole in one of the two galaxies.
Endsley adds, “While nobody expected to find this kind of object in the very early Universe, its discovery takes a step towards building a much better understanding of how billion solar mass black holes were able to form so early on in the lifetime of the Universe, as well how the most massive galaxies first evolved.”
END
New discovery sheds light on very early supermassive black holes
2023-02-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
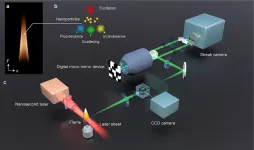
World’s fastest laser camera films combustion in real time
2023-02-24
By illuminating a sample surface with short laser beam pulses, it is possible to film sequences of various chemical and physical reactions. A research team that included researchers from the University of Gothenburg has now developed the world’s fastest single-shot laser camera, which is at least a thousand times faster than today’s most modern equipment for combustion diagnostics. The discovery has enormous significance for studying the lightning-fast combustion of hydrocarbons.
What happens ...
Exercise more effective than medicines to manage mental health
2023-02-24
University of South Australia researchers are calling for exercise to be a mainstay approach for managing depression as a new study shows that physical activity is 1.5 times more effective than counselling or the leading medications.
Published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine, the review is the most comprehensive to date, encompassing 97 reviews, 1039 trials and 128,119 participants. It shows that physical activity is extremely beneficial for improving symptoms of depression, anxiety, and distress.
Specifically, the review showed that exercise interventions ...
Faster and sharper whole-body imaging of small animals with deep learning
2023-02-24
It takes a few moments for the sound of thunder to reach our ears after a flash of lightning. This phenomenon is due to the photoacoustic (PA) effect where materials near the lightning instantly expand as the optical energy of the lightning is absorbed and converted into thermal energy. Using this PA effect, photoacoustic computed tomography (PACT) has become a premier preclinical and clinical imaging modality to take images inside the body without using a contrast medium. However, its low-quality images, which can be improved with multiple ultrasound sensors and a multi-channel data acquisition (DAQ) system, ...
Calming the destructive cells of ALS by two independent approaches
2023-02-24
· Diseased neurons have pathology in which proteins become misfolded and toxic
· Normally supportive cells attack the diseased neurons and destroy them
· This pathology occurs in 90% of ALS patient brains and in frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer’s disease
CHICAGO --- Northwestern Medicine scientists have discovered two ways to preserve diseased upper motor neurons that would normally be destroyed in ALS, based on a study in mice. Upper motor neurons initiate movement, ...
Marine heatwaves decimate sea urchins, molluscs and more at Rottnest
2023-02-24
Curtin University researchers believe rising sea temperatures are to blame for the plummeting number of invertebrates such as molluscs and sea urchins at Rottnest Island off Western Australia, with some species having declined by up to 90 per cent between 2007 and 2021.
Lead author Adjunct Professor Fred Wells, from Curtin’s School of Molecular and Life Sciences, said the west end of Rottnest Island had suffered a “catastrophic decline” in biodiversity.
“Since 1982, we have monitored biodiversity of marine molluscs and echinoderms ...
Ultrafast synthesis of cobalt/carbon nanocomposites by magnetic induction heating for oxygen evolution reaction
2023-02-24
This study is led by Dr. Shaowei Chen (University of California). Natural gas reforming accounts for 95% of the hydrogen gas produced in the United States; yet the hydrogen is non-sustainable and “grey”, as it originates from fossil fuels . To obtain sustainable “green” hydrogen gas, electrochemical water splitting by using renewable electricity has emerged as one of the most promising technologies, which consists of hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) at the cathode and oxygen evolution reaction (OER) at the anode . Yet, due to the sluggish electron-transfer kinetics and complex reaction pathways, OER typically entails a large overpotential and severely ...
Building an ideal knowledge management system
2023-02-24
By Jovina Ang
SMU Office of Research & Tech Transfer – There are many reasons why knowledge management is important for an organisation.
Among the many reasons, the most mentioned are:
Speed up access to information and knowledge, or to people who hold the information you need;
Improve decision-making processes;
Promote innovation due to the sharing of ideas, collaboration and access to the latest information;
Improve the efficiency and productivity via reducing the tendency to “reinvent the wheel”;
Increase customer ...
KIST offers a novel paradigm for social robots
2023-02-24
After competing in the finals with the University College London, which presented Bubble Worlds, the research team led by Dr. Sona Kwak from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST; President Seok Jin Yoon) presented "CollaBot" and received the best award in the "hardware, design, and interface" category at the Robot Design Competition hosted by the International Conference on Social Robotics (ICSR) 2022, which was held at the Chamber of Commerce in Florence, Italy (December 13-16, 2022).
Previous studies on social robots were primarily based on humanoid robots that understand the context of situations and provide a range ...
Are dual-class shares good, bad, or a necessary evil?
2023-02-24
By Alvin Lee
SMU Office of Research & Tech Transfer – When Chinese consumer electronics giant Xiaomi (小米) listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange (SEHK) in June 2018, it followed the well-beaten path travelled by earlier mainland companies, ranging from high-tech predecessors Tencent (腾讯, 0700.HK) to non-tech companies such as Tsingtao Brewery (0168.HK) and China Eastern Airlines (0670.HK).
While the IPO raised US$4.72 billion in the tech world’s biggest float in four years, it garnered extra attention for being the first SEHK listing with dual-class shares ...
Mitigating heat impacts for cooler cities
2023-02-24
By Alistair Jones
SMU Office of Research & Tech Transfer – The life of a researcher is not for everyone, but for Yuliya Dzyuban, a Research Fellow in the new College of Integrative Studies at Singapore Management University (SMU), it's a perfect fit.
“With time, I realised that studying is what I do best and enjoy the most. Research offers opportunities for endless learning,” she says.
“There are always new projects, new challenges, new ideas and evolving methods. I love the fact that I can learn something ...