(Press-News.org) Regular physical activity can improve adolescents’ mental health and help with behavioural difficulties, research suggests.
Engaging in regular moderate to vigorous physical activity at age 11 was associated with better mental health between the ages of 11 and 13, the study found.
Physical activity was also associated with reduced hyperactivity and behavioural problems, such as loss of temper, fighting with other children, lying, and stealing, in young people.
Researchers from the Universities of Edinburgh, Strathclyde, Bristol, and Georgia in the United States explored data from the Children of the 90s study (also known as the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children; ALSPAC). They looked at the levels of physical activity of 4755 11-year-olds which was measured using devices.
The devices recorded levels of moderate physical activity – typically defined as brisk walking or cycling – as well as vigorous activity which boosts heart rate and breathing, such as aerobic dancing, jogging or swimming.
The young people and their parents reported on their levels of depressive symptoms from age 11 and at age 13 years. Participants’ parents and teachers were also quizzed about the young people’s general behaviour and emotional difficulties.
In analysing the impact of moderate to vigorous exercise on the young people’s mental health and behaviour, the team also considered factors such as age, sex and socio-economic status.
They found that higher levels of moderate or intense physical activity had a small but detectable association with decreases in depressive symptoms and emotional difficulties.
Regular exercise had a small but detectable association with reduced behavioural problems, even after controlling for other possible influences, the study found.
The findings suggest regular moderate and intense physical activity may have a small protective influence on mental health in early adolescence, researchers say.
Dr Josie Booth, of the University of Edinburgh’s Moray House School of Education and Sport, said: “This study adds to the increasing evidence base about how important physical activity is for all aspects of young people’s development – it can help them feel better, and do better at school. Supporting young people to lead healthy active lives should be prioritised.”
Researchers say the study is the first to offer such a comprehensive approach to examining mental health and exercise in young people.
Professor John Reilly, at the University of Strathclyde, said: “While it might seem obvious that physical activity improves mental health the evidence for such a benefit in children and young people has been scarce, so the study findings are important. The findings are also important because levels of moderate-to-vigorous intensity activity globally are so low in pre-teens globally – less than a third achieve the 60 minutes per day recommended by the WHO and UK Health Departments.”
The study is published in Mental Health and Physical Activity. An Open Access version of the paper is available here: https://www.research.ed.ac.uk/en/publications/associations-between-objectively-measured-physical-activity-and-m
The research was funded by the Bupa Foundation. Researchers used data from the Children of the 90s study, also known as the ALSPAC birth cohort, based at the University of Bristol. The study is a long-term health-research project that enrolled more than 14,000 pregnant women in 1991 and 1992.
Children of the 90s has been following the health and development of the parents and their children in detail and is currently recruiting the children and the siblings of the original children into the study. It receives core funding from the Medical Research Council, the Wellcome Trust and the University of Bristol.
For further information, please contact: Joanne Morrison, Press and PR Office, tel +44 131 651 4266, joanne.morrison@ed.ac.uk
END
Physical activity can help mental health in pre-teen years
Regular physical activity can improve adolescents’ mental health and help with behavioural difficulties, research suggests.
2023-03-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
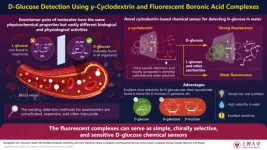
New fluorescent chiral-selective receptor system represents a breakthrough in molecular detection with potential for applications in diabetes management
2023-03-02
Diabetes mellitus, simply called diabetes, is a metabolic disorder characterized by the presence of abnormally high concentrations of glucose in blood. Existing methods for the diagnosis of diabetes rely on traditional techniques of detecting glucose in blood serum samples—a process that is typically tedious and expensive.
Molecular recognition is the science of accurately detecting specific compounds by exploiting their binding properties. Here, a receptor molecule–a kind of sensor–selectively binds to a target molecule. This process triggers some reaction, say, a change ...
Sleep too much or too little and you might get sick more, scientists find
2023-03-02
A good night’s sleep can solve all sorts of problems – but scientists have now discovered new evidence that sleeping well may make you less vulnerable to infection. Scientists at the University of Bergen recruited medical students working in doctors’ surgeries to hand out short questionnaires to patients, asking about sleep quality and recent infections. They found that patients who reported sleeping too little or too much were more likely also to report a recent infection, and patients ...
Study suggests EHR-focused interventions can significantly reduce unnecessary urine cultures among hospital patients
2023-03-02
Study Suggests EHR-Focused Interventions Can Significantly Reduce Unnecessary Urine Cultures Among Hospital Patients
Initiative highlighted in AJIC provides model for resource-limited institutions to decrease overdiagnosis and overtreatment of asymptomatic bacterial infections
Arlington, Va., March 2, 2023 – Physicians in the largest safety-net hospital system in the United States used two electronic health record (EHR)-focused interventions to significantly reduce inappropriate urine cultures among hospitalized patients. Findings from their study, published in the ...
Edible electronics: How a seaweed second skin could transform health and fitness sensor tech
2023-03-02
Scientists at the University of Sussex have successfully trialed new biodegradable health sensors that could change the way we experience personal healthcare and fitness monitoring technology.
The team at Sussex have developed the new health sensors – such as those worn by runners or patients to monitor heart rate and temperature – using natural elements like rock salt, water and seaweed, combined with graphene. Because they are solely made with ingredients found in nature, the sensors are fully biodegradable, making them more environmentally friendly than commonly used rubber and plastic-based alternatives. Their natural ...
Cocaethylene cardiotoxicity in emergency department patients with acute drug overdose
2023-03-01
Des Plaines, IL — When compared to cocaine exposure alone, cocaine and ethanol exposure in emergency department (ED) patients with acute drug overdose was significantly associated with higher occurrence of cardiac arrest, higher mean lactate concentrations, and lower occurrence of myocardial injury. This is the conclusion of a study titled, Cocaethylene cardiotoxicity in emergency department patients with acute drug overdose published in the February issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM), the peer-reviewed journal of the Society for Academic Emergency ...
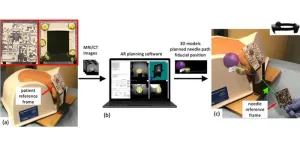
Free-hand, real-time needle guidance for prostate cancer diagnosis with augmented reality
2023-03-01
According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death among men. One of the standard approaches for the diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer involves transperineal (TP) biopsy. This involves inserting a needle through the perineum wall to collect tissue samples. Current methods for TP biopsy generally include a pre-operation MRI scan and a transrectal ultrasound. These images are then fused together and shown on a monitor to the urologist, who then inserts the needle. The needle insertion can be ...
Special Selection
2023-03-01
A team of global experts has discovered new signals of natural selection in humans.
Led by UC Santa Barbara Tsimane Health and Life History Project co-director Michael Gurven, the team studied two populations living in the Bolivian Amazon rainforest — the Tsimane and the Moseten. Previous studies show that these tropical populations are exposed to many parasites and a variety of pathogens; at the same time, the Tsimane rarely suffer from cardiovascular diseases and dementia. This new research suggests that the Tsimane genome has undergone selection ...
Bronze Age well contents reveal the history of animal resources in Mycenae, Greece
2023-03-01
A large Bronze Age debris deposit in Mycenae, Greece provides important data for understanding the history of animal resources at the site, according to a study published March 1, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Jacqueline Meier of the University of North Florida and colleagues.
Animals were an important source of subsistence and symbolism at the Late Bronze Age site of Mycenae in Greece, as evidenced by their depictions in art and architecture, but more research is needed on the animals ...
What distinguishes fans from celebrity stalkers?
2023-03-01
A survey study of U.S. college students provides new insights into factors associated with the tendency to engage in celebrity stalking behaviors. Maria Wong (Idaho State University, U.S.), Lynn McCutcheon (North American Journal of Psychology, U.S.), Joshua Rodefer (Mercer University, U.S.) and Kenneth Carter (Emory University, U.S.) present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on March 1, 2023.
Celebrities around the world deal with the threat of unwanted and threatening or intimidating attention or harassment—commonly known as stalking. A growing body of research is exploring and identifying factors that are associated ...
Pregnant Shark birth tracking technology provides key data for species protection
2023-03-01
Most people find sharks threatening. Who doesn’t have an image in their mind of a menacing shark fin racing through the ocean in search of its next meal?
But it is the shark that is threatened.
According to Defenders of Wildlife, a national nonprofit dedicated to protecting imperiled species, 75% of shark species are threatened with extinction and up to 73 million sharks are being killed each year for their fins.
Habitats that were once secure places for sharks to give birth have also been affected. And the fact that sharks have long gestation periods, giving birth ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Physical activity can help mental health in pre-teen yearsRegular physical activity can improve adolescents’ mental health and help with behavioural difficulties, research suggests.