(Press-News.org) Washington, AAAS Annual Meeting. Imagine having a third arm – a robotic one – to assist you with daily living. Silvestro Micera from EPFL, Switzerland, is engineering the human nervous system to make this a possibility.
For decades, professor Silvestro Micera of EPFL has dedicated his research to helping people with sensory and motor deficits to re-gain independence and quality of life by developing wearable and implantable technologies. But this is changing, as he begins to explore what it means to augment the human body.
The neuroengineer has thus far avoided the subject of transhumanism, which is a movement to enhance the human body and cognition with the help of technology. Now, this year AAAS in Washington, Micera will be presenting his “third arm” research that aims to equip health individuals with a robotic arm, essentially giving them a third arm to control. The third-arm project aims to provide a wearable robotic arm to assist in daily tasks, using non-invasive techniques. The challenges are both technical and cognitive, but he believes that third-arm control is no longer a thing of the future.
“Research on three arm control could help us understand how learning is achieved in activities of daily living but these devices could also be used in logistics to facilitate complicated tasks,” explains Micera.
Micera is known for being the first to provide sensory feedback – in real-time – to an amputee, with a bionic hand, during clinical trials that took place in 2013 with results that were published in 2014. This bionic technology relied on providing sensory feedback via transversal electrodes that were surgically implanted into major nerves in the amputee’s arm. Since then, he and colleagues have been building on that technology, providing improved touch resolution of textures with a bionic fingertip, improved embodiment of the prosthetic limb, and working towards a permanent, wearable prosthetic hand. This technology will be soon used to restore other motor and sensory function in other cases such as spinal cord injury or stroke.
While Micera’s initial work about intelligent neuroprosthetics continue in parallel, one cannot help but imagine a future that is entering the realm of science-fiction. Will we be equipping healthy individuals with transversal electrodes with sensory feedback, allowing them to control a third robotic arm as an extension of their own body?
https://aaas.confex.com/aaas/2023/meetingapp.cgi/Session/29964
https://aaas.confex.com/aaas/2023/meetingapp.cgi/Paper/30741
END
Augmenting the human body with a wearable robotic arm
Approaching the cognitive challenges of equipping healthy individuals with an extra robotic arm.
2023-03-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Developing individualized, optimized brain injury rehabilitation
2023-03-03
More than 500,000 people in the United States undergo rehabilitation following a stroke or brain injury every year. Movement impairments following a stroke are a major cause of adult disability in the United States, and routine treatments are not currently optimized for individual patient needs.
University of Oklahoma biomedical engineer Yuan Yang, Ph.D., has received a Faculty Early Career Development Award, known as a CAREER award, from the National Science Foundation to advance the scientific study of brain functional changes after a stroke and pioneer a tailored rehabilitation strategy that fits individual needs.
“The way a stroke victim’s brain adapts to the ...
New research highlights importance of meeting caregivers’ needs
2023-03-03
Helping caregivers take better care of themselves can improve the quality of care they provide to individuals with neurological disabilities, according to experts writing in NeuroRehabilitation
Amsterdam, March 3, 2023 – Research on caregiving after neurotrauma and neurological disability extends the focus beyond individuals with neurological conditions to caregivers - family, friends, and significant others who also are also greatly impacted. In this thematic issue published in NeuroRehabilitation, noted experts present the latest research ...
American College of Cardiology honors women’s heart disease pioneer
2023-03-03
Noel Bairey Merz, MD, professor of cardiology and the director of the Barbra Streisand Women’s Heart Center in the Smidt Heart Institute, will receive the 2023 Master of the ACC Award from the American College of Cardiology (ACC) in honor of her pioneering contributions to the cardiovascular profession.
She will be recognized during the ACC’s Annual Scientific Session on Monday, March 6, in New Orleans.
The Master of the ACC Award recognizes and honors ACC Fellows who have served with distinction, consistently contributing to the goals and programs ...
New insights: Eye damage in Alzheimer's disease patients
2023-03-03
Cedars-Sinai investigators have produced the most extensive analysis to date of changes in the retina—a layer of tissue at the back of the eye where visual information originates—and how those retinal changes correspond to brain and cognitive changes in Alzheimer’s disease patients.
Their analysis, published in the peer-reviewed journal Acta Neuropathologica, is an important step toward understanding the complex effects of Alzheimer’s disease on the retina, especially at the earliest stages of cognitive impairment. Experts believe this understanding is key for the development of more effective treatments that could prevent ...
Too many babies are still dying from serious intestinal disease, as improvements slow and disparities persist
2023-03-03
A study published in JAMA Network Open has found that in the US between 1999 and 2020, Black infants disproportionately died from necrotizing enterocolitis compared to White infants, despite overall improvements in the rates of death from the disease.
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is one of the most common causes of death in preterm infants. Medically-fragile term infants, such as neonates born with a congenital heart defect, are also at an elevated risk of NEC. Two prior studies reported conflicting trends in NEC rates. One study from 2000-2011 showed increasing rates of death from the condition over time. Another study reported declining rates of NEC from 2006-2017.
Researchers ...
Senior researcher at Illinois VA Hospital named 2023 VA Magnuson Award winner
2023-03-03
Dr. Richard L. Lieber, a senior research career scientist at the Edward Hines, Jr., VA Hospital in Hines, Ill., has received the 2023 Paul B. Magnuson Award for his work to return functional capacity, mobility, and quality of life to Veterans with physical disabilities. The Magnuson Award recognizes outstanding achievement in VA rehabilitation research.
Lieber is also a professor in the departments of physiology, biomedical engineering, and physical medicine and rehabilitation at Northwestern University in Evanston, Ill., and the chief scientific officer and senior vice president at the Shirley Ryan Ability ...
One-year adverse outcomes among adults with long COVID vs those without COVID-19
2023-03-03
About The Study: This case-control study leveraged a large commercial insurance database and found increased rates of adverse outcomes over a 1-year period for a post–COVID-19 condition (long COVID) cohort surviving the acute phase of illness. The results indicate a need for continued monitoring for at-risk individuals, particularly in the area of cardiovascular and pulmonary management.
Authors: Andrea DeVries, Ph.D., of Elevance Health, Inc., in Indianapolis, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
Association of structural fires in New York City with inequities in safe heating for immigrant communities
2023-03-03
About The Study: This study found that the frequency of heating complaints was significantly associated with the frequency of structural fires in New York City. Importantly, this association varied across community districts, with more fires occurring in districts with greater proportions of Black and Latinx residents.
Authors: Clifford C. Sheckter, M.D., of the Santa Clara Valley Medical Center in San Jose, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.1575)
Editor’s Note: Please see the ...
Skilled nursing facilities continued to provide high quality care for those hospitalized during the pandemic
2023-03-03
Older adults who entered skilled nursing facilities (SNF) for care after hospitalizations after the pandemic received rehabilitation care comparable to the levels of care that were provided pre-pandemic, according to research published in the JAMA Health Forum.
Despite exceptional challenges during the pandemic, SNFs provided post-acute rehabilitation with only a modest decline in intensity, said the researchers. This suggests that SNFs were largely able to adapt and provide post-acute care ...
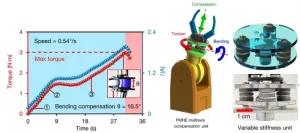
Scientists develop self-tunable electro-mechano responsive elastomers
2023-03-03
Recently, a team led by Prof. ZHANG Shiwu from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) and their collaborators from UK and Australia developed a new electro-mechano responsive elastomer that autonomously adjust stiffness, conductivity and strain sensitivity in response to changes in external mechanical loads and electrical signals. Their research was published in Science Advances.
Nowadays, more and more application scenarios like soft robotics and medical surgical equipment call for self-tunable intelligent materials. A widely adopted solution is composite material composed of low melting ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
[Press-News.org] Augmenting the human body with a wearable robotic armApproaching the cognitive challenges of equipping healthy individuals with an extra robotic arm.