Scientists thread rows of metal atoms into nanofiber bundles
Intercalation of indium into nanostructures promises applications to nanocircuitry
2023-03-04
(Press-News.org)
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have successfully threaded atoms of indium metal in between individual fibers in bundles of transition metal chalcogenide nanofibers. By steeping the bundles in indium gas, rows of atoms were able to make their way in between the fibers to create a unique nanostructure via intercalation. Through simulations and resistivity measurements, individual bundles were shown to have metallic properties, paving the way for application as flexible nanowires in nanocircuitry.
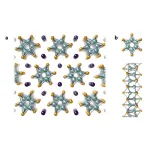
Atomic wires of transition metal chalcogenides (TMCs) are nanostructures consisting of a transition metal and a group 16 element like sulfur, selenium, and tellurium. They are able to self-assemble into a wide range of structures with different dimensionality, putting them at the heart of a revolution in nanomaterials that has been the focus of intense research in recent years. In particular, a class of 3D TMC structures have garnered particular interest, consisting of bundles of TMC nanofibers held together by metallic atoms in between the fibers, all forming a well-ordered lattice in its cross section (see Figure 1). Depending on the choice of metal, the structure could even be made to become a superconductor. Furthermore, by making the bundles thin, they could be made into flexible structures that conduct electricity: this makes TMC nanostructures a prime candidate for use as wiring in nanocircuitry. However, it has been difficult to make these structures into the long, thin fibers that are required to study them in depth, as well as for nanotechnology applications.
A team led by Assistant Professor Yusuke Nakanishi and Associate Professor Yasumitsu Miyata has been studying synthesis techniques for TMC nanostructures. In recent work, they showed that they could produce long, thin bundles of TMCs (with no metal) over unprecedentedly large length scales. Now, they have used a vapor phase reaction to thread atomically-thin rows of indium into thin bundles of tungsten telluride. By exposing their long nanofiber bundles to indium vapor under vacuum at 500 degrees Celsius, the indium metal atoms made their way into the space between the individual nanofibers that make up the bundles, forming an intercalating (or bridging) row of indium that binds the fibers together.
Having successfully produced large amounts of these threaded TMC bundles, they proceeded to study the properties of their new nanowires. By looking at the resistivity as a function of temperature, they showed conclusively that individual bundles behave like a metal and thus conduct electricity. This agreed with computer simulations, and also demonstrated how well-ordered the structures were. Interestingly, they found that this structure was slightly different to bulk batches of bundled nanofibers, in that the intercalated rows caused each nanofiber to rotate slightly about its axis.
The team’s technique is not only limited to indium and tungsten telluride, nor to this particular structure. They hope their work might inspire a new chapter for nanomaterial development and the study of their unique properties.
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers JP18H01810, JP20H02572, JP20H02605, JP20J21812, JP20K05413, JP20H05664, JP20H05862, JP20H05867, JP20K15178, JP21H05232, JP21H05233, JP21H05234, JP21H05235, JP21H05236, JP22H00215, JP22H00280, JP22H00283, JP22H01899, JP22H04957, JP22H05478, and JP22K19059, JST CREST Grant Numbers JPMJCR1715, JPMJCR1993, JPMJCR20B1, and JPMJCR20B5, and FOREST Grant Number JPMJFR213X.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-03-03
Mason Associate Professor of Infectious Diseases and Microbiology, Ramin M. Hakami has received a total of $35,000 in grants from Intellifoods Labs, LLC to continue examining methods to reduce the time to detect the presence of bacteria in food samples.
Numbers and types of foodborne disease occurrences have increased over time and are a major global public health concern. Hakami and his team seek to reduce the time to identify both live and dead bacteria in food samples using fluorescence detection. The team aims to optimize the detection ...
2023-03-03
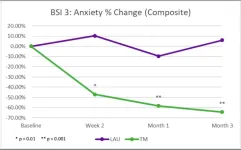
Healthcare providers (HCP) at three Miami hospitals during the height of the Covid crisis, who practiced the Transcendental Meditation technique (TM), showed a rapid and highly significant reduction in stress-related burnout symptoms such as somatization, depression, anxiety, sleep disturbances, and emotional exhaustion, as well as significant improvement in mental well-being, compared to a parallel matched lifestyle-as-usual group (LAU), according to a new study published today in PLOS ONE.
A total of 65 healthcare providers at the three Miami hospitals (Baptist, ...
2023-03-03
The first piece of a series of concrete structures was lowered into the water off the coast of Miami Beach on Wednesday morning, a massive crane on the deck of a floating barge hoisting the unit into the air and sinking it to the seabed.
During the next six hours, crewmembers aboard the barge would repeat that process until the structures, some stacked on top of each other, were settled on the seafloor, 14 feet below the surface.
To casual observers onshore, the daylong operation might have seemed routine. But this maritime activity was hardly run-of-the-mill.
In ...
2023-03-03
A scientist from Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) will premiere a new piece of music at the SXSW EDU festival that has been created using data beamed back to Earth from interstellar space.
On Thursday, 9 March, Dr Domenico Vicinanza will be joined on stage in Austin, Texas, by Dr Alyssa Schwartz, Visiting Assistant Professor of Flute and Musicology at Fairmont State University, to perform music shaped by scientific readings collected by NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft.
Dr Vicinanza, a Senior Lecturer in ARU’s School of Computing and Information Science, is a leading expert ...
2023-03-03
Oil palm trees are the most productive oil crop and global demand is increasing. However, their productivity is due to conventional management practices including high fertilizer usage and herbicide application, resulting in severe environmental damage. A new study by an international, multidisciplinary research team led by the University of Göttingen, shows that shifting to mechanical weeding and reducing fertilizer usage lead to significant increases in both ecosystem multifunctionality and profit. The scientists compared different environmental measures and economic indicators in mechanical weeding, herbicide application, and combinations of these with high and reduced fertilizer ...
2023-03-03
A team of researchers has developed a machine learning model that draws from the contents of news articles to effectively predict locations that face risks of food insecurity. The model, which could be used to help prioritize the allocation of emergency food assistance across vulnerable regions, marks an improvement over existing measurements.
“Our approach could drastically improve the prediction of food crisis outbreaks up to 12 months ahead of time using both real-time news streams and a predictive model that is simple to interpret,” says Samuel Fraiberger, a visiting researcher at ...
2023-03-03
Cancer cells have an innate randomness in their ability to respond to chemotherapy, which is another tool in their arsenal of resisting treatment, new research led by the Garvan Institute of Medical Research shows.
Understanding why some tumour cells become resistant to chemotherapy is a core challenge in cancer research, as chemotherapy is still a frontline treatment for most cancers.
The new research shows that tumour cells from neuroblastoma – cancer that develops in the body’s ‘fight or flight’ sympathetic nervous system – can move between states of responding, or not, to chemotherapy.
“We showed there is ‘noise’ in the process of cell ...
2023-03-03
As a social media user, you can be eager to share content. You can also try to judge whether it is true or not. But for many people it is difficult to prioritize both these things at once.
That’s the conclusion of a new experiment led by MIT scholars, which finds that even considering whether or not to share news items on social media reduces people’s ability to tell truths from falsehoods.
The study involved asking people to assess whether various news headlines were accurate. But if participants were first asked whether they would share that content, they were 35 percent worse at telling truths from ...
2023-03-03
The researchers discovered evidence of horse riding by studying the remains of human skeletons found in burial mounds called kurgans, which were between 4500-5000 years old. The earthen burial mounds belonged to the Yamnaya culture. The Yamnayans had migrated from the Pontic-Caspian steppes to find greener pastures in today´s countries of Romania and Bulgaria up to Hungary and Serbia.
Yamnayans were mobile cattle and sheep herders, now believed to be on horseback.
“Horseback-riding seems to have evolved not long ...
2023-03-03
Researchers at UCL and University of Ghana have successfully predicted whether children have anaemia using only a set of smartphone images.
The study, published in PLOS ONE, brought together researchers and clinicians at UCL Engineering, UCLH and Korle Bu Teaching Hospital, Ghana to investigate a new non-invasive diagnostic technique using smartphone photographs of the eye and face.
The advance could make anaemia screening more widely available for children in Ghana (and other low- and middle-income countries) where ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists thread rows of metal atoms into nanofiber bundles
Intercalation of indium into nanostructures promises applications to nanocircuitry