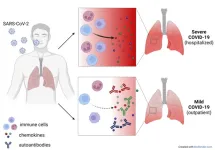
(Press-News.org) Sometimes in the laboratory there are unexpected results. "Previously it had been observed that autoantibodies are common in severe Covid patients, those who end up in intensive care," says Jonathan Muri, postdoctoral fellow at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB, affiliated with the Università della Svizzera italiana) and co-author of the study. "Instead, in this case we discovered the opposite."
The autoantibodies in question neutralize chemokines, molecules that direct immune cell trafficking. "Chemokines are a bit like traffic lights: they tell our immune cells when and where to go in the case of an infection so that they can fight it" adds Valentina Cecchinato, also at the IRB and coauthor of the study. "In the presence of the autoantibodies, the traffic lights are blocked and the influx of the cells that make inflammation chronic decreases." In short, it helps to turn off the inflammatory response.
Initially incredulous, the researchers also analyzed blood from patients recovering after Covid-19 from two other hospitals, with the same result. But how does blocking the immune response help in Covid? "The immune system in some cases is a double-edged sword," says Mariagrazia Uguccioni, co-director of the study, "it is important to activate it promptly to neutralize the coronavirus, but it must also be turned off at the right time, otherwise it can do damage." In fact, what usually brings patients to the hospital is excessive inflammation induced by the infection. So autoantibodies against chemokines could have a beneficial anti-inflammatory effect. "There is still a lot of work to be done," adds Davide Robbiani, co-director of the study and director of the IRB, "for now we can say that the presence of these 'good autoantibodies' is associated with a milder course and a lower risk that symptoms will continue for a long time," as observed in many patients who unfortunately still suffer for weeks or even months after Covid-19.
The study, published today in the journal Nature Immunology, was conducted by researchers from the IRB (Bellinzona, Switzerland) and carried out in collaboration with colleagues from Humanitas Research Hospital and Humanitas University in Milan, the Universities of Zurich and Bern, the Moncucco Hospital Group, the Ente Ospedaliero Cantonale, and universities in the United States, the United Kingdom, and Italy.
END
'Good autoantibodies' could help against long Covid
In Covid-19 disease, antibodies against the coronavirus protect, while those that attack ourselves are harmful. A new class of 'good autoantibodies' has now been discovered, which is associated with a favorable course and lower risk of long-Covid
2023-03-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Drones and deep learning: researchers develop a new technique to quantify rice production
2023-03-06
Rice, a major food crop, is cultivated on nearly 162 million hectares of land worldwide. One of the most commonly used methods to quantify rice production is rice plant counting. This technique is used to estimate yield, diagnose growth, and assess losses in paddy fields. Most rice counting processes across the world are still carried out manually. However, this is extremely tedious, laborious, and time-consuming, indicating the need for faster and more efficient machine-based solutions.
Researchers from China ...
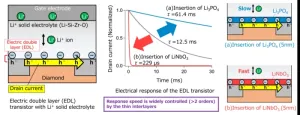
Controlling electric double layer dynamics for next generation all-solid-state batteries
2023-03-06
In our quest for clean energy and carbon neutrality, all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries (ASS-LIBs) offer considerable promise. ASS-LIBs are expected to be used in a wide range of applications including electric vehicles (EVs). However, commercial application of these batteries is currently facing a bottleneck—their output is reduced owing to their high surface resistance. Moreover, the exact mechanism of this surface resistance is hitherto unknown. Researchers have alluded it to a phenomenon called the “electric ...
Study finds silicon, gold and copper among new weapons against COVID-19
2023-03-06
New Curtin research has found the spike proteins of SARS-CoV-2, a strain of coronaviruses that caused the COVID-19 pandemic, become trapped when they come into contact with silicon, gold and copper, and that electric fields can be used to destroy the spike proteins, likely killing the virus.
Lead researcher Dr Nadim Darwish, from the School of Molecular and Life Sciences at Curtin University said the study found the spike proteins of coronaviruses attached and became stuck to certain types of surfaces.
“Coronaviruses have spike proteins on their periphery that allow them to penetrate host cells and cause infection and we have found these proteins becomes stuck to the surface ...
Electronic messages improved influenza vaccination rates in nationwide Danish study
2023-03-06
Approximately one billion people are infected with influenza around the world each year, with more than half a million deaths estimated to result from the disease. Despite the disease’s potential severity, especially among older populations and those with cardiometabolic risk factors, approximately 30 percent of U.S. adults over age 65 were not vaccinated during the 2019-2020 flu season. To evaluate best strategies for increasing vaccination rates, researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare ...
Quantifying genetic variations in bacterial cultures the qSanger way
2023-03-06
Genetic variations, such as mutations, recombinations, or transpositions occur naturally in cultured microorganisms and are often considered nonneutral mutations. Neutral mutations are neither beneficial nor harmful to an organism and only affect a small proportion of the total population. On the other hand, nonneutral mutations can affect a larger proportion of the population by potentially changing the gene pool, depending upon the advantages or disadvantages provided by the genetic variant. These ...
Eradicating polio will require changing the current public health strategy
2023-03-06
The recent public health emergency declarations in New York and London due to polio infections and detection of the virus in these cities’ wastewater strongly indicate that polio is no longer close to being eradicated.
Now, four members of the Global Virus Network (GVN) proposed changes in global polio eradication strategy to get the world back on track to one day eliminating polio’s threat. Authors of the recommendations included University of Maryland School of Medicine Institute of Human Virology’s ...
Southwest Research Institute develops device to test friction, wear associated with EV fluids
2023-03-06
SAN ANTONIO — March 6, 2023 —A Southwest Research Institute team has developed a mechanical testing device to analyze fluids and lubricants formulated for electric vehicles. The team modified a commercial tribology testing device to give it the capability to evaluate the impact of electric currents in fluids, measuring the wear and friction on the automobile parts in the presence of an applied voltage.
“The electrification of the automotive industry has accelerated over recent years, ...
Can certain nutrients protect against the effects of fetal alcohol exposure?
2023-03-06
Fetal alcohol exposure at any stage of pregnancy can lead to congenital malformations, as well as cognitive, behavioral, and emotional impairments in offspring. New research conducted in mice and published in The FASEB Journal indicates that even very early embryos exposed to alcohol can experience growth restriction, brain abnormalities, and skeletal delays, but feeding pregnant mothers certain nutrients prior to conception and throughout pregnancy can reduce the incidence and severity of the alcohol-induced defects.
The beneficial effects were seen with a combination of four nutrients—folic acid, choline, betaine, and vitamin B12.
The authors stress that the ...
Diversity training for police officers: one-and-done efforts aren't enough
2023-03-06
What explains persistent racial disparities in policing, despite police departments’ repeated investments in bias-training programs? A wide range of data indicate that police in the United States tend to stop, arrest, injure, or kill more Black people than White people. Calvin K. Lai (Washington University in St. Louis) and Jaclyn A. Lisnek (University of Virginia) analyzed the effectiveness of a day-long implicit-bias-oriented diversity training session designed to increase U.S. police officers’ knowledge of bias, concerns about bias, and use of evidence-based strategies to mitigate bias. Their ...
As naloxone treatment becomes more widespread heroin use is not on the rise among adolescents
2023-03-06
March 6, 2023-- The adoption of laws around naloxone use is not associated with changes in adolescent lifetime heroin or injection drug use (IDU), finds a new study at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. According to latest results, naloxone access and pharmacy naloxone distribution were more consistently associated with decreases rather than increases in lifetime heroin and IDU among adolescents. While some critics contend that naloxone expansion may inadvertently promote high-risk substance use behaviors among adolescents, until now this question had not been directly investigated. The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] 'Good autoantibodies' could help against long CovidIn Covid-19 disease, antibodies against the coronavirus protect, while those that attack ourselves are harmful. A new class of 'good autoantibodies' has now been discovered, which is associated with a favorable course and lower risk of long-Covid