(Press-News.org) A study at Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) found that intraoperative three-dimensional (3D) imaging was superior to two-dimensional radiographs in confirming the accuracy of pedicle screw placement during spine surgery. The research was presented today at the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) Annual Meeting in Las Vegas.
Many spinal surgeries require the use of implants called pedicle screws to stabilize the spine. Precise positioning of these screws is critical for a successful outcome. “Two-dimensional biplanar radiographs [BPR] have been the gold standard to confirm pedicle screw placement in spine fusion surgery for many years. However, when utilizing BPR, there is the potential that a two-dimensional image alone will not properly demonstrate the successful placement of a screw,” said Darren Lebl, MD, a spine surgeon at HSS and principal investigator of the study. “As an alternative, three-dimensional intraoperative imaging systems are now available, offering improved visualization.”
Dr. Lebl and colleagues set out to compare the accuracy of BPR versus 3D imaging when assessing intraoperative pedicle screw placement. “Our study is the first to compare the differences in intraoperative biplanar radiography and 3D imaging for pedicle screw accuracy in thoracic and lumbar cases using robotic technology,” Dr. Lebl noted.
Investigators analyzed data from 103 patients who underwent spinal fusion by a single surgeon from 2019 to 2022. Pedicle screw placement was assessed with both intraoperative BPR and 3D imaging in each case.
“CT scans taken after surgery were compared to the findings of intraoperative BPR and 3D imaging to detect either false-positive or false-negative readings,” explained Fedan Avrumova, BS, an HSS clinical research coordinator who presented the study at the AAOS meeting. “False positive findings are instances when BPR imaging suggests the screw was not in an acceptable position, while in fact a more advanced 3D image (intraoperative 3D scan or postoperative CT scan) showed the screw to be in an acceptable position. Conversely, a false negative instance was when a BPR image led one to believe or looked as though the screw was in an acceptable position, when in fact a more advanced 3D image or post-operative CT scan showed that it was in fact not acceptable.”
Postoperative CT imaging revealed a clinically significant number of patients who had false-negative and false-positive screw placement readings on BPR. However, screw position shown on intraoperative 3D imaging was found to be much more accurate, Avrumova added.
“Based on our study, BPR imaging may lead one to think a screw is acceptable when in fact it is not, and also may miss many screws that are not in fact acceptable. In our study, it was approximately one percent of cases where this occurred. However, for surgeons and centers that implant hundreds and thousands of screws per year, this is going to result in a significant clinical impact for many people,” Dr. Lebl noted. “Even one misplaced screw can have a significant impact for a patient, a surgeon, and a hospital system. Therefore, based on these findings, we suggest that for intraoperative confirmation of screw position 3D imaging may soon represent a new standard of care.”
Authors: Fedan Avrumova, BS; George Gorgy, MD; Philip K. Paschal, MS; John A. Carrino, MD, MPH; Darren R. Lebl, MD (HSS)
About HSS
HSS is the world’s leading academic medical center focused on musculoskeletal health. At its core is Hospital for Special Surgery, nationally ranked No. 1 in orthopedics (for the 13th consecutive year), No. 3 in rheumatology by U.S. News & World Report (2022-2023), and the best pediatric orthopedic hospital in NY, NJ and CT by U.S. News & World Report “Best Children’s Hospitals” list (2022-2023). In a survey of medical professionals in more than 20 countries by Newsweek, HSS is ranked world #1 in orthopedics for a third consecutive year (2023). Founded in 1863, the Hospital has the lowest complication and readmission rates in the nation for orthopedics, and among the lowest infection rates. HSS was the first in New York State to receive Magnet Recognition for Excellence in Nursing Service from the American Nurses Credentialing Center five consecutive times. An affiliate of Weill Cornell Medical College, HSS has a main campus in New York City and facilities in New Jersey, Connecticut and in the Long Island and Westchester County regions of New York State, as well as in Florida. In addition to patient care, HSS leads the field in research, innovation and education. The HSS Research Institute comprises 20 laboratories and 300 staff members focused on leading the advancement of musculoskeletal health through prevention of degeneration, tissue repair and tissue regeneration. The HSS Innovation Institute works to realize the potential of new drugs, therapeutics and devices. The HSS Education Institute is a trusted leader in advancing musculoskeletal knowledge and research for physicians, nurses, allied health professionals, academic trainees, and consumers in more than 145 countries. The institution is collaborating with medical centers and other organizations to advance the quality and value of musculoskeletal care and to make world-class HSS care more widely accessible nationally and internationally. www.hss.edu.
END
Study: intraoperative 3-D imaging can improve accuracy of pedicle screw placement in spine surgery
2023-03-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
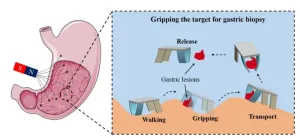
Magnetically actuated quadruped soft microrobot toward gastric biopsy
2023-03-07
Recently, a research team from Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, proposed a bionic quadruped soft thin-film microrobot actuated by magnetic fields with a mass of only 41 mg, which promises to be applied to stomach examination and treatment. Researchers realized the multimodal locomotion control of the soft microrobot in magnetic fields and the grasping and transportation of micro-objects by the soft microrobot.
The new paper, published in Cyborg and Bionic System, details the process ...
Scientists observe “quasiparticles” in classical systems for the first time
2023-03-07
Starting with the emergence of quantum mechanics, the world of physics has been divided between classical and quantum physics. Classical physics deals with the motions of objects we typically see every day in the macroscopic world, while quantum physics explains the exotic behaviors of elementary particles in the microscopic world.
Many solids or liquids are composed of particles interacting with one another at close distances, which sometimes results in the rise of “quasiparticles.” Quasiparticles are long-lived excitations that behave effectively as weakly interacting particles. The idea of quasiparticles was introduced by the Soviet physicist Lev Landau in 1941, and ...
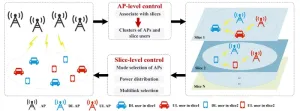
Slicing capacity-centered mode selection and resource optimization for network-assisted full-duplex cell-free distributed massive MIMO systems
2023-03-07
Network-assisted full-duplex (NAFD) systems enable uplink and downlink communications within the same time-frequency resources, so as to avoid the overhead of switching uplink/downlink modes. However, as the number of users and access points (APs) proliferated, mass access brings significant overhead in mode selection. In addition, the differentiated service demands among users also makes the effective utilization of resources difficult. Combined with network slicing technology, a slicing capacity-centered mode selection and resource optimization scheme is proposed. This scheme adopts a double-layer deep reinforcement ...
Do you see me? New study examines how women of colour experience invisibility in the workplace
2023-03-07
“As a Black woman, I’m invisible. They just erase your humanity. You don’t exist in front of them.” (Tessa, 33-year-old Black research assistant)
“It wasn’t about disliking what I did or being judgmental of what I did. It was a different kind of problem, to not be acknowledged. They didn’t care. There was no curiosity. They didn’t give a f***. We were invisible.” (Brinda, 30-year-old South Asian consultant)
Invisibility is a salient and recurring experience of mistreatment for women of colour working in traditionally white and male professions, two ...
Muffins that could be good for your health
2023-03-07
Love muffins? We’re talking about a tasty, fluffy muffin that has no artificial additives and that simultaneously contains lots of beneficial nutrients. As remarkable as it might sound, a recently published study led describes the development of just such a new muffin in the journal Foods.
From muffins to functional food
The new super muffin has been named Roselle, because it contains calyx extract from the tropical plant Hibiscus sabdariffa, which is often referred to by the same name.
[caption id="attachment_79738" align="aligncenter" width="559"] Here's a look at the different formulations that researchers tested. Photo: Screenshot from Food ...
Join us at #DiscoverBMB 2023 for the latest molecular life sciences research
2023-03-07
Will AI drive the next biomedical revolution? Why is RNA so powerful? What can we learn from studying bias? You’ll get the answers to these questions and more at Discover BMB, the annual meeting of the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, to be held March 25–28 in Seattle.
Reporters are invited to register for a complimentary press pass to attend #DiscoverBMB in Seattle or to access press materials electronically.
This year’s #DiscoverBMB program features leading ...
The colors on these ancient pots hint at the power of an empire
2023-03-07
Color plays a huge role in our lives — the hues we wear and decorate with are a way for us to signal who we are, where we’re from, and what we care about. And it’s been that way for a long time. In a new study in the Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, archaeologists compared the colors on pieces of ancient Peruvian pottery. They found that potters across the Wari empire all used the same rich black pigment to make ceramics used in rituals: a sign of the empire’s influence.
The Wari empire spread over Peru’s highlands and coastal areas from 600-1050 ...
Does current shellfish anti-predator gear curb ‘crunching’ rays?
2023-03-07
According to NOAA Fisheries, more than 80 percent of marine aquaculture production in the United States consists of bivalve mollusks such as oysters, clams and mussels. However, it’s not just humans who enjoy eating these shellfish, so do marine rays. They like to “crunch” on clams, which can sometimes take a big bite out of clammers’ profits.
Part of the process of culturing hard clams (Mercenaria mercenaria) involves deploying them in submerged bottom leases in the marine environment where clams can grow to market size. When deployed onto the clam lease, clammers incorporate a variety of anti-predator ...
Understanding what makes senior towns in Iowa “smart”
2023-03-07
AMES, IA — With the youngest baby boomers sliding into retirement, adults aged 65 and older are expected to outnumber children by 2030. The demographic shift will be a first in U.S. history. But many rural areas, especially in the Midwest and Great Plains, are already experiencing this.
Researchers are looking to small towns in Iowa to understand how some support aging in place better than others. Their findings, published in Journal of Rural Studies, could help communities plan for the ...
Researchers create mutant mice to study bipolar disorder
2023-03-07
Bipolar disorder (BD) is a debilitating condition characterized by alternating states of depression (known as depressive episodes) and abnormal excitement or irritability (known as manic episodes). Large-scale genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have revealed that variations in the genes present on the fatty acid desaturase (FADS) locus are linked to an increased risk of BD. Enzymes coded by FADS genes—FADS1 and FADS2—convert or "biosynthesize" omega-3 fatty acids into the different forms required by the human body. Omega-3 fatty acids like ...