(Press-News.org) Coffee is important to the economies of coffee producing regions. A study published in PLOS Climate by Doug Richardson at CSIRO Oceans & Atmosphere, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia and colleagues suggests that climate change may significantly affect land where coffee is cultivated.
Coffee plants are sensitive to climate variability and change. However, the impact of synchronous climate hazards occurring in multiple areas important for coffee production is unknown. In order to better understand how large-scale climate modes such as El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) may lead to simultaneous coffee crop failures in multiple countries, researchers conducted a systematic analysis of climate hazards and compound events in coffee producing regions from 1980-2020. They identified 12 climate hazards that threaten coffee crops in the top 12 coffee-producing countries, for example, exceeding daily maximum temperature that coffee plants can tolerate.
The researchers found that the number of climate hazards and compound events has increased in every coffee-growing region between 1980 and 2020. Additionally, the type of hazards have shifted from overly cool conditions to overly warm. More research is needed, however, to understand what kind of adaptations might mitigate global coffee crop failures.
According to the authors, “Our results suggest that El Niño is the primary mode in explaining compound climate event variability, both globally and regionally. Region-level hazards are therefore indicative of systemic risk to coffee production, rather than local risk. As with other crops, a systemic risk to the global coffee trade is posed by synchronized crop failures. With climate change projections showing a continued rise in temperatures in the tropics is likely, we posit that coffee production can expect ongoing systemic shocks in response to spatially compounding climate hazards.”
The authors add: “Since 1980, global coffee production has become increasingly at risk of synchronised crop failures, which can be driven by climate hazards that affect multiple key coffee-producing areas simultaneously.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Climate: https://journals.plos.org/climate/article?id=10.1371/journal.pclm.0000134
Citation: Richardson D, Kath J, Byrareddy VM, Monselesan DP, Risbey JS, Squire DT, et al. (2023) Synchronous climate hazards pose an increasing challenge to global coffee production. PLOS Clim 2(3): e0000134. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pclm.0000134
Author Countries: Australia
Funding: DR, DPM, JSR, DTS and CRT were supported by the Australian Climate Service https://www.acs.gov.au/. JK and VMB were supported by the Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety—International Climate Initiative (IKI) https://www.international-climate-initiative.com/en/. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Anthropogenic climate change poses systemic risk to coffee cultivation
Study suggests the frequency of spatially compounded climate risks to coffee are increasing
2023-03-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Celebrity sightings have a built-in contradiction
2023-03-08
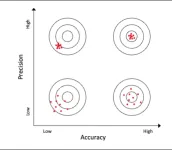
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Their popularity makes celebrities easy to spot. Strangers, however, can also get mistaken for celebrities, resulting in cases of false “celebrity sightings.” In attempting to explain the contradiction, a University of California, Riverside, study reports that celebrity faces are remembered more precisely but less accurately.
Precision, in this context, refers to how memories for a particular face resemble each other over repeated memory retrievals, which can be likened to the clustering of arrows on a target in archery. Accuracy measures ...
A new class of drugs could prevent resistant COVID-19 variants, study finds
2023-03-08
New Haven, Conn. — The constant evolution of new COVID-19 variants makes it critical for clinicians to have multiple therapies in their arsenal for treating drug-resistant infections. Researchers have now discovered that a new class of oral drugs that acts directly on human cells can inhibit a diverse range of pathogenic SARS-CoV-2 strains.
In their newly published study, the team found a novel mechanism through which the gene that expresses angiotensin converting enzyme-2 (ACE-2)—the cellular receptor to which SARS-CoV-2 ...
Swan Hellenic and SETI Institute announce lecturers for Explore Space at Sea Series
2023-03-08
March 8, 2023, Mountain View, CA – The SETI Institute and Swan Hellenic announce SETI Institute guest lecturers who will offer cruise guests expert insights into the history and latest discoveries in astronomy, astrophysics, astrobiology and planetary science, and the quest to find other forms of life within and beyond our solar system. This quest takes SETI Institute researchers to the planet’s most remote and inhospitable corners to explore life, including Antarctica, where the Swan Hellenic fleet is present for several months every year.
Outlining ...
New articles for Geosphere posted early online
2023-03-08
Boulder, Colo., USA: GSA’s dynamic online journal, Geosphere, posts articles online regularly. Topics this month include an analysis of geoscience job applications; Uturuncu volcano, Bolivia; Picture Gorge Basalt; and the Red Bluff Granite Suite. You can find these articles at https://geosphere.geoscienceworld.org/content/early/recent .
Critical workforce skills for bachelor-level geoscientists: An analysis of geoscience job advertisements
G.W. Shafer; K. Viskupic; A.E. Egger
Understanding the skills ...
Human Brain Project: spin-off receives EIC grant to develop energy-efficient AI technology
2023-03-08
The European Innovation Council (EIC) has recently announced that it will award a Transition grant to SpiNNcloud Systems GmbH, a deep-tech startup based in Saxony, Germany.
The team from SpiNNcloud Systems GmbH, a spin-off from Professor Christian Mayr’s research group at Technische Universität Dresden, is receiving a grant of 2.5 million euros for their groundbreaking project, “SpiNNode: SpiNNaker2 on the edge.”
“SpiNNaker2 is a bio-inspired supercomputer which was developed at my Chair in collaboration with Prof. Steve Furber’s research group at the University of Manchester as part ...
New GSA Bulletin articles published online ahead of print
2023-03-08
Boulder, Colo., USA: The Geological Society of America regularly publishes articles online ahead of print. GSA Bulletin topics studied this month include the nature and dynamics of China and Tibet; the Lower Mississippi Valley, USA; and the polarity of Mesozoic arcs along the western margin of North America. You can find these articles at https://bulletin.geoscienceworld.org/content/early/recent .
Magmatic-hydrothermal evolution of long-lived Nb-Ta-(Sn) mineralization in Lianyunshan, NE Hunan, South China
Nuerkanati Madayipu; Huan Li; Safiyanu Muhammad Elatikpo; Michael W. Förster; Hou-Xiang Zhou ...
The ...
Group exercise program for older adults led to more independent exercise despite pandemic restrictions, MU study finds
2023-03-08
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- Sticking with an exercise program can be tough, even during the best of times. But what about during a pandemic?
A new study by the University of Missouri and Oklahoma State University found that even when gyms were closed and there were other COVID-19 restrictions limiting face-to-face meetings, older adults who completed the Stay Strong, Stay Healthy exercise program — created at MU in 2005 — continued to maintain long-term exercise habits independently, which resulted in improved lifestyle changes and an increase in both physical energy and self-confidence.
“We ...
Incident atrial fibrillation appears to heighten dementia risk
2023-03-08
People with a recent diagnosis of atrial fibrillation (AF), the most common irregular heart rhythm, have a modestly higher risk of developing dementia than people without the condition, according to research published today.
“Previous studies that have examined the link between atrial fibrillation and dementia have yielded conflicting results, and we hope that our study’s large sample size helps to establish confidence in our findings,” said Dr. Nisha Bansal, a professor of medicine at the University of Washington School of Medicine. “The study also included a community based, diverse population, which may increase the generalizability ...
Lunar telescope will search for ancient radio waves
2023-03-08
UPTON, NY—Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory are leading a new effort to land a radio telescope on the moon. If successful, the project will mark the first step towards exploring the Dark Ages of the universe.
The Dark Ages are an early era of cosmological history starting about 380,000 years after the Big Bang. There were no stars or planets in the Dark Ages. It’s a point in time that scientists have never been able to observe. Though radio waves from the Dark Ages still linger in space, the abundance of radio interference on Earth has masked these signals from scientists seeking to study them.
If ...
How a metabolite causes inflammation and disease
2023-03-08
A new study shows for the first time a connection between a mitochondrial metabolite and the activation of an inflammatory response. Mitochondria are functional units of our cells that fulfil important tasks, i.e. chemical reactions, for the functioning of the cell. One of these tasks is the production of energy that is necessary for cell growth and reproduction. If certain chemical reactions in the mitochondrion change, diseases occur. For example, deficiencies in fumarate hydratase (FH) in the Krebs cycle, one of the most important metabolic pathways in mitochondria, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
[Press-News.org] Anthropogenic climate change poses systemic risk to coffee cultivationStudy suggests the frequency of spatially compounded climate risks to coffee are increasing