(Press-News.org) Harlequin ichthyosis (HI) is a severe genetic skin disorder characterized by thick white, brown, or dark brown patches on the skin covering a newborn's entire body. HI has a low incidence of 1 per 300,000 live births but comes with the highest mortality rate among skin conditions. It is caused by a mutation in the ABCA12 gene, which codes for a protein involved in transporting lipids necessary for the formation of the skin barrier. Such protein shortage leads to a weaker epidermal barrier.
A recent study, co-authored by BGI Genomics Dr. Thomas Qiu, published in Frontiers in Pediatrics covers the case of an infant born prematurely at the Vietnam Quang Ninh Obstetrics and Pediatrics Hospital with a birth weight of 2.2 kg and covered with thick plate-like scales separated by dark red fissures of the skin, who was then diagnosed with HI disorder.
Five days after birth, the child was transferred to the Vietnam National Hospital of Pediatrics with severe infection, other HI-related symptoms, breathing difficulties and died 15 hours after.
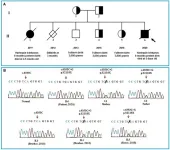
The infant had an older sister, born 8 months premature who died at 2.5 weeks old with HI symptoms as well, and a stillborn brother at 12 weeks gestation. He also has two brothers and a sister, full health. A blood sample for whole exome sequencing (WES) was collected on the patient to find the cause of the disease.
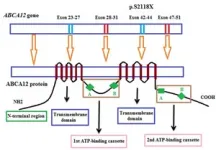
Whole exome sequencing results show that a homozygous mutation (c.6353C > G, p.S2118X) leads to a truncated ABCA12 protein, commonly reported among HI cases. The formed protein is severely dysfunctional and this is responsible for the serious phenotype in the patient. The mutation c.6353C > G (p.S2118X) has not been reported yet in previous studies and in the databases (1,000 Genome, gnomAD, NCBI, HGMD, UCSC, ExAc, and NHLBI). This mutation has been submitted in dsSNP under accession number rs1553520447 and Gene Dx under accession number SCV000710591.2, as well as identified as a pathogenic variant in the ClinVar database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar) (accession number RCV000598766.1).
WES also reveals that members of the family who carry the mutation in the heterozygous state do not show HI symptoms, thus emphasizing the importance of genetic screening and DNA-based prenatal diagnosis for families with a history of this disease. While the mortality rate remains high, early intervention with systemic retinoids can improve survival rates. Further research into the pathogenesis of HI and the development of new therapies is crucial to improve the outlook for those affected by this condition.
About BGI Genomics
BGI Genomics, headquartered in Shenzhen China, is the world's leading integrated solutions provider of precision medicine. Our services cover over 100 countries and regions, involving more than 2,300 medical institutions. In July 2017, as a subsidiary of BGI Group, BGI Genomics (300676.SZ) was officially listed on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange.
END
Novel rare skin mutation gene identified by whole exome sequencing - BGI Case Report
Identification of a novel rare mutation in ABCA12 gene linked to Harlequin Ichthyosis through BGI genetic tests
2023-03-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Like a flexible Lego railway track: How stable microtubules form within cells
2023-03-09
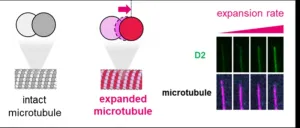
Like poles support a tent, microtubules—hollow cylindrical structures made of tubulin protein—support eukaryotic cells. But microtubules provide more than just mechanical strength; they help prepare the cell for cell division and migration and work as a railway track on which motor proteins transport materials within the cell. The formation of microtubules within cells resembles how a child assembles a Lego train track. The tubulins—Lego bricks—constantly assemble and disassemble to make the microtubule—train track—longer and shorter in processes called polymerization and depolymerization. The processes are regulated by microtubule-associated proteins such ...
What if California didn’t close down during the pandemic?
2023-03-09
SAN FRANCISCO (March 9, 2023) — Researchers at the California Academy of Sciences, along with a collaborator at Denison University, have developed an innovative new model to assess how the California economy might have fared without economic closures to slow the spread of the coronavirus pandemic. Their initial findings—published today in Frontiers in Physics—reveal that under a “business-as-usual” approach wherein there were no business closures, California’s economy would have generally been better off than in reality. However, the economic impacts would still have been substantial and ...
Americans share fake news to fit in with social circles
2023-03-09
Both conservative and liberal Americans share fake news because they don’t want to be ostracized from their social circles, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“Conformity and social pressure are key motivators of the spread of fake news,” said lead researcher Matthew Asher Lawson, PhD, an assistant professor of decision sciences at INSEAD, a business school in France. “If someone in your online tribe is sharing fake news, then you feel pressure to share it as well, even if you don’t ...
A safe synthesis of hydrogen peroxide inspired by nature
2023-03-09
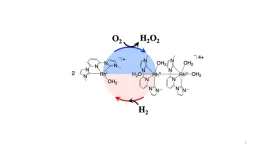
Fukuoka, Japan—Hydrogen peroxide is a ubiquitous chemical found in most homes and used in everything from dying hair to treating wounds. It is also an invaluable agent for many industries from food, textiles, and even in semiconductor production.
Reporting in JACS, researchers at Kyushu University have developed a new process to synthesize this chemical utilizing a new homogeneous catalyst inspired by nature. Moreover, the process is significantly safer than conventional methods.
Scientists have been reporting the synthesis ...
A novel mechanism may be effective in patients with severe hypertriglyceridemia and prior episodes of acute pancreatitis
2023-03-09
A novel type of therapy, known as ANGPTL3 inhibitor therapy, was effective in lowering triglycerides in certain types of patients with severe hypertriglyceridemia (sHTG) who had a prior episode(s) of acute pancreatitis. sHTG is a well-established risk factor for recurrent episodes of acute pancreatitis. These high-risk patients were the focus of a phase 2 study that was led by the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and sponsored and funded by Regeneron.
This ANGPTL3 inhibitor therapy, the intravenous drug evicanumab-dgnb, inhibits two important regulators of lipoprotein metabolism. ...
Researchers unveil smart contact lens, capable of implementing AR-based navigation
2023-03-09
With the advent of the Metaverse era, there have been growing expectations that virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies will likely to enhance convenience in everyday life, as well as industry productivity performance.
A joint research team, affiliated with UNIST has introduced core technology for smart contact lenses that can implement AR-based navigation through a 3D printing process. According to the research team, the new smart contact lenses can be worn inside the eye of a person, like a normal contact lens.
Published in the February 2023 issue of Advanced Science, this breakthrough has been jointly led by ...
3D battery imaging reveals the secret real-time life of lithium metal cells
2023-03-09
Innovative battery researchers have cracked the code to creating real-time 3D images of the promising but temperamental lithium metal battery as it cycles. A team from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, have succeeded in observing how the lithium metal in the cell behaves as it charges and discharges.
The new method may contribute to batteries with higher capacity and increased safety in our future cars and devices.
“We’ve opened a new window in order to understand – and in the long term to optimise – the lithium metal batteries of the future. When we can study exactly what happens to the lithium in ...
Naturally occurring peptide may tackle the ‘root cause’ of obesity-related conditions
2023-03-09
Research published today shows that a peptide (small protein) called PEPITEM could provide a revolutionary approach to reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes and other obesity-related diseases such as hepatic steatosis (fatty liver).
The researchers used an animal model of obesity to investigate whether PEPITEM, delivered by a slow-release pump, could prevent or reverse the effects that a high fat diet has on the pancreas. Excitingly, the results showed that administration of PEPITEM significantly reduced the enlargement of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas and ...
C-reactive protein reduces the immune response in inflammatory disease
2023-03-09
The biological function of the C-reactive protein, CRP, has long been unknown. Researchers at Linköping University in Sweden now show that this protein has a beneficial function in systemic lupus erythematosus, SLE, an inflammatory disease. But this is true only for one of CRP’s two forms, according to the study published in Journal of Autoimmunity.
Most of us have had a CRP blood test on more than one occasion. This is a very common routine health care test used to detect infection or systemic inflammation in the body. What is measured is the level of C-reactive protein, or CRP for short.
“CRP ...
Study: Higher fracture risk after total hip replacement when cementless implant used to treat femoral neck fracture
2023-03-09
A study by Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) and other centers found that total hip replacement performed with a cementless prosthesis for a femoral neck fracture led to a higher rate of a second fracture and subsequent revision surgery. The research was presented today at the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) Annual Meeting in Las Vegas. The results were also published online in The Journal of Arthroplasty in October 2022.
Treatments for a femoral neck fracture range from nonoperative management to total hip replacement. When hip replacement is the best treatment option, it can be performed with or without bone cement to secure the prosthesis.
“Femoral ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
[Press-News.org] Novel rare skin mutation gene identified by whole exome sequencing - BGI Case ReportIdentification of a novel rare mutation in ABCA12 gene linked to Harlequin Ichthyosis through BGI genetic tests