(Press-News.org) About The Study: The results of this survey study suggest that the prevalence of metabolically healthy obesity (people with obesity who do not have obesity-related cardiometabolic abnormalities) increased among U.S. adults during the past 2 decades, but differences in trends existed across sociodemographic subgroups. Effective strategies are needed to improve metabolic health status and prevent obesity-related complications in adults with obesity.
Authors: An Pan, Ph.D., of the Huazhong University of Science and Technology in Wuhan, China, and Kun Yang, M.D., of the Hubei University of Medicine in Shiyan, China, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.2145)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.2145?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=030923
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Trends in the prevalence of metabolically healthy obesity among adults
JAMA Network Open
2023-03-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists develop predictable method to downregulate gene translation in plants
2023-03-09
GAO Caixia's group from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has developed a new method of downregulating gene translation to a predictable and desired level in plants by precisely engineering upstream open reading frames (uORFs).
The study was published online in Nature Biotechnology on Mar. 9.
The development and application of genome editing in plants has revolutionized molecular design-based crop breeding. Developing methods for fine-tuning ...
Life in the smoke of underwater volcanoes
2023-03-09
Deep down in the ocean at tectonic plate boundaries, hot fluids rise from so-called hydrothermal vents. The fluids are devoid of oxygen and contain large amounts of metals such as iron, manganese or copper. Some may also transport sulfides, methane and hydrogen. When the hot water mixes with the cold and oxygenated surrounding seawater, so-called hydrothermal plumes develop containing smoke-like particles of metal sulfide. These plumes rise hundreds of meters off the seafloor and disperse thousands of kilometers away from their source. Hydrothermal ...
St Andrews research shows automated sorting can diagnose cancer faster
2023-03-09
This type of automated sorting would allow prioritisation of malignant slides so that pathologists can review them first and reduce the time to diagnosis for patients with cancer.
The final model was able to correctly detect 97% of malignant slides and correctly detect 90% of all slides.
The final model is in two stages. Firstly, the very large images are split into smaller patches and a deep learning model is trained to classify each patch as malignant or not.
Next, a second stage model combines the small patches back together and predicts a classification ...
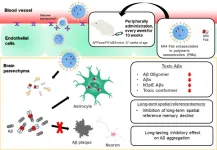
Transporting antibodies across the blood–brain barrier to treat Alzheimer’s disease
2023-03-09
Researchers led by Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) find that antibody fragments encapsulated in nanomicelles cross the blood–brain barrier and reduce the levels of toxic Aβ species in the brain of an Alzheimer’s disease model mouse
Tokyo, Japan — Sometimes the best things in life come by chance, when we happen to be in the right place at the right time. Now, researchers from Japan have found a way to ensure that new medications are delivered to the right place in the body and at the right timepoint in disease progression, so that they have the best effect.
In a study published recently in the Journal ...
Shedd Aquarium and the Morton Arboretum named new centers for species survival
2023-03-09
CHICAGO – Today, the Species Survival Commission (SSC) of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the world’s largest conservation organization, announces that two iconic Chicago institutions - Shedd Aquarium and The Morton Arboretum - have been named as Centers for Species Survival. These new designations elevate the role of the Chicago region as an international leader in biodiversity conservation. What’s more, the two Centers will give the aquarium and the arboretum the opportunity to collaborate on conservation efforts, advancing projects that highlight the importance ...
Detoxing body of 2 fat by-products could extend lifespan, UVA researchers discover
2023-03-09
University of Virginia scientists have identified a promising approach to delay aging by detoxifying the body of glycerol and glyceraldehyde, harmful by-products of fat that naturally accumulate over time.
The new findings come from UVA researcher Eyleen Jorgelina O’Rourke, PhD, and her team, who are seeking to identify the mechanisms driving healthy aging and longevity. Their new work suggests a potential way to do so by reducing glycerol and glyceraldehyde’s health-draining effects.
“The discovery was unexpected. We went after a very well-supported hypothesis that the secret to longevity was the activation of a cell-rejuvenating ...
In the world’s smallest ball game, scientists throw and catch single atoms using light
2023-03-09
WASHINGTON —In many baseball-obsessed countries like Korea, Japan and the United States, with spring months comes the start of the season and quite a few balls flying through the air. But it’s not just balls that can be thrown. On the tiniest field imaginable, scientists have now shown they can also throw and catch individual atoms using light.
This amazing feat was achieved with optical traps, which use a highly focused laser beam to hold and move tiny objects. Although optical traps have been used to move individual atoms before, this is the first time ...
HSS presents research at 2023 AAOS Annual Meeting
2023-03-09
At this year’s American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) Annual Meeting, held March 7 to 11 in Las Vegas, Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) presented new research on a variety of topics in orthopedic surgery, including studies related to minimally invasive surgery, racial disparities, and opioid alternatives for pain management in spine care.
What follows are some highlights from the meeting:
Intravenous versus Oral Administration of Acetaminophen Perioperative to Instrumented Lumbar Fusion: A Single-Center, Randomized Controlled Trial
In patients undergoing ...
CityU researchers identify a protein that promotes cancer metastasis, providing a new potential treatment target
2023-03-09
Cancer metastasis is a major cause of cancer-related death. A research team at City University of Hong Kong (CityU) recently identified a protein that triggers the migration of liver and pancreatic cancer cells and metastasis, and is correlated with shortening the survival time of patients. The research findings were verified by in vitro and in vivo models, supported with clinical data, and are expected to provide a new potential target for cancer therapy.
“Cancer metastasis is a complex process. Stiffness in tumours and the surrounding tissues is known to increase along with the tumour growth, which creates confined spaces or channel-like tracks of pores for tumour ...
An on-chip viscoelasticity sensor for biological fluids
2023-03-09
A research paper by scientists at the Hebei University of Technology and Shenzhen University developed an on-chip viscoelasticity sensor for biological fluids.
The new research paper, published on Jan. 10, 2023 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, reported a double-layered microfluidic sensor to detect the ultra-weak viscoelasticity in biological fluids.
“Most of human body fluids are non-Newtonian liquids, and the influence of viscoelasticity is often ignored for the sake of simplification of analysis. However, we ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
[Press-News.org] Trends in the prevalence of metabolically healthy obesity among adultsJAMA Network Open