(Press-News.org) Eliminating hazards around the home, such as clutter, stairs without railings and poor lighting, can reduce the risk of falls for older people by around a quarter, according to a new Cochrane review.
The review did not find any compelling evidence for other measures to reduce falls, such as making sure older people have the correct prescription glasses, special footwear, or education on avoiding falls.
It also found that decluttering and reducing hazards had the most benefit for older people who are at risk of falls, for example because they have recently had a fall and been hospitalised or need support with daily activities such as dressing or using stairs.
Nearly one third of people aged 65 years and older fall each year. Most falls occur in the home.
Lindy Clemson, Professor Emeritus at the University of Sydney, Australia was lead author of the review. She said: “Falls are very common among older people. They can cause serious injury or even death, but they are preventable. In this review we wanted to examine which measures could have the biggest impact on reducing falls among older people living at home.”
Professor Clemson and her colleagues analysed the results of 22 studies including data on 8,463 older people living in the community.
They found that taking measures to reduce fall hazards around the home lowers the overall rate of falls by 26%. This typically includes an assessment of fall hazards in and around the home and recommendations for lowering the risk, for instance by removing clutter and adding handrails and non-slip strips to steps. These measures have the biggest effect (38% fewer falls) for people who are at a higher risk of falls. Based on their analyses, the reviewers found that if 1,000 people who had previously had a fall followed these measures for about a year, the total number of falls would come down from 1,847 to 1,145.
Professor Clemson said: “Having had a fall or starting to need help with everyday activities are markers of underlying risk factors, such as being unsteady on your feet, having poor judgement or weak muscles. These risk factors make negotiating the environment more challenging and increase the risk of a trip or slip in some situations.
“The research shows that, for those at risk of falls, being aware of fall hazards in and around the home, removing hazards and adapting with safe behaviours can significantly reduce the risk of falling. It appears that interventions to reduce fall hazards around the home need certain elements of assessment and support to work, not just a short check list of things to tick off. So, while everyone can take more care about their home environment and should do exercise for balance and lower limb strength, professional support from an occupational therapist is an important intervention for many people living at home.
“We encourage all people, as they age, to reduce fall hazards. These are often simple things like removing or changing slippery floor mats, improving lighting on stairs or de-cluttering the home. It seems this is not always ‘common sense’. People tend not to notice clutter around their home or realise that climbing ladders the way they always have is potentially a fall risk, particularly if their mobility or balance is not as it used to be.”
While the review showed fewer falls with hazard reduction, there was not enough data from the studies to determine if there were fewer admissions to hospital due to a fall. The authors found limited evidence for the other approaches to prevent falls that they examined – assistive technologies and education. They also found there was a lack of research on the impact on fall reduction of providing equipment or modifications to help older people carry out daily activities, such as showering or as cooking a meal.
Professor Clemson added: “Preventing falls is a really important way of helping people to remain healthy and independent as they grow older, and our review also highlights the need for more research in this area.”
END
Reducing trip hazards and decluttering can prevent falls among older people living at home
Eliminating hazards around the home, such as clutter, stairs without railings and poor lighting, can reduce the risk of falls for older people by around a quarter, according to a new Cochrane review
2023-03-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Online ‘personal brands’ key to job success for Gen Z
2023-03-10
New research reveals how Generation Z perceive online ‘personal brands’ as a crucial tool to gain more advantage in job markets.
The study, led by the University of East Anglia in collaboration with the University of Greenwich, demonstrates the importance of authentically building online personal branding strategies and tactics to bridge the gap between Gen Z’s desired and perceived images on social media when job seeking.
Gen Z - the generation of people born between the late 1990s and early 2010s - are also in favour of a more dynamic, interactive, work-in-progress style of authentic personal brands, which may not necessarily show them as “perfect”, ...
Ozone pollution is linked with increased hospitalizations for cardiovascular disease
2023-03-10
Sophia Antipolis, 10 March 2023: The first evidence that exceeding the World Health Organization (WHO) ozone limit is associated with substantial increases in hospital admissions for heart attack, heart failure and stroke is published today in European Heart Journal, a journal of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1 Even ozone levels below the WHO maximum were linked with worsened health.
“During this three-year study, ozone was responsible for an increasing proportion of admissions ...
Development of a photonic dispersion solver
2023-03-10
An exponential increase in the amount of information required in society is making the development of new optoelectronic devices increasingly important. Recently, photonic crystals have emerged as an alternative to overcome the limitations of conventional photonic devices thanks to their ability to control photons freely in microscopic space to introduce the next generation of highly integrated devices. A research team at POSTECH has developed a photonic dispersion solver that may act as the foundation of studies on photonic crystals.
Professor Junsuk Rho (Department of Mechanical Engineering and Department of Chemical Engineering) at POSTECH along with a team from Gwangju Institute ...
Ancient virus genome drives autism?
2023-03-10
Although autism is a common neurodevelopmental disorder, the multiple factors behind its onset are still not fully understood. Animal models of idiopathic autism*1, especially mice, are often used to help researchers understand the complicated mechanisms behind the disorder, with BTBR/J being the most commonly used mouse model in the world.
Now, an international research collaboration including Kobe University’s Professor TAKUMI Toru and Researcher Chia-wen Lin et al. have made new discoveries regarding autism onset in mouse models.
In their detailed series of experiments and analyses of BTBR/J mice and the other subspecies BTBR/R, they revealed that endogenous ...
If you think you understand how incentives work, think again
2023-03-09
How can people be incentivized to drive more fuel-efficient cars, be more innovative at work, and get to the gym on a regular basis? Uri Gneezy, professor of economics and strategy at the Rady School of Management at UC San Diego explains this in his new book “Mixed Signals: How Incentives Really Work.”
In the book, Gneezy, a pioneering behavioral economist, reveals how we can create reward systems that minimize unintended consequences and maximize happiness, health, wealth and success. “Mixed Signals” was recently included in Adam Grant’s ...
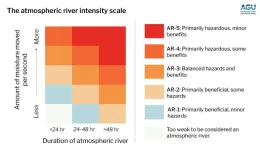
The world’s atmospheric rivers now have an intensity ranking like hurricanes
2023-03-09
American Geophysical Union
9 March 2023
AGU Release No. 23-10
For Immediate Release
This press release and accompanying multimedia are available online at: https://news.agu.org/press-release/the-worlds-atmospheric-rivers-now-have-an-intensity-ranking-like-hurricanes/
AGU press contact:
Rebecca Dzombak, +1 (202) 777-7492, news@agu.org (UTC-5 hours)
Contact information for the researchers:
Bin Guan, University of California Los Angeles and California Institute of Technology, bin.guan@jpl.nasa.gov (UTC-8 hours)
WASHINGTON — Atmospheric rivers, which are long, narrow bands of water vapor, are becoming more intense and frequent with climate ...
Complex learned social behavior discovered in bee’s ‘waggle dance’
2023-03-09
Passing down shared knowledge from one generation to the next is a hallmark of culture and allows animals to rapidly adapt to a changing environment.
While widely evident in species ranging from human infants to naked mole rats or fledgling songbirds, early social learning has now been documented in insects.
Publishing in the journal Science, a University of California San Diego researcher and his colleagues uncovered evidence that social learning is fundamental for honey bees. Professor James Nieh of the School of Biological Sciences and his collaborators discovered that the “waggle dance,” which signals the location ...
Social signal learning enhances a honey bee’s waggle dance performance
2023-03-09
Social learning plays an important role in a honey bee’s ability to “waggle dance,” report researchers, who observed that honey bees not exposed to the dances of older, more experienced nestmates produced disordered dances full of errors. The findings demonstrate that social learning shapes this complex form of insect communication, just as it does in humans, birds, and other social vertebrate species. The waggle dance is a behavior that honey bee foragers use to communicate spatial information about the precise location of a food source to other nestmates. ...
Island dwarfs and giants are disproportionality prone to human-mediated extinctions
2023-03-09
Island dwarfs and giants are more susceptible to extinction than other species, particularly following the arrival of humans to their insular homes, according to a new analysis of island species over millions of years. The findings highlight the vulnerability of some of Earth’s most unique species and could be used to inform conservation strategies to preserve them. Although they cover less than 7% of the planet’s surface, islands are hotspots of biodiversity. Due to their isolation, islands often contain species ...
Presenting a synapse-by-synapse map of an insect’s brain
2023-03-09
Researchers have presented the connectome – or synaptic wiring diagram – of an entire Drosophila larva brain. This first-ever insect whole-brain connectome is larger and more complex than previously reported connectomes and represents a valuable resource for future experimental and theoretical studies of neural circuits and brain function. The brain comprises complex networks of interconnected neurons that communicate through synapses. Understanding the brain’s network architecture is critical to understanding brain function. However, due to technological constraints, imaging entire brains with electron microscopy (EM) and reconstructing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers determine structural motifs of water undecamer cluster
Researchers enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of covalent organic frameworks by constitutional isomer strategy
Molecular target drives immunogenicity in cancer immunotherapy
Plant cell structure could hold key to cancer therapies and improved crops
Sustainable hydrogen peroxide production: Breakthroughs in electrocatalyst design for on-site synthesis
Cash rewards for behavior change: A review of financial incentives science in one health contexts and implications
One Health antimicrobial resistance modelling: from science to policy
Artificial feeding platform transforms study of ticks and their diseases
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
[Press-News.org] Reducing trip hazards and decluttering can prevent falls among older people living at homeEliminating hazards around the home, such as clutter, stairs without railings and poor lighting, can reduce the risk of falls for older people by around a quarter, according to a new Cochrane review