(Press-News.org) Rapid access to information is one of the largest barriers we have to deal with as a group of people in the Internet Age. Earth Map is a free application designed to be easily used and accessible to anyone with an internet connection and the desire to observe any environment at any time, with zero expertise (or travel) required.
This new tool features an intuitive point-and-click way of interfacing with the program, lending further to its ease of use.
The researchers published their results on January 12th in the Journal of Remote Sensing.
The authors underline the importance of getting their technology out into the hands of the public who can make change happen.
“Earth Map allows to transform big data into actionable information by everyone, thus democratizing the application of remotely sensed data. It enables a broader array of actors to take an active role in monitoring lands currently impacted by human activities” said Carmen Morales, lead author and researcher at the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations.
With a wide array of users comes a large amount of data that can be used for environmental monitoring and remote sensing applications. Earth Map uses Earth Observation (EO) data to measure various parameters (such as temperature, rainfall or vegetation) to keep track of the climate and environment and how it changes year over year. These parameters can be used to measure how well natural resources are managed and give people insight into how human interactions with the environment can have direct and long-lasting impacts on the earth as we currently know it.
“The next 10 years will be decisive to avoid catastrophic climate change effects and mass extinctions. More than 3 quarters of Earth’s land surface is impacted by human activity. It is therefore more important than ever that countries, organizations, communities, and individuals are conscious of current, past, and future land characteristics and dynamics” said Morales. While 10 years is not a lot of time, there can be exponential improvements in policy change to drive large-scale action.
Ideally, Earth Map is a tool that can be used to introduce the subject of climate and resource/land usage to users such as policy-makers, research institutions, and interested citizens who have the interest but no prior knowledge of navigating software geared towards environmental and climate analysis.
Since the climate is largely affected by policies established by governing bodies, the goal would be to use Earth Map as a jumping-off point for decision-makers at different levels to inform themselves of the current state of the climate and what meaningful policy changes can be enacted to navigate away from climate disaster.
“Using the app at its full capacity, Earth Map is a powerful tool to undertake research on the world’s most pressing environmental problems and the impacts of the climate change emergency and develop science-based policy interventions, leverage investments, and sustain livelihoods” Morales said.
The app will help to provide researchers and institutions with valuable data to further delve into the science of climate and resource management to hopefully bring about a more sustainable world.
Carmen Morales, Alfonso Sanchez-Paus Diaz, Daniel Dionisio, Laura Guarnieri, Giulio Marchi, Danae Maniatis, and Danilo Mollicone of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations contributed to the work done for this research.
The contributions of the Government of Germany via the International Climate Initiative from the Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation, Nuclear Safety and Consumer Protection, and other projects at FAO supported this research.
END
Earth Map works in tandem with its users to achieve a more conscious, climate-aware and environmental-friendly world
2023-03-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Northern and southern resident orcas hunt differently, which may help explain the decline of southern orcas
2023-03-10
Link to Google Drive folder containing images with caption and credit information:
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1Ye7QXkoTHfq7L4qEcJ33r6I6w7aB2-Mn?usp=share_link
In the Pacific Northwest and British Columbia, scientists have been sounding the alarm about the plight of southern resident orcas. Annual counts show that population numbers, already precarious, have fallen back to mid-1970s levels. Most pregnancies end in miscarriage or death of the newborn. They may not be catching enough food. And many elderly orcas — ...
Dim lights before bedtime to reduce risk of gestational diabetes
2023-03-10
Gestational diabetes mellitus is a common pregnancy complication with significant health risks for both mother and offspring
Gestational diabetes is rising fast and is now 7.8% of all births in U.S.
Mother with gestational diabetes has increased risk of diabetes, heart disease and dementia; offspring more likely to have obesity and hypertensio
CHICAGO --- Pregnant persons should dim the lights in their home and turn off or at least dim their screens (computer monitors and smartphones) a few hours before ...
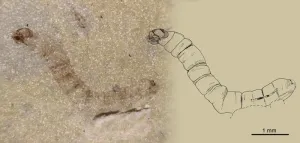
Discovery of oldest known fossil gnat shows how insects adapted to a postapocalyptic world
2023-03-10
Near the small harbour of Estellencs at the northeast of Mallorca (Balearic Islands, Spain), a pebbly beach can be found at the base of an impressive scarp that threatens rockfall. Remains of plants, crustaceans, insects, and fish have been discovered in the grey-blue rock layers formed from sediments deposited 247 million years ago. Fossils in these rocks are of great interest since they offer a window into the time where the planet was recovering from the greatest mass extinction.
A few years ago, Mallorcan ...
Sea temperatures control the distributions of European marine fish
2023-03-10
An analysis extending from southern Portugal to northern Norway highlights the importance of temperature in determining where fish species are found.
By confirming temperature as a key driver of large-scale spatial variation in fish assemblages the study was able to use future climate projections to predict where species will be most common by 2050 and 2100. The results show that overall, the greatest community-level changes are predicted at locations with greater warming, with the most pronounced effects further north - at higher latitudes.
The study was the first of its ...
McMaster researcher crafting post-COVID-19 condition guidelines, commonly known as long COVID
2023-03-10
Hamilton, ON (March 9, 2023) - McMaster University clinician-researcher Holger Schünemann is receiving $9 million in federal funding to develop official guidelines for post-COVID-19 Condition (PCC), commonly known as long COVID.
Schünemann’s project, titled McMaster Development and Dissemination of Post COVID-19 Condition (PCC) Guidelines and Knowledge Translation Products, is being developed by McMaster in collaboration with the Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC).
Schünemann said that Cochrane Canada and ...
USC research identifies existential threats to the iconic Nile River Delta
2023-03-10
Large-scale heavy metal pollution, coastal erosion and seawater intrusion pose an existential threat to the Nile River Delta and endanger 60 million people (about twice the population of Texas) in Egypt who depend on its resources for every facet of life, according to new research from the USC Viterbi School of Engineering. Furthermore, the Nile River Delta is a critical stopover for migrating birds across their journey along the East African flyway.
The study, led by Essam Heggy from the USC Viterbi Innovation Fund Arid Climates ...
Researchers unveil new AI-driven method for improving additive manufacturing
2023-03-10
Many industries rely on metal additive manufacturing to rapidly build parts and components. Rocket engine nozzles, pistons for high performance cars, and custom orthopedic implants are all made using additive manufacturing, a process that involves building parts layer-by-layer using a 3D printer.
Additive manufacturing allows users to build complex parts quickly, but structural defects that form during the building process is one of the reasons that have prevented this approach from being widely adopted. Researchers from the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne ...
Advanced imaging may help in clinical treatment of prostate cancer
2023-03-10
An advanced imaging method is showing promise as a way to improve the diagnosis of prostate cancer by giving clinicians a clearer view of suspected tumours during biopsy.
A trial conducted at the University Hospital Bonn, in Germany, has been testing the benefit of a scanning method known as PSMA-PET/CT to help target where to take biopsy samples.
Interim results reveal that when used alongside standard imaging techniques, the additional scans might help clinicians make improved decisions about subsequent courses of treatment.
Compared to the standard scans alone, when PSMA-PET/CT was used clinicians changed ...
UK study reveals ethnic differences in obstetric anesthesia care
2023-03-10
Black Caribbean-British women in the UK are 58% more likely than white women to be given general anaesthesia for elective caesarean births; for Black African-British women, they are 35% more likely to have general anaesthesia
For emergency Caesarean births, Black Caribbean-British women are 10% more likely than white women to be given general anaesthesia
For vaginal births, Bangladeshi-British (by 24%), Pakistani-British (by 15%) and Black Caribbean-British (by 8%) women less likely than white women to receive an epidural
Black women are approximately 40% less likely to have an assisted vaginal birth (forceps/ventouse [suction] delivery) compared to white women but instead are more likely ...
Emergency department visits for attempted suicides rose globally among youth during pandemic
2023-03-10
EMBARGOED UNTIL 4:30 PM MST, MARCH 9
Calgary, AB – Even though pediatric emergency department visits decreased greatly overall during the COVID-19 pandemic, a newly published study led out of the University of Calgary shows there was also a sharp increase in emergency department visits for attempted suicide and suicide ideation among children and adolescents in that same period of social isolation.
Dr. Sheri Madigan, a clinical psychologist in the Department of Psychology, is the lead author on the study, published today (March 9) in Lancet Psychiatry, which ...