(Press-News.org) FRANKFURT. Leukaemia (blood cancer) is a group of malignant and aggressive diseases of the blood-forming cells in the bone marrow. Very intensive chemotherapy and in some cases a bone marrow transplant are the only cure. Like all cancers, leukaemia is caused by changes in the DNA, the heredity material present in human cells in the form of 46 chromosomes. In many forms of leukaemia, large parts of these chromosomes are altered. People with Down syndrome, who have three copies of chromosome 21 (trisomy 21) are highly vulnerable: the risk of developing aggressive Acute Myeloid Leukaemia (AML) in the first four years of their life is more than 100 times greater for children with Down syndrome. Down syndrome is the most common congenital genetic disorder, affecting about one in 700 newborn babies.
RUNX1 transcription factor is responsible
The research group led by Professor Jan-Henning Klusmann, Director of the Department of Paediatric and Adolescent Medicine at University Hospital Frankfurt, has now discovered how the additional chromosome 21 can promote AML. With the help of genetic scissors (CRISPR-Cas9), they examined each of the 218 genes on chromosome 21 for its carcinogenic effect. It emerged that the RUNX1 gene is responsible for the chromosome’s specific carcinogenic properties. In further analyses, the researchers were able to corroborate that only one particular variant – or isoform – of the gene promotes the development of leukaemia. Klusmann explains: “Other RUNX1 isoforms were even able to prevent the cells from degenerating. This explains why RUNX1 has so far not stood out – in several decades of extensive cancer research.”
The RUNX1 gene encodes a “transcription factor” – a protein responsible for regulating the activity of other genes. RUNX1 regulates many processes, including embryonic development and early and late haematopoiesis, or blood formation. Disruption of this important regulator is therefore a key event in the development of AML. “Thanks to our research results, we now have a better understanding of what happens in leukemogenesis,” explains Klusmann, an expert in paediatric cancer. “The study underlines how important it is to examine all gene variants in carcinogenesis. In many cases, certain mutations in cancer cells alter how these variants form,” he says.
Development of more sophisticated therapeutic approaches
These insights are important for a better understanding of the complex mechanisms of carcinogenesis, as Klusmann explains: “In this way, we have laid the groundwork for developing more sophisticated therapeutic approaches. Through our biochemical analyses, we now know exactly how the gene variant alters the blood cells. From there, we were able to use specific substances that block the disease mechanism.” The intention now is to further explore the effect of these substances for use in medical care. Klusmann: “On the basis of our expertise, we now want to develop therapies to correct this malfunction. Applying them in clinical practice will certainly take a few more years, but hopefully they will lead in the future to sparing our young patients from intensive chemotherapy.”
END
Cause of leukemia in trisomy 21
Defect in gene regulation is responsible for high leukaemia risk in children with Down syndrome – biochemical analysis creates basis for therapy development
2023-03-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A study analyzes the notion of spectacle through the figure of Antigone
2023-03-10
A research study at Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M) analyzes the notion of spectacle as an enunciative space that is located beyond mediatic logic. In contrast to the generalized concept of spectacle laden with negative connotations, the study proposes a distancing of that concept from that of entertainment. UC3M Full Professor Pilar Carrera, in her essay Antígona o la razón espectacular (2023), published in the review Signa,advocates the notion of spectacle from the perspective of spectacular distance ...
Outperforms state-of-the-art algorithms in deep learning tasks
2023-03-10
Deep learning based semi-supervised learning algorithms have shown promising results in recent years. However, they are not yet practical in real semi-supervised learning scenarios, such as medical image processing, hyper-spectral image classification, network traffic recognition, and document recognition. In these types of scenarios, the labeled data is scarce for hyper-parameter search, because they introduce multiple tunable hyper-parameters. A research team has proposed a novel meta-learning based semi-supervised learning algorithm called Meta-Semi, that requires tuning only one additional hyper-parameter. Their Meta-Semi approach outperforms state-of-the-art ...
Social intelligence is the next frontier for AI, researchers say
2023-03-10
Siri and Google Assistant may be able to schedule meetings on request, but they don’t have the social understanding to independently prioritize the appointments — yet. According to researchers based in China, artificial intelligence (AI) may be smart, but it is stunted by a lack of social skills.
They published their review of the current state and call for future directions on March 10 in CAAI Artificial Intelligence Research.
“Artificial intelligence has changed our society and our daily life,” said first author Lifeng Fan, National Key Laboratory of General Artificial Intelligence, Beijing Institute for General Artificial ...
$3 million grant backs international effort to help children live healthier lives
2023-03-10
An international team of researchers has received $3 million to support an ambitious effort to understand how early gut development can profoundly shape children’s health throughout life.
The funding from the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative will allow scientists at the University of Virginia School of Medicine, Boston Children’s Hospital, University of Mississippi Medical Center and Pakistan’s Aga Khan University to “map” the healthy gut in children ages 5 and younger down to the ...
Pandemic shift to telemedicine helped maintain quality of care for depression
2023-03-10
March 10, 2023 – The rapid transition from in-person to care to telemedicine visits at the start of the COVID‑19 pandemic did not adversely affect the quality of care – and even improved some aspects of care – for patients with major depression in a major integrated health system, according to a new report. The study appears as part of a special "Virtual Visits" supplement to Medical Care, published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"A rapid shift to virtual behavioral health care was possible without compromising health care-related practices," according to the new research, led by Nancy ...
Astrocyte cells critical for learning skilled movements
2023-03-10
From steering a car to swinging a tennis racket, we learn to execute all kinds of skilled movements during our lives. You might think this learning is only implemented by neurons, but a new study by researchers at The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory at MIT shows the essential role of another brain cell type: astrocytes.
Just as teams of elite athletes train alongside staffs of coaches, ensembles of neurons in the brain’s motor cortex depend on nearby astrocytes to help them learn to encode when and how to move, and the ...
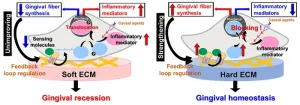
Study reveals that soft gums are more prone to inflammation
2023-03-10
The tissue area that surrounds our teeth is known as the gingiva, and healthy teeth will nestle firmly into the gums thanks to the many gingival fibers that connect the tooth to the gingiva. The gingiva is home to fibroblasts - cells that contribute to the formation of connective tissue. A group of scientists from Tohoku University have discovered that the gingiva stiffness influences the properties of gingival fibroblasts, which in turn affects whether inflammation is likely to occur and make gingival fibers difficult to form.
Their findings were published in the journal Scientific ...
HKU Marine Scientist contributes to research assessing the potential risks of ocean-based climate intervention technologies on deep-sea ecosystems
2023-03-10
The deep sea is one of the least well-known areas on Earth, comprising multiple vulnerable ecosystems that play critical roles in the carbon cycle. However, the deep sea is directly exposed to the effects of human-induced climate change and may now face additional challenges arising from efforts to counteract climate change artificially. These efforts have evolved into geoengineering solutions that could operate on vast spatial scales.
Ocean-based climate interventions (OBCIs) are increasingly claimed as promising solutions to mitigate climate change. These interventions use different technologies to remove carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and sequester the carbon ...
The future of dentistry is digital
2023-03-10
Digitalisation, one of the megatrends of the future, has arrived in the world of dentistry. Modern technologies underpin precision applications while also making treatments less invasive for patients. At the beginning of June 2023, an international congress will bring dentistry experts from all over Europe to Vienna to discuss the broad range of application options opened up by the latest breakthroughs.
The University Clinic of Dentistry Vienna is a renowned international innovation driver, especially ...
The perils of bacteria’s secret weapons
2023-03-10
Did you know that bacteria can hide their antimicrobial resistance? Much like storing military defence equipment without revealing it to the enemy, bacteria can mask their ability to resist antimicrobials. This hidden antimicrobial resistance can pass under the radar and cause treatment failure in patients.
A recent study published by researchers at UiT The Arctic University of Norway sheds light on this “hidden resistance”. The researchers describe that this phenomenon is often so rare that you cannot detect it through traditional testing methods, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
[Press-News.org] Cause of leukemia in trisomy 21Defect in gene regulation is responsible for high leukaemia risk in children with Down syndrome – biochemical analysis creates basis for therapy development