(Press-News.org) A bone marrow transplant can be a lifesaving treatment for people with relapsed blood cancers, but a potentially lethal complication known as graft-versus-host disease put limitations on this procedure. New research from the University of Wisconsin–Madison is helping to change that by identifying the cell population that causes GVHD, a target that may make bone marrow transplants safer and more effective.
An allogenic (from a donor) bone marrow transplant is a common treatment for blood cancers and other diseases of the immune system. During the transplant, the patient’s immune cells are replaced with the donor’s healthy cells. While the donor cells can help cure the patient’s blood cancer, they can also cause GVHD — in which donor T cells, a specialized immune cell in the blood, attack the patient’s healthy cells. This causes complications similar to an autoimmune disease that can be lethal.
“Graft versus host disease is one of the most common complications after an allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation procedure, and the field knows quite well that the T cells from the donor are the ones mediating the disease,” says the study’s lead author Nicholas Hess, a scientist at UW–Madison’s Carbone Cancer Center. “Before this study, there was no finite T cell population that we've been able to identify as the cause of GVHD, so all our treatment regimens generally impacted the entire T cell population. But targeting all the T cells is not ideal, as they don't just cause this detrimental disease, they also have a beneficial impact on the ability to prevent relapses.”
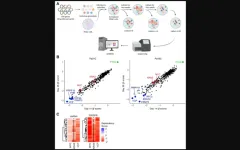
Today in Science Advances, Hess and collaborators including Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine Center members Christian Capitini, professor of pediatrics, and Peiman Hematti, professor of medicine, published their findings, identifying cells called CD4/CD8 double positive T cells (DPT) causing GVHD in immunodeficient mice. To further confirm their findings, the researchers directly investigated human patient samples.
“We looked at over 400 clinical samples from 35 patients as a part of this study and found double positive T cells to be predictive of GVHD. We also found four other biomarkers which are predictive of not just GVHD, but also relapse in general,” says Hess. “Based on that, our next step is to merge the biomarkers into a machine learning algorithm that can output a risk prediction model. Clinicians could then use this model to understand a patient’s risk of relapse and GVHD.”
A team of physicians and scientists at UW–Madison is working on ways to address the problematic cells in patients while leaving healthy and helpful T cells to flourish. Hess says that while the team is very confident the double positive T cells are directly involved in GVHD, the key step in bringing this discovery to the clinic will be developing a targeted depletion strategy and this prediction model.
“When we can gain confidence in this biomarker research and our ability to identify patients at risk, then we will potentially be able to treat them before they have all the detrimental effects of this disease,” Hess says.
The study won a Best Abstracts Award from the American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy and was presented at the American Association of Immunologists (AAI) and ECOG-ACRIN conferences, creating excitement based on the findings’ potential impact beyond blood cancer and transplantation.
“I’ve learned that DPTs have been found in a variety of chronic human inflammatory diseases, which goes to show that this is not a specific thing to graft-versus-host disease. It's probably a wider phenomenon that these human T cells are doing that we've never really appreciated before,” says Hess. “It's very exciting because it gives us something to study further. I've always been interested in taking something you discover in the lab and translating it to the clinic. I think it's what gets me up every day. It is kind of the ultimate goal in my life to be able to say I participated in something that helped patients in some way.”
This research was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (T32-AI125231, T32-HL07899, UL1-TR002373, R21-AI116007, R01-AI136500 and R01-CA215461), National Science Foundation (EEC-1648035), St. Baldrick's Foundation, the MACC Fund and the American Association for Cancer Research.
END
UW researchers identify cell type that could be key to preventing marrow transplant complication
UW researchers at the Carbone Cancer Center have identified the cells that can cause graft-versus-host disease, the most common complication of bone marrow transplants.
2023-03-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Buprenorphine after nonfatal opioid overdose results in reduced risk of overdose death
2023-03-24
Receiving medication for opioid use disorders, such as buprenorphine after an overdose, leads to lower mortality risk, according to a Rutgers study.
Drug overdose deaths are a significant public health concern in the United States. According to the National Center for Health Statistics, there were more than 105,000 drug overdose deaths in 2021, which were largely attributed to opioids. Rutgers researchers found that opioid-involved overdose deaths following nonfatal overdose events are largely preventable with buprenorphine medication for opioid use disorder.
The medication, approved by the Food and Drug Administration, is a highly effective ...
Narrowing the digital divide for health care
2023-03-24
Many parts of rural America with less access to health care also have limited broadband internet that could help them take advantage of increasingly popular online health services.
A new study by the University of Cincinnati highlighted disparities in access to digital technology that could widen the gap in access to health care. The study found that socially vulnerable communities in the United States face more barriers to adequate health care, live in areas with fewer health care resources and have less access to high-speed internet.
UC researchers ...
Corporate investment could improve climate-tech innovation
2023-03-24
MADISON—Corporate investments in climate-tech start-ups are a growing but overlooked aspect of energy innovation. According to a new report from Morgan Edwards, a professor at the La Follette School of Public Affairs at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, and her lead co-author at University of Maryland, these investments should be more fully considered as methods to advance climate technology. The report was published in the journal Joule on March 17.
Start-up companies have the potential to rapidly commercialize innovation, but they don’t always have the resources to make such ventures successful. Corporations, on the other ...
Genes & Cancer | VCP/p97 as a therapeutic target in KRAS-mutant pancreatic cancer
2023-03-24
“In summary, our goal was to identify additional therapeutic targets for KRAS-driven PDAC.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 24, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Genes & Cancer on March 10, 2023, entitled, “VCP/p97, a pleiotropic protein regulator of the DNA damage response and proteostasis, is a potential therapeutic target in KRAS-mutant pancreatic cancer.”
Researchers have recently shown that proteins involved in the DNA damage response (DDR) are critical for KRAS-mutant pancreatic ductal ...
Finding the sweet spot in sugar reductions
2023-03-24
Putting less sugar in sodas and reducing the package size of sodas sold in supermarkets may help reduce our collective sugar intake and thus lower the associated health risks. Good news for consumers, but how does it affect manufacturers? Research conducted in the US has shown that marketing diet or sugar-free varieties does not lead to an increase in the overall turnover of soda manufacturers. This is because consumers tend to switch from sugary to sugar-free versions of the same brand. However, reducing the package size of soda does have a positive effect on the sales ...
New study about the ‘tsunami’ in Venus’s clouds
2023-03-24
A group of scientists from the University of Seville, in collaboration with experts from the University of the Basque Country, has led the first detailed study of the evolution of the discontinuity of Venus’s clouds, a gigantic atmosphere wave with the appearance of a “tsunami” that is propagated in the planet’s deepest clouds and which, it is believed, may be playing a very significant role in the acceleration of Venus’s fast-moving atmosphere. The observations were carried out non-stop for more than 100 days. “This observational ...
Substance use disorders do not increase the likelihood of COVID-19 deaths
2023-03-24
BOSTON – New research from Boston Medical Center found that substance use disorders do not increase the likelihood of dying from COVID-19. Published in Substance Abuse: Research and Treatment, the study showed that the increased risk for severe COVID-19 in people with SUD that has been seen may be the result of co-occurring medical conditions.
Multiple large cohort studies from early in the pandemic have shown higher rates of hospitalization, intubation, and death from COVID-19 in those with SUD, while other studies found no ...
Black Americans, low-income Americans may benefit most from stronger policies on air pollution
2023-03-24
Embargoed for release: Friday, March 24, 2023, 12:00 PM ET
Key points:
The Environmental Protection Agency is currently considering new limits on PM2.5 air pollution. Implementing stronger limits would protect the health of all Americans, and in particular could reduce mortality rates among communities that are most threatened by air pollution—including Black and low-income Americans—by up to 7%.
Structural racism and poverty combine to change PM2.5 susceptibility, but structural racism may be more impactful when determining susceptibility.
Stronger air quality policies may also drive innovative ways to reduce the emission of heat-trapping gasses and could save ...
A molecule that has been spreading emotions for millions of years
2023-03-24
When someone smiles at us, we tend to smile back. On the other hand, if we spend time with someone who is mad or stressed, we end up absorbing these negative emotions. This tendency to align with the emotions of others is called emotional contagion. This basic form of empathy has been programmed in our brain for thousands of years and it is not difficult to get why. When there is a threat, this phenomenon allows fear to spread quickly, increasing the chances of survival. Besides, by mimicking emotions, we establish social bonds with others.
But this behavior is not exclusive to humans. New data from the Instituto Gulbenkian de Ciência (IGC) confirm that the ...
When theoretical and practical collide: researchers introduce new optimal recommendations for fungicide resistance management
2023-03-24
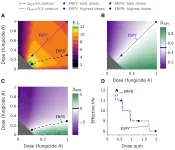
Fungicide application, while helpful in controlling plant diseases, has complicated limitations that may cost growers both peace of mind and quantity of yield. Plant pathogens which would otherwise be killed off by fungicides can evolve to avenge their dead siblings, developing resistance that renders the standard dose of fungicide application ineffective. To delay fungicide resistance, growers commonly use mixtures of fungicides to treat yield-limiting fungal diseases—based on extensive research outlining how to construct these mixtures. However, this research does not completely translate to the common, real-world scenario where one fungicide ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tundra tongue: The science behind a very cold mistake
Targeting a dangerous gut infection
Scientists successfully harvest chickpeas from “moon dirt”
Teen aggression a warning sign for faster aging later in life
Study confirms food fortification is highly cost-effective in fighting hidden hunger across 63 countries
Special issue elevates disease ecology in marine management
A kaleidoscope of cosmic collisions: the new catalogue of gravitational signals from LIGO, Virgo and KAGRA
New catalog more than doubles the number of gravitational-wave detections made by LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA observatories
Antifibrotic drug shows promise for premature ovarian insufficiency
Altered copper metabolism is a crucial factor in inflammatory bone diseases
Real-time imaging of microplastics in the body improves understanding of health risks
Reconstructing the world’s ant diversity in 3D
UMD entomologist helps bring the world’s ant diversity to life in 3D imagery
ESA’s Mars orbiters watch solar superstorm hit the Red Planet
The secret lives of catalysts: How microscopic networks power reactions
Molecular ‘catapult’ fires electrons at the limits of physics
Researcher finds evidence supporting sucrose can help manage painful procedures in infants
New study identifies key factors supporting indigenous well-being
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
[Press-News.org] UW researchers identify cell type that could be key to preventing marrow transplant complicationUW researchers at the Carbone Cancer Center have identified the cells that can cause graft-versus-host disease, the most common complication of bone marrow transplants.