(Press-News.org) INDIANAPOLIS, March 26, 2023 — The cold blast of an air conditioner can be a welcome relief as temperatures soar, but “A/C” units require large amounts of energy and can leak potent greenhouse gases. Today, scientists report an eco-friendly alternative — a plant-based film that gets cooler when exposed to sunlight and comes in a variety of textures and bright, iridescent colors. The material could someday keep buildings, cars and other structures cool without requiring external power.
The researchers will present their results at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Spring 2023 is a hybrid meeting being held virtually and in-person March 26–30 and features more than 10,000 presentations on a wide range of science topics.
“To make materials that remain cooler than the air around them during the day, you need something that reflects a lot of solar light and doesn’t absorb it, which would transform energy from the light into heat,” says Silvia Vignolini, Ph.D., the project’s principal investigator. “There are only a few materials that have this property, and adding color pigments would typically undo their cooling effects,” Vignolini adds.
Passive daytime radiative cooling (PDRC) is the ability of a surface to emit its own heat into space without it being absorbed by the air or atmosphere. The result is a surface that, without using any electrical power, can become several degrees colder than the air around it. When used on buildings or other structures, materials that promote this effect can help limit the use of air conditioning and other power-intensive cooling methods.
Some paints and films currently in development can achieve PDRC, but most of them are white or have a mirrored finish, says Qingchen Shen, Ph.D., who is presenting the work at the meeting. Both Vignolini and Shen are at Cambridge University (U.K.). But a building owner who wanted to use a blue-colored PDRC paint would be out of luck — colored pigments, by definition, absorb specific wavelengths of sunlight and only reflect the colors we see, causing undesirable warming effects in the process.
But there’s a way to achieve color without the use of pigments. Soap bubbles, for example, show a prism of different colors on their surfaces. These colors result from the way light interacts with differing thicknesses of the bubble’s film, a phenomenon called structural color. Part of Vignolini’s research focuses on identifying the causes behind different types of structural colors in nature. In one case, her group found that cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs), which are derived from the cellulose found in plants, could be made into iridescent, colorful films without any added pigment.
As it turns out, cellulose is also one of the few naturally occurring materials that can promote PDRC. Vignolini learned this after hearing a talk from the first researchers to have created a cooling film material. “I thought wow, this is really amazing, and I never really thought cellulose could do this.”
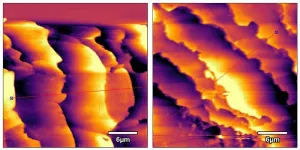
In recent work, Shen and Vignolini layered colorful CNC materials with a white-colored material made from ethyl cellulose, producing a colorful bi-layered PDRC film. They made films with vibrant blue, green and red colors that, when placed under sunlight, were an average of nearly 40 F cooler than the surrounding air. A square meter of the film generated over 120 Watts of cooling power, rivaling many types of residential air conditioners. The most challenging aspect of this research, Shen says, was finding a way to make the two layers stick together — on their own, the CNC films were brittle, and the ethyl cellulose layer had to be plasma-treated to get good adhesion. The result, however, was films that were robust and could be prepared several meters at a time in a standard manufacturing line.
Since creating these first films, the researchers have been improving their aesthetic appearance. Using a method modified from approaches previously explored by the group, they’re making cellulose-based cooling films that are glittery and colorful. They’ve also adjusted the ethyl cellulose film to have different textures, like the differences between types of wood finishes used in architecture and interior design, says Shen. These changes would give people more options when incorporating PDRC effects in their homes, businesses, cars and other structures.
The researchers now plan to find ways they can make their films even more functional. According to Shen, CNC materials can be used as sensors to detect environmental pollutants or weather changes, which could be useful if combined with the cooling power of their CNC-ethyl cellulose films. For example, a cobalt-colored PDRC on a building façade in a car-dense, urban area could someday keep the building cool and incorporate detectors that would alert officials to higher levels of smog-causing molecules in the air.
The researchers acknowledge support and funding from Purdue University, the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, the European Research Council, the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council, the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council, the European Union and Shanghai Jiao Tong University.
A recorded media briefing on this topic will be posted Monday, March 27, by 10 a.m. Eastern time at www.acs.org/acsspring2023briefings. Reporters can request access to media briefings during the embargo period by contacting newsroom@acs.org.
For health and safety information for ACS Spring 2023, please visit the FAQ webpage.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note to journalists: Please report that this research was presented at a meeting of the American Chemical Society.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
Title
Structurally colored radiative cooling cellulosic films
Abstract
Daytime radiative cooling (DRC) materials offer a sustainable approach to thermal management by exploiting net positive heat transfer to deep space. While such materials typically have a white or mirror-like appearance to maximize solar reflection, extending the palette of available colors is required to promote their real-world utilization. However, the incorporation of conventional absorption-based colorants inevitably leads to solar heating, which counteracts any radiative cooling effect. In this work, efficient sub-ambient DRC (Day: −4 °C, Night: −11 °C) from a vibrant, structurally colored film prepared from naturally derived cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs), is instead demonstrated. Arising from the underlying photonic nanostructure, the film selectively reflects visible light resulting in intense, fade-resistant coloration, while maintaining a low solar absorption (~3%). Additionally, a high emission within the mid-infrared atmospheric window (>90%) allows for significant radiative heat loss. By coating such CNC films onto a highly scattering, porous ethylcellulose (EC) base layer, any sunlight that penetrates the CNC layer is backscattered by the EC layer below, achieving broadband solar reflection and vibrant structural color simultaneously. Finally, scalable manufacturing using a commercially relevant roll-to-roll process validates the potential to produce such colored radiative cooling materials at a large scale from a low-cost and sustainable feedstock.
END
Colorful films could help buildings, cars keep their cool
2023-03-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New ways to measure curls and kinks could make it easier to care for natural hair
2023-03-26
INDIANAPOLIS, March 26, 2023 — Black women and others with curly or kinky hair encounter a vast and confusing array of haircare options. Advice on the best products to use for a certain type of hair is often contradictory, and the results can be highly variable. Now, scientists are bringing order to this chaos by identifying properties such as the number of curls or coils in a given length of hair that could eventually help users pick the perfect product and achieve consistent results.
The researchers will present their findings today at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Spring 2023 is a hybrid meeting being held virtually and in-person ...
Two meteorites are providing a detailed look into outer space
2023-03-26
INDIANAPOLIS, March 26, 2023 — If you’ve ever seen a shooting star, you might have actually seen a meteor on its way to Earth. Those that land here are called meteorites and can be used to peek back in time, into the far corners of outer space or at the earliest building blocks of life. Today, scientists report some of the most detailed analyses yet of the organic material of two meteorites. They’ve identified tens of thousands of molecular “puzzle pieces,” including a larger amount of oxygen atoms than they had expected.
The researchers will present their results at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society ...
The more traumatic the childhood, the angrier the adult
2023-03-26
Scientists have found that depression and anxiety sufferers who have had a traumatic childhood tend to grow up as angry adults, and the worse the trauma, the angrier the adult. This can affect personal mental health and social interaction, but also makes it more difficult to treat the depression and anxiety. This work is presented at the European Congress of Psychiatry in Paris.
Previously, the researchers had found that more than 40% of patients with both anxiety and depression had a tendency towards anger. This compares to only around 5% of healthy controls. The present ...
Scientists show that odors from other people’s sweat can help treat social anxiety
2023-03-26
A group of European researchers have shown that exposure to human odours, extracted from other people’s sweat, might be used to boost treatment for some mental health problems.
In a preliminary study, the researchers were able to show that social anxiety was reduced when patients underwent mindfulness therapy while exposed to human ‘chemo-signals’, or what we commonly refer to as body odour, obtained from underarm sweat from volunteers. Presenting the results of a pilot study at the European Congress of Psychiatry in Paris, lead researcher Ms Elisa Vigna, of the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm said:
“Our state of mind causes us to produce molecules ...
Childhood trauma linked to adult mental health problems: women harmed more by abuse, men by neglect
2023-03-26
A new study shows that men and women are affected differently by childhood trauma: women are more affected by childhood emotional trauma and sexual abuse, whereas men are more affected by childhood emotional and physical neglect.
Lead researcher, Dr Thanavadee Prachason (from the University of Maastricht in the Netherlands) said, “Our findings indicate that exposure to childhood maltreatment increases the risk of having psychiatric symptoms in both men and women. However, exposure to emotionally or sexually abusive experiences during childhood increases the risk of a variety of psychiatric symptoms particularly ...
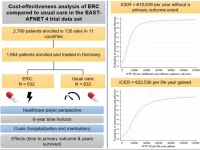
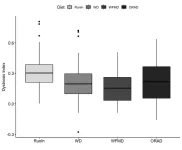
Is early rhythm control in atrial fibrillation care cost-effective?
2023-03-26
Sophia Antipolis, 27 March 2023: Patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) benefit from early rhythm control therapy. It reduces cardiovascular deaths, strokes, and other adverse outcomes by 20% compared to usual care. The beneficial effects of early rhythm control were shown by the pan-European EAST – AFNET 4 trial and confirmed by other large health studies. However, what is the price of the new treatment strategy? A cost-effectiveness analysis revealed: the health benefits of early rhythm control come at reasonable additional costs. The analysis was published today in EP Europace, a journal of the European ...
The heart benefits of walnuts likely come from the gut
2023-03-25
A new study examining the gene expression of gut microbes suggests that the heart-healthy benefits of walnuts may be linked to beneficial changes in the mix of microbes found in our gut. The findings could help identify other foods or supplements with similar nutritional benefits.
Researchers led by Kristina S. Petersen from Texas Tech University in Lubbock found that introducing walnuts into a person’s diet may alter the gut’s mix of microbes — known as the microbiome — in a way that increases the body’s production of the ...
The addition of gemcitabine with cisplatin and intensity-modulated radiation therapy improves outcomes for women with locally advanced vulvar cancer
2023-03-25
Results from the NRG Oncology Phase II NRG-GOG-0279 clinical study indicate that women with locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the vulva who received gemcitabine concurrently with cisplatin and intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) exhibited increased rate of pathologic complete responses (pCR). This is also the first clinical trial to standardize IMRT. These findings were presented during the Plenary Session at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology (SGO) 2023 Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer.
“Women with locally ...
The utilization of atezolizumab as a primer for chemoradiation results in promising immune system alterations for women with locally advanced cervical cancer
2023-03-25
Locally advanced cervical cancer remains an area of high therapeutic need, with recent trials failing to demonstrate evidence of benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy or immune checkpoint blockade administered concurrent with chemoradiation. Results from the NRG-GY017 randomized trial comparing the anti-PD-L1 inhibitor atezolizumab before and concurrent with chemoradiation (CRT) indicated favorable outcomes for 2-year disease-free survival (DFS) and demonstrated evidence of improved immunogenicity with neoadjuvant atezolizumab in patients with locally advanced cervical cancer. These findings were presented during the Plenary Session at the Society of Gynecologic ...
Women are more likely to experience long-term anxiety after cardiac arrest than men
2023-03-25
Marseille, France – 26 March 2023: More than 40% of women report anxiety four months after a cardiac arrest compared with 23% of men, according to research presented today at ESC Acute CardioVascular Care 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
“Cardiac arrest occurs with little or no warning and it’s common to feel anxious and low afterwards,” said study author Dr. Jesper Kjaergaard of Rigshospitalet - Copenhagen University Hospital, Denmark. “After the initial shock and confusion, patients and their families have an abrupt change in their way of life, with medical investigations ...