(Press-News.org) The results of a study published in “Advances in Nutrition” that compared dietary and nutrition recommendations from dozens of clinical practice guidelines around the world for treating, managing and preventing major chronic diseases should increase clinician confidence on recommending consumption of fruits, vegetables, legumes and whole grains.
The meta-epidemiological study from the American College of Lifestyle Medicine (ACLM) reviewed 78 clinical practice guidelines published between 2010 and 2021 in North America, Europe and Asia and found close alignment in their recommendations for encouraging daily intake of plant food sources, while limiting consumption of alcohol, salt or sodium.
The paper states that the findings are important because patients have reported confusion caused by contradictory nutrition messaging, in part due to fad diets and pseudo-expert advice on the Internet. However, physicians, whose expertise is frequently sought by patients, often receive insufficient nutrition education in medical school to feel confident giving dietary guidance to patients for the treatment of chronic disease.
“Clinicians depend on clinical practice guidelines developed from the most current and rigorous medical research to help steer their diagnoses, treatment and management of common chronic diseases,” said Beth Frates, MD, FACLM, DipABLM, ACLM President and Clinical Assistant Professor at Harvard Medical School. “The results of this comprehensive review of evidence-based clinical practice guidelines are important because they can benefit both clinicians and their patients by reducing the variability in dietary and nutrition guidance that often prevents clinicians from providing optimal care.”
Clinical practice guidelines reviewed for the study were developed by governments, major medical professional societies and large health stakeholder associations to improve the health of adults with chronic diseases, such as type 2 diabetes, cancer, cardiovascular disease, digestive diseases, weight-related conditions and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Dietary patterns, food groups and food components were of primary interest in the study, with macronutrient and micronutrient recommendations a secondary interest.
For food groups, nearly three quarters of clinical practice guidelines recommended including or increasing intake of vegetables, which was the highest percentage of any food group. No guidelines recommended excluding or reducing vegetables. After vegetables, fruit at 69%, whole grains at 58% and legumes at 47% were the most commonly recommended food groups. The food groups most often recommended to limit or reduce among guideline recommendations were red meat at 32%, followed by processed meat at 27% and refined grains at 19%.
Among food components, 62% of guidelines recommended excluding, decreasing or limiting alcohol and 56% recommended the same of salt or sodium. The most recommended food components were vegetable oils at 35% and soy protein at 18%.
“These findings demonstrate that global dietary and nutrition guidelines support and are aligned with ACLM’s recommendation that, for the treatment, reversal and prevention of lifestyle-related chronic disease, the optimal eating plan is predominantly based on a variety of minimally processed vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, nuts and seeds,” said Micaela Karlsen, PhD, MSPH, ACLM Senior Director of Research and senior study author.
The Global Burden of Disease Report has confirmed that unhealthy diet is responsible for more deaths globally than any other risk factor, including tobacco smoking. To the authors’ knowledge, this was the first study to compare dietary recommendations across current clinical practice guidelines for multiple major chronic diseases.
“The growing prevalence of overweight and obesity and the associated chronic conditions are a serious public health threat that must be urgently addressed,” said Kelly C. Cara, MS, doctoral student at Tufts University Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy, the study’s first author. “Patients look to health care professionals for dietary guidance, so it is critical that physicians are fully informed and confident when offering recommendations to patients in order to provide the best outcomes. We hope the results of this study will assist physicians in developing the foundation of knowledge needed to achieve those outcomes.”
END
Study of dietary and nutrition recommendations from worldwide clinical practice guidelines finds close alignment on benefits of plant food groups for treatment and prevention of chronic disease
The findings should increase clinician confidence in recommending daily intake of unrefined plant foods amid a public discourse clouded by conflicting guidance from fad diets or Internet pseudo-experts.
2023-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Don Quixote gives his name to a new plant species only known from La Mancha, Spain
2023-03-27
The knowledge of biodiversity in allegedly well-known places is not as complete as one would expect and its detailed study by researchers continues to offer surprises, is what we find out in a new study of the flora of south-central Spain.
Now, Spanish botanists from Pablo de Olavide University (Seville, Spain) have described a new plant species of the papyrus family (Cyperaceae) restricted to the La Mancha region in south-central Spain. This region is in fact well-known for classic literary fans, who might recognise the name ...
SwRI-developed instrument delivered for lunar lander mission
2023-03-27
SAN ANTONIO — March 27, 2023 —Southwest Research Institute recently delivered the Lunar Magnetotelluric Sounder (LMS) to Firefly Aerospace in Cedar Park, Texas, for integration into the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander scheduled to arrive at the Moon in 2024. The sounder will determine the electrical conductivity of the interior of the Moon by measuring low-frequency electric and magnetic fields.
“For more than 50 years, scientists have used magnetotelluric techniques, which use natural characteristics of the Earth’s electromagnetic fields to determine the electrical resistivity of the subsurface for research and resource exploration,” said SwRI’s Bob Grimm, ...
Socially vulnerable carry disproportionate COVID burden due to lower likelihood of vaccination not vaccine effectiveness
2023-03-27
INDIANAPOLIS – The burden of the pandemic has disproportionately affected socially vulnerable populations. One of the first studies to look at the intersection of social vulnerability with COVID-19 vaccine utilization and effectiveness has found that while vaccination rates have varied substantially between socially vulnerable and communities that are not socially vulnerable, there has been no difference in vaccine effectiveness between those who are socially vulnerable and those who are not.
“We found that protection against emergency room and urgent care center visits, hospitalization and death conveyed by a COVID-19 mRNA vaccination ...
Positive experiences in close relationships are associated with better physical health, new research suggests
2023-03-27
Social relationships influence physical health, but questions remain about the nature of this connection. New research in Social Psychological and Personality Science suggests that the way you feel about your close relationships may be affecting the way your body functions.
Previous smaller-scale studies have examined the connection between relationship conflict or satisfaction with stress levels and blood pressure. The new research examines the effects of positive and negative relationship experiences on the body, as well as how these experiences and health outcomes change ...
Research may speed identification of patients who need liver transplants
2023-03-27
Research findings from Rutgers, the University of Michigan, the University of Texas Southwestern, and the Medical University of South Carolina could save lives by enabling faster and more accurate identification of hospitalized patients who need liver transplants or are likely to recover.
Retrospective analysis of blood samples and medical records from 270 patients admitted to the hospital with acute liver failure (ALF) found that concentrations of a short-lived but abundant serum protein called carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS1) helped predict which patients survive or die without a transplant.
“We still need to validate these results in more patients to ...
Finger-prick test developed for ‘trich’ a common, undiagnosed STI
2023-03-27
PULLMAN, Wash. – A quick, affordable diagnostic test developed by a Washington State University researcher may help curb one of the most prevalent but least discussed sexually transmitted infections.
More common than chlamydia or gonorrhea, Trichomonas vaginalis, also known as trich, causes no symptoms in about 70% of those infected. Even when asymptomatic, trich is linked to a host of bad health outcomes, including increased susceptibility to HIV, prostate cancer in men and infertility and pregnancy complications in women.
Trich is easily ...
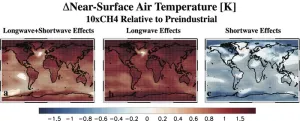
Surprise effect: Methane cools even as it heats
2023-03-27
Most climate models do not yet account for a new UC Riverside discovery: methane traps a great deal of heat in Earth’s atmosphere, but also creates cooling clouds that offset 30% of the heat.
Greenhouse gases like methane create a kind of blanket in the atmosphere, trapping heat from Earth’s surface, called longwave energy, and preventing it from radiating out into space. This makes the planet hotter.
“A blanket doesn’t create heat, unless it’s electric. You feel warm because ...
A puff of air could deliver your next vaccine (video)
2023-03-27
INDIANAPOLIS, March 27, 2023 — Nobody likes needles, but they’re necessary for delivering many vaccines and biologics into the body. But what if those could be puffed through the skin instead, with just a little pressure, like being hit in the arm with a foam toy? Today, scientists report steps toward making that a reality. Using powdered vaccines that don’t require refrigeration and a system driven by compressed gas, their “MOF-Jet” could easily deliver therapeutics against cancer and other diseases in a relatively painless way.
The researchers will present their results at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS ...
Human cells help researchers understand squid camouflage
2023-03-27
INDIANAPOLIS, March 27, 2023 — Squids and octopuses are masters of camouflage, blending into their environment to evade predators or surprise prey. Some aspects of how these cephalopods become reversibly transparent are still “unclear,” largely because researchers can’t culture cephalopod skin cells in the lab. Today, however, researchers report that they have replicated the tunable transparency of some squid skin cells in mammalian cells, which can be cultured. The work could not only shed light on basic squid biology, but ...
Genetic tests unexpectedly find genes linked to heart disease — now what?
2023-03-27
Statement Highlights:
As health care professionals, researchers and consumers increasingly use genetic testing, they are uncovering incidental genetic abnormalities, or variants, that are associated with cardiovascular diseases.
The statement writing committee cautions that incidentally identified single gene variants may or may not be risk factors for disease, so it is important to interpret them correctly and cautiously.
The new scientific statement offers a framework to support health care professionals in appropriately assessing individual genetic variants, communicating findings with patients and families, and, when ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
New research: Nighttime road traffic noise stresses the heart and blood vessels
Meningococcal B vaccination does not reduce gonorrhoea, trial results show
AAO-HNSF awarded grant to advance age-friendly care in otolaryngology through national initiative
Eight years running: Newsweek names Mayo Clinic ‘World’s Best Hospital’
Coffee waste turned into clean air solution: researchers develop sustainable catalyst to remove toxic hydrogen sulfide
Scientists uncover how engineered biochar and microbes work together to boost plant-based cleanup of cadmium-polluted soils
Engineered biochar could unlock more effective and scalable solutions for soil and water pollution
Differing immune responses in infants may explain increased severity of RSV over SARS-CoV-2
The invisible hand of climate change: How extreme heat dictates who is born
Surprising culprit leads to chronic rejection of transplanted lungs, hearts
[Press-News.org] Study of dietary and nutrition recommendations from worldwide clinical practice guidelines finds close alignment on benefits of plant food groups for treatment and prevention of chronic diseaseThe findings should increase clinician confidence in recommending daily intake of unrefined plant foods amid a public discourse clouded by conflicting guidance from fad diets or Internet pseudo-experts.