(Press-News.org) Cannabis use disorder is defined by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders as a problematic pattern leading to clinically significant impairment or distress, with symptoms that may include increased tolerance, withdrawal symptoms, strong desire to use marijuana and spending large amounts of time using cannabis.
Tammy Chung, director of the Center for Population Behavioral Health at Rutgers Institute for Health, Health Care Policy and Aging Research, along with colleagues Marc Steinberg of Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School and Mary Barna Bridgeman of the Rutgers Ernest Mario School of Pharmacy, published a commentary in JAMA Psychiatry calling for an important clarification of the way cannabis use disorder is diagnosed,specifically for people who use cannabis for therapeutic purposes. Chung explains why.
What are the challenges to accurately diagnosing cannabis use disorder?
Chung: One of the challenges involves the rapid increase in state-level legalization of cannabis for therapeutic purposes – also known as medical marijuana.
Specifically, the manual used to define substance-use disorders was developed before the sharp rise in cannabis use for therapeutic purposes. This means that the diagnostic manual considers cannabis to be an illicit substance, even if a person reports cannabis use only for therapeutic purposes and uses cannabis purchased from a dispensary under appropriate medical supervision, with a valid medical cannabis card.
We suggest the diagnostic manual take into account, as separate from recreational cannabis use, the use of cannabis for therapeutic purposes, given its increasing prevalence. This important distinction is made to avoid misdiagnosis, particularly for individuals who only use cannabis for therapeutic purposes under appropriate medical supervision. This suggested modification to diagnosing cannabis use disorder is similar to the way in which other substances – such as opioids and sedatives, both prescribed and also considered illicit substances – are already treated in the diagnostic manual.
Since cannabis for therapeutic purposes is only recommended, not prescribed, this raises other challenges, such as the absence of a standard dose due to different ways of consuming cannabis (vaping, edible), the lack of dosing guidelines for specific health conditions, the need for greater regulation of cannabis products and limited or mixed evidence regarding the therapeutic effects of cannabis for many health conditions.
What do you see as the issue with the current version of this diagnosis protocol?
Chung: The manual’s diagnosis of cannabis use disorder requires an individual to meet only two or more of 11 criteria. These criteria might include only increased tolerance for cannabis and withdrawal symptoms, which are commonly reported by individuals who use cannabis for therapeutic reasons.
People who report these two criteria would technically meet criteria for a cannabis use disorder diagnosis. However, these two symptoms alone may not represent problematic use.
Explain the changes you propose to the diagnosis.
Chung: In our proposed model, tolerance to cannabis effects and withdrawal symptoms cannot be the only two criteria used to determine if an individual shows impairment in daily activities when taking cannabis for therapeutic purposes. If two or more other symptoms are reported, such as difficulties cutting down on cannabis use or use in hazardous situations – like driving while feeling the effects of cannabis – the standard model of diagnosing an individual with cannabis use disorder can still be used.
Our suggested model is based on the one used to diagnose substance use disorder in an individual who has been prescribed medication, such as opioids or sedatives. When taking a prescribed medication, such as a sedative or a recommended therapeutic, such as cannabis under appropriate medical supervision, symptoms of tolerance and withdrawal may occur as a result of a daily-dosing regimen. Notably, the manual uses different guidelines for diagnosing substance use disorder for a prescription medication and for an illicit substance. We suggest a similar approach could be used to avoid misdiagnosis among individuals who use cannabis only or mainly for therapeutic purposes under appropriate medical supervision.
Why is it important to clarify how cannabis use disorder is diagnosed?
Chung: There are limitations to the criteria used to diagnose cannabis use disorder when applied to people who use cannabis for therapeutic purposes. Specific training in assessing the criteria in the context of an individual who uses cannabis for therapeutic purposes could improve the validity of cannabis use disorder diagnoses.
Our model addresses the critical need to improve how cannabis use disorder is diagnosed in individuals who use cannabis for therapeutic purposes. Misdiagnosis, particularly overdiagnosis, represents a medical error with stigmatizing consequences for an individual. Critically, this error could result in flawed understanding of the effects of therapeutic use of cannabis on health because there is potential for misdiagnosis when using the standard diagnostic model for patients who use cannabis only or mainly for therapeutic purposes.
END
Can cannabis use disorder be accurately diagnosed?
Rutgers researchers propose new way to assess medical marijuana use
2023-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
SCAI and HRS release expert consensus on transcatheter left atrial appendage closure
2023-03-27
WASHINGTON (March 27, 2023) – Today, the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) and the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) released an updated expert consensus statement on transcatheter left atrial appendage closure (LAAC). SCAI and HRS prioritized the development of an updated consensus statement to provide recommendations on contemporary, evidence-based best practices for transcatheter LAAC focusing on endovascular devices.
Left atrial appendage closure is a minimally invasive procedure that is used to reduce the risk of stroke associated with atrial fibrillation. ...
Beaver fossil named after Buc-ee’s
2023-03-27
A new species of ancient beaver that was rediscovered by researchers in The University of Texas at Austin’s fossil collections has been named after Buc-ee’s, a Texas-based chain of popular travel centers known for its cartoon beaver mascot.
The beaver is called Anchitheriomys buceei, or “A. buceei” for short.
Steve May, a research associate at the UT Jackson School of Geosciences, said that the beaver’s Texas connection and a chance encounter with a Buc-ee’s billboard are what inspired the name.
May is the lead author of the paper that describes A. buceei, along with another, much smaller, species of fossil beaver. Published ...
James Chappell wins NSF CAREER Award
2023-03-27
HOUSTON – (March 27, 2023) – Rice University bioscientist and synthetic biologist James Chappell has won a National Science Foundation CAREER Award to develop RNA programming methods to improve human health and the environment.
“Synthetic biology has progressed a lot in the past decade, and we’ve gotten really good at genetically programming microbes in confined laboratory environments where conditions are ideal,” said Chappell, an assistant professor both of biosciences and of bioengineering. “But, of course, most microbes on the planet don't live in pure cultures where the temperature is always 37 degrees ...
In bid to make child cancer treatments safer, scientists find possible warning signs of severe reaction
2023-03-27
Scientists seeking a way to eliminate an adverse reaction to treatments for acute lymphocytic leukemia, a common childhood cancer, have found what they believe to be an early warning indicator.
Mouse studies conducted by Rutgers researchers as part of a larger scientific team are pointing to vitamin A levels as a signal that a patient may or may not be vulnerable to a dangerous toxicity.
Summarizing their findings in Science Translational Medicine, the scientists found that, in patients being treated for acute lymphocytic leukemia with the chemotherapy drug asparaginase, there is an ...
HIV can persist for years in myeloid cells of people on antiretroviral therapy
2023-03-27
A subset of white blood cells, known as myeloid cells, can harbor HIV in people who have been virally suppressed for years on antiretroviral therapy, according to findings from a small study supported by the National Institutes of Health. In the study, researchers used a new quantitative method to show that HIV in specific myeloid cells—short-lived monocytes and longer-lived monocyte-derived macrophages—can be reactivated and infect new cells. The findings, published in Nature Microbiology, suggest that ...
The Greenland Ice Sheet is close to a melting point of no return
2023-03-27
American Geophysical Union
Press Release 23-11
27 March 2023
For Immediate Release
This press release is available online at: https://news.agu.org/press-release/the-greenland-ice-sheet-is-close-to-a-melting-point-of-no-return/
AGU press contact:
Rebecca Dzombak, +1 (202) 777-7492, news@agu.org (UTC-4 hours)
Contact information for the researchers:
Dennis Höning, Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, dennis.hoening@pik-potsdam.de (UTC+1 hour)
WASHINGTON — The Greenland Ice Sheet covers 1.7 million ...
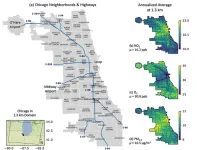
Chicago pollution varies by neighborhood
2023-03-27
New simulation combines emissions with weather and chemistry in an air-quality model
First neighborhood-scale simulation of its kind focused on Chicago tracks air quality hour by hour across areas as small as 1.3 kilometers-sized blocks
Simulation can show how pollutants move across space and time throughout the city and surrounding areas
Air pollution along highways is consistently worse than other areas, regardless of season or time of day
EVANSTON, Ill. — If you live along one of the major interstate highways running through Chicago or directly next to Lake Michigan, you are regularly exposed to more air pollution than ...
Moffitt researchers discover two-pronged approach to stimulate STING antitumor activity
2023-03-27
TAMPA, Fla. – Immunotherapies have greatly improved the outcomes of many patients with melanoma. But there is still a need for new approaches for the subset of patients who do not respond well to this type of therapy. Moffitt Cancer Center researchers are looking at new targets to help inhibit tumor development and promote antitumor immunity, one being the STING signaling pathway. In a new article published in Nature Communications, a team of Moffitt and University of Miami Miller School of Medicine investigators demonstrate that targeting the STING pathway with a combination strategy ...
Making immunizations more effective
2023-03-27
In addition to an antigen, many vaccines also contain substances, called adjuvants, which stimulate the immune system. By using computer-aided molecular design and machine learning, a Chinese research team has now developed two novel broad-spectrum adjuvants that can significantly amplify the immune response to vaccines. As reported in the journal Angewandte Chemie, they were able to enhance the effectiveness of immunization against certain forms of cancer in animal models.
Adjuvants amplify and prolong the effect of vaccine immunizations. Aluminum salts have been successfully used ...
JWST confirms giant planet atmospheres vary widely
2023-03-27
ITHACA, N.Y. – An international team of astronomers has found the atmospheric compositions of giant planets out in the galaxy do not fit our own solar system trend.
Using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), the researchers discovered that the atmosphere of exoplanet HD149026b, a ‘hot Jupiter’ orbiting a star comparable to our sun, is super-abundant in the heavier elements carbon and oxygen – far above what scientists would expect for a planet of its mass.
These findings, published in “High atmospheric metal enrichment for a Saturn-mass ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
Accounting for soil saturation enhances atmospheric river flood warnings
The research that got sick veterans treatment
Study finds that on-demand wage access boosts savings and financial engagement for low-wage workers
Antarctica has lost 10 times the size of Greater Los Angeles in ice over 30 years
Scared of spiders? The real horror story is a world without them
New study moves nanomedicine one step closer to better and safer drug delivery
Illinois team tests the costs, benefits of agrivoltaics across the Midwest
Highly stable self-rectifying memristor arrays: Enabling reliable neuromorphic computing via multi-state regulation
Composite superionic electrolytes for pressure-less solid-state batteries achieved by continuously perpendicularly aligned 2D pathways
Exploring why some people may prefer alcohol over other rewards
How expectations about artificial sweeteners may affect their taste
[Press-News.org] Can cannabis use disorder be accurately diagnosed?Rutgers researchers propose new way to assess medical marijuana use