(Press-News.org)
Fukuoka, Japan—Solid oxide fuel cells, or SOFC, are a type of electrochemical device that generates electricity using hydrogen as fuel, with the only 'waste' product being water. Naturally, as we strive to reduce our carbon output and mitigate the casualties of the climate crisis, both business and academia have taken major interest in the development of SOFCs.
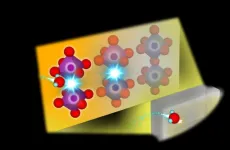
In what can potentially accelerate the development of more efficient SOFCs, a research team led by Kyushu University has uncovered the chemical innerworkings of a perovskite-based electrolyte they developed for SOFCs. The team combined synchrotron radiation analysis, large-scale simulations, machine learning, and thermogravimetric analysis, to uncover the active site of where hydrogen atoms are introduced within the perovskite lattice in its process to produce energy. The results were published in journal Chemistry of Materials.
At the fundamental level, a fuel cell is just a device that generates electricity by facilitating the split of a hydrogen atom into its positively charged proton and negatively charged electron. The electron is used to generate electricity, and then comes together with a proton and oxygen and produces water as a 'waste' product.
The material at the literal center of all this is the electrolyte. This material acts an atomic sieve that facilitates transfer of specific atoms across the fuel cell. Depending on the type of fuel cell, those atoms could be protons or oxygen.
While SOFCs may be an uncommon term to many people, the technology has already been commercialized in generators for single family homes. Nonetheless, they remain expensive, with one of the largest obstacles being its high operating temperature.
"Conventional SOFCs need to be at 700-1000℃ for the electrolyte to perform efficiently." explains Professor Yoshihiro Yamazaki at Kyushu University's Platform of Inter-/Transdisciplinary Energy Research, who led the research. "Naturally, there's a global race to develop SOFC electrolytes that can operate at lower temperatures of around 300-450℃. One such promising materials are perovskites."
Perovskites are a category of material with a specific crystalline structure that allows them to possess unique physical, optical, and even electrical properties. Moreover, since they can be artificially synthesized with different atoms, a large body of research focuses on developing and testing a near infinite number of possible perovskites.
One such case is in developing better SOFC electrolytes.
"In our past work we developed a Barium and Zirconium based perovskite with the chemical composition BaZrO3. By replacing the Zr site with a high concentration of Scandium, or Sc, we succeeded in making a high-performance electrolyte that can function at our target temperature of 400℃," explains Yamazaki. "Of course, that was only a part of what we wanted to find. We also were investigating a question that hadn't been solved for over three decades: where in the electrolyte's lattice do the protons get introduced?"
Probing the inner workings of SOFCs had been difficult due to its high operating temperature and changing pressure from water, the fuel cell's source of hydrogen.
To get around these issues, the team conducted X-ray absorption spectroscopy experiments on their perovskite electrolyte using synchrotron radiation—the electromagnetic radiation emitted from particle accelerators—while the fuel cell was active at around 400℃.
"These results gave us insight into where in the material's chemical structure the protons would be incorporated. From there we applied machine learning, and using a supercomputer calculated possible structural configurations of the material," continued Yamazaki. "By carefully comparing the predicted results with experimental data we were able to clarify the structural changes the electrolyte undertakes when active."
"Now that we have the fundamental innerworkings of the electrolyte we can being optimizing its nanostructures and even propose new materials that can lead to more efficient fuel cells, and even ones that work at wider temperature ranges," concludes Yamazaki.
###
For more information about this research, see "Probing Local Environments of Oxygen Vacancies Responsible for Hydration in Sc-Doped Barium Zirconates at Elevated Temperatures: In Situ X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy, Thermogravimetry, and Active Learning Ab Initio Replica Exchange Monte Carlo Simulations," Kenta Hoshino, Shusuke Kasamatsu, Junji Hyodo, Kentaro Yamamoto, Hiroyuki Setoyama, Toshihiro Okajima, and Yoshihiro Yamazaki, Chemistry of Materials, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.2c02116
About Kyushu University
Kyushu University is one of Japan’s leading research-oriented institutes of higher education since its founding in 1911. Home to around 19,000 students and 8,000 faculty and staff, Kyushu U's world-class research centers cover a wide range of study areas and research fields, from the humanities and arts to engineering and medical sciences. Its multiple campuses—including one of the largest in Japan—are located around Fukuoka City, a coastal metropolis on the southwestern Japanese island of Kyushu that is frequently ranked among the world’s most livable cities and historically known as Japan’s gateway to Asia. Through its Vision 2030, Kyushu U will ‘Drive Social Change with Integrative Knowledge.’ Its synergistic application of knowledge will encompass all of academia and solve issues in society while innovating new systems for a better future.
END
Can monetary policy such as the United States Federal Reserve raising interest rates affect the environment? According to a new study by Florida Atlantic University’s College of Business, it can.
Using a stylized dynamic aggregate demand-aggregate supply (AD-AS) model, researchers explored the consequences of traditional monetary tools – namely changes in the short-term interest rate – to the environment. Specifically, they looked at how monetary policy impacts CO2 emissions in the short and long run. The AD-AS model conveys several interlocking relationships between the four macroeconomic goals of growth, unemployment, inflation and a sustainable balance ...
Endometrial cancer, which makes up about 90% of uterine cancers, will be diagnosed in more than 65,000 people in the United States this year. It is the fourth most common cancer in women and is one of the few cancers that is increasing in incidence and mortality. Unfortunately, very few treatments have been developed specifically for endometrial cancer.
Now, new research published March 27, 2023, in The New England Journal of Medicine finds adding the immunotherapy drug pembrolizumab (Keytruda®) to standard chemotherapy greatly improves patient outcomes in both patients whose tumors have a genetic alteration leading ...
The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology submitted testimony to the U.S. House Appropriations Committee March 22 outlining its recommended budgets for major scientific funding agencies. Notably, the society requested a significant 10% increase in the budget for the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, which is part of the National Institutes of Health.
“The ASBMB has a longstanding history of advocating for NIGMS and its researchers, and the majority of our members are funded by and rely on NIGMS to advance their research,” Sarina Neote, public affairs director of the ASBMB, said. “The ...
WHAT:
Scientists have identified an autoinflammatory disease caused by mutations in the LYN gene, an important regulator of immune responses in health and disease. Named Lyn kinase-associated vasculopathy and liver fibrosis (LAVLI), the identification sheds light on how genes linked to certain illnesses can potentially be targets for treatment by repurposing existing drugs. The research, published in Nature Communications, was led by Adriana A. de Jesus, M.D. Ph.D., and Raphaela Goldbach-Mansky, M.D., M.H.S. of the Translational ...
The Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Kim Byung-suk) developed a smart sensor that detects signs of ground or structure collapses and a real-time remote monitoring system.
The development of the sensor and system began with a search for a method of instant sensing of the collapse of slopes or buildings caused by ground movement for immediate response. This led to the development of a smart sensor that turns on a LED warning light upon detecting ground movement. The ...
Replacement per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) heralded as safe for use in food packaging break down into toxic PFAS that leak into our food and environment, suggests a study published today in Environmental Science & Technology Letters.
Due to the known exposure risks of using smaller PFAS molecules like PFOA and PFOS in food-contact materials, many companies have pivoted to using larger polymeric PFAS to make their wrappers, bowls, and other fast-food packaging water- and grease-repellant. ...
Gaithersburg, MD—March 28, 2023 – Cartesian Therapeutics, a fully integrated biopharmaceutical company pioneering RNA cell therapy for autoimmune diseases and cancer, today announced the appointment of five internationally recognized experts in autoimmune diseases. Cartesian’s appointments include distinguished physicians and scientists as leaders in clinical trials and medicine.
“Cartesian is proud to have these prestigious, multidisciplinary advisors committed to treating other autoimmune diseases,” said Miloš Miljković, M.D., Chief Medical Officer at Cartesian Therapeutics. “Their perspectives will provide the utmost value ...
Researchers at the University of Toronto, Indiana University and University of Notre Dame have detected levels of toxic PFAS chemicals—short for per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances—for the first time in Canadian fast-food packaging, specifically water-and-grease repellent paper alternatives to plastic.
Published today in Environmental Science and Technology Letters, the findings suggest that food packaging exposes people directly to PFAS, which have been linked to serious health effects such as increased cancer risk and immune system damage, by contaminating the food they eat. Further, once discarded packaging enters waste streams, PFAS enter the environment, where these ...
HOUSTON – (March 28, 2023) – The road to a net-zero future must be paved with greener concrete, and Rice University scientists know how to make it.
The production of cement, an ingredient in concrete, accounts for roughly 8% of the world’s annual carbon dioxide emissions, making it a significant target of greenhouse gas emissions reduction goals. Toward those efforts, the Rice lab of chemist James Tour used flash Joule heating to remove toxic heavy metals from fly ash, a powdery ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — As new environmental regulations are rolling out to mitigate the industry-retired long-chain chemicals known as PFAS in drinking water, there are concerns regarding a new breed of “forever chemicals” called short-chain PFAS. Research from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign is helping shift the focus to include mitigation of the chemicals – which researchers say are just as persistent as, more mobile and harder to remove from the environment than their long-chain counterparts.
A ...