(Press-News.org) SAN FRANCISCO – The Public Library of Science (PLOS) is pleased to announce that PLOS Global Public Health and PLOS Digital Health are now fully indexed in PubMed Central (PMC), expanding our reach and furthering our mission of ensuring research content is accessible and discoverable as widely as possible.
Both journals have an explicit mandate to promote equity in research that can tackle the most urgent priorities for the field, such as access to healthcare, or addressing bias in AI and developing machine learning tools for underserved communities. PLOS is proud to feature perspectives from all over the world, and we make sure that research is peer reviewed by experts with significant, context-appropriate expertise.
“With over 1000 published articles, a diverse editorial board of over 600 editors, and now indexing in PubMed Central, PLOS Global Public Health is excited to continue our vision of enhancing diversity, equity and inclusion in global public health,” said Dr. Madhu Pai and Catherine Kyobutungi, Co-Editors-in-Chief of PLOS Global Public Health.
“Indexing in PubMed acknowledges the time and effort that our authors, reviewers, and editors have contributed to creating a community that values diversity in the research at the intersection of technology and healthcare,” said Dr. Leo Anthony Celi, Editor-in-Chief of PLOS Digital Health. “I’m excited to grow this village whose goal is to improve health equity through digital technologies."
Work published in PLOS Digital Health and PLOS Global Public Health will now be accessible to an even wider audience, meeting researchers where it is convenient for them to access knowledge. With the vast majority of article views coming from PMC or Google Scholar searches, it is imperative that research in both journals be highly visible on these platforms.
Critically, the inclusion of PLOS Digital Health and PLOS Global Public Health in PMC is an endorsement of the rigor and reliability of the work published within and is the principal reason that researchers prefer to browse research on the platform. Journals indexed in PMC have undergone both technical and scientific benchmarking checks, allowing researchers to trust the findings, methods, and datasets shared. Of particular importance to the mission of both journals, this means local perspectives and expertise reported in rigorously reviewed published research will receive the attention and visibility that it deserves.
For PLOS Global Public Health, PLOS hopes that this discoverability will help connect research and researchers from different parts of the world and will ultimately further our fundamental mission: to broaden the range and diversity of perspectives at the forefront of public health and advance the health of all humankind.
This news serves as an important milestone for a journal like PLOS Digital Health, which actively promotes code sharing and data accessibility as a means to further inclusive participation, trust and reproducibility within this growing field of research. Accessibility beyond the journal platform for a high-quality body of open research, as well as open research artifacts extends the reach, impact, and use of authors’ work. It’s a testament to the growing desire for researchers to share their work in a reputable Open Access title that encourages transparency.
#########
About the Public Library of Science
PLOS is a nonprofit, open access publisher empowering researchers to accelerate progress in science and medicine by leading a transformation in research communication. Since our founding in 2001, PLOS journals have helped break boundaries in research communication to provide more opportunities, choice, and context for researchers and readers. For more information, visit http://www.plos.org.
END
PLOS Global Public Health and PLOS Digital Health now indexed in PubMed Central
2023-03-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Some coastal salt marshes are keeping up with sea level rise — for now
2023-03-28
American Geophysical Union
Press Release 23-12
28 March 2023
For Immediate Release
This press release is available online at: https://news.agu.org/press-release/some-coastal-salt-marshes-are-keeping-up-with-sea-level-rise-for-now
Some coastal salt marshes are keeping up with sea level rise — for now
Salt marshes on the U.S. East Coast have accumulated soil more quickly over the past century, and some appear to be keeping pace with rising waters. But that won’t last forever.
AGU press contact:
Rebecca Dzombak, +1 (202) ...
Epigenetic fingerprint as proof of origin for chicken, shrimp and salmon
2023-03-28
Free-range organic chicken or factory farming? Scientists at the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) have developed a new detection method that can reveal such differences in husbandry. The so-called epigenetic method is based on the analysis of the characteristic patterns of chemical markers on the genome of the animals.
Was the salmon for dinner with friends really caught wild or did it come from aquaculture? What to make of the alleged "biolabel quality“ of the shrimp for the seafood salad? And was the chicken for the Sunday roast really allowed to spend its life in the open air?
Food analysis laboratories can only answer ...
Drugs against drought
2023-03-28
Abscisic acid (ABA) is a plant hormone with essential functions in plant physiology. It is involved in developmental and growth processes and the adaptive stress response. Thus, the plant adaptation to stress situations caused by water deficit can be favored by activating this phytohormone pathway. In this project, the teams led by Pedro Luis Rodríguez at the IBMCP in Valencia and Armando Albert at the IQRF in Madrid developed a genetic-chemical method to activate this route in an inducible way and without penalizing plant growth.
Based ...
Naloxone prescriptions increased at US hospitals between 2012 and 2019
2023-03-28
Rates of prescriptions for naloxone to people at high risk for opioid overdose, as well as co-prescribing with opioids, has increased in emergency departments throughout the United States over the past decade, providing insight on the positive impact of federal policies and regulations, according to a Rutgers study.
Federal opioid prescribing guidelines in 2016 made it easier for doctors to prescribe naloxone to patients at high risk for opioid overdose. When used properly, naloxone is highly effective at reversing or reducing the life-threatening adverse effects of ...
Review: Multiple ways to address telehealth barriers for stroke survivors
2023-03-28
While the outpatient management of stroke survivors through telehealth is prone to multiple barriers, it offers many advantages for addressing health equity in stroke survivors, according to a review from UTHealth Houston.
The review – written by Anjail Sharrief, MD, MPH, first author and associate professor of neurology with McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston – was published recently in Stroke.
Telehealth has seen rapid expansion into chronic care management over the past several years because of the COVID-19 pandemic, Sharrief said. However, there is limited ...
Preschoolers prefer to learn from a competent robot than an incompetent human, Concordia study shows
2023-03-28
Who do children prefer to learn from? Previous research has shown that even infants can identify the best informant. But would preschoolers prefer learning from a competent robot over an incompetent human?
According to a new paper by Concordia researchers published in the Journal of Cognition and Development, the answer largely depends on age.
The study compared two groups of preschoolers: one of three-year-olds, the other of five-year-olds. The children participated in Zoom meetings featuring a video of a young woman and a small robot with humanoid characteristics (head, ...
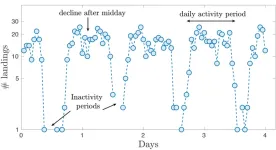
Prepare for landing: making airports more efficient
2023-03-28
WASHINGTON, March 28, 2023 – Air traffic is a significant and complex problem. Near misses between passenger planes on runways have been making headlines lately and raising safety concerns as airports try to accommodate more travelers in the wake of COVID-19. Also, as any disgruntled air traveler knows, a single aircraft’s late arrival at a busy airport can trigger an avalanche effect and cause a series of subsequent delays.
In Chaos, from AIP Publishing, a team of scientists from Spain and Argentina presented an original oscillating short-term memory model, with just two parameters, to study the dynamics of landing events at 10 ...
What should we call evolution driven by genetic engineering? Genetic welding, says researcher
2023-03-28
With CRISPR-Cas9 technology, humans can now rapidly change the evolutionary course of animals or plants by inserting genes that can easily spread through entire populations. Evolutionary geneticist Asher Cutter proposes that we call this evolutionary meddling “genetic welding.” In an opinion paper publishing March 28 in the journal Trends in Genetics, he argues that we must scientifically and ethically scrutinize the potential consequences of genetic welding before we put it into practice.
“The capability to do genetic welding has only taken off in the last few years, and much of the thinking about it has focused on what can happen ...
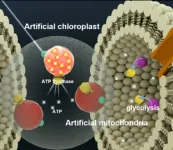
The powerhouse of the future: Artificial cells
2023-03-28
WASHINGTON, March 28, 2023 – Energy production in nature is the responsibility of chloroplasts and mitochondria and is crucial for fabricating sustainable, synthetic cells in the lab. Mitochondria are not only “the powerhouses of the cell,” as the middle school biology adage goes, but also one of the most complex intracellular components to replicate artificially.
In Biophysics Reviews, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Sogang University in South Korea and the Harbin Institute of Technology in China identified the most promising advancements and greatest challenges of artificial mitochondria ...
Pediatric mental health hospitalizations at acute care hospitals in the US
2023-03-28
About The Study: In this analysis of a national data set representing an estimated 4.7 million pediatric hospitalizations between 2009 and 2019, the number and proportion of pediatric acute care hospitalizations due to mental health diagnoses increased significantly. The majority of mental health hospitalizations in 2019 included a diagnosis of attempted suicide, suicidal ideation, or self-injury, underscoring the increasing importance of this concern.
Authors: Mary Arakelyan, M.P.H., of the Dartmouth Hitchcock Medical ...