(Press-News.org) Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0282024
Article Title: Pedestrian street behavior mapping using unmanned aerial vehicles. A case study in Santiago de Chile
Author Countries: Spain
Funding: OM has received funding from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation of the Government of Spain (RyC RYC2020-029441-I). This research was also funded by the Ministry of Science and Innovation of the Government of Spain [grant number PID2019-104344RB-I00].
END
Drones could be used reliably to map how and why pedestrians use city streets, according to a pilot study in Santiago de Chile
2023-03-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
We are not yet approaching any maximum human lifespan, according to an examination of human mortality over time and across 19 countries
2023-03-29
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281752
Article Title: Mortality postponement and compression at older ages in human cohorts
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Stereotypes about senior employees lead to premature retirements
2023-03-29
Unproductive, inflexible, and less motivated... these are some of the most common stereotypes about senior employees. Even though the stereotypes are usually unfounded, they nevertheless influence how senior employees perceive themselves and their status in the workplace. And they thus become a key factor in many senior employees’ retirement decisions, conclude University of Copenhagen researchers in a new study published in PLOS ONE.
“In our study, we refer to the uncertainty that senior employees feel about their status as ‘the worn-out syndrome’, which ...
Earth prefers to serve life in XXS and XXL sizes: UBC research
2023-03-29
Life comes in all shapes in sizes, but some sizes are more popular than others, new research from the University of British Columbia has found.
In the first study of its kind published today in PLOS ONE, Dr. Eden Tekwa, who conducted the study as a postdoctoral fellow at UBC’s department of zoology, surveyed the body sizes of all Earth’s living organisms, and uncovered an unexpected pattern. Contrary to what current theories can explain, our planet’s biomass—the material that makes up all living organisms—is ...
Nature favors all creatures great and small over medium size
2023-03-29
Life may come in all shapes and sizes, but in nature the most extreme size ranges predominate, according to Rutgers researchers.
A survey of body sizes of Earth organisms, published Wednesday, March 29, in the science journal PLoS ONE, shows that the planet’s biomass – the material that makes up all living organisms – is concentrated in organisms at either end of the size spectrum.
“This conclusion – that life on earth comes packaged predominantly in the largest and smallest sizes – was a discovery that surprised us,” said Malin Pinsky, an associate professor ...
Sox9 protein enables molecular time travel that can lead to colorectal cancer
2023-03-29
Study Title: Aberrant cell state plasticity mediated by developmental reprogramming precedes colorectal cancer initiation
Publication: Science Advances: March 29, 2023, 2:00pm ET 10.1126/sciadv.adf0927
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute author: Pratyusha Bala, PhD, Jonathan P. Rennhack, PhD, Daulet Aitymbayev, MS, Matthew B. Yurgelun, MD, William C. Hahn, MD, PhD, Nilay S. Sethi, MD, PhD
Summary:
Normally the lining of the colon forms a series of steep hills and valleys. At the surface, where the hills peak, are functional colon cells that do the organ’s work of absorption and secretion. Deep in the valleys are stem cells that constantly ...
Ancient African empires’ impact on migration revealed by genetics
2023-03-29
Traces of ancient empires that stretched across Africa remain in the DNA of people living on the continent, reveals a new genetics study led by UCL researchers.
Published in Science Advances, the collaboration between UCL geneticists working alongside anthropologists, archaeologists, historians and linguists in Africa and beyond found evidence for when different peoples intermixed across the continent. Their findings indicate migration linked to vast empires such as the Kanem-Bornu and the kingdoms of Aksum and Makuria, ...
Method for improving seasonal flu vaccines also aids pandemic prediction
2023-03-29
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – March 29, 2023) Improving the seasonal influenza vaccine and public health specialists’ ability to predict pandemic potential in new flu strains may be possible due to new findings from scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital. The key is the stability of a viral protein that gains entry into human cells. The findings were published today in Science Advances.
“We found that the protein flu viruses use to enter cells, hemagglutinin, needs to be relatively stable and resistant to acid in an effective H3N2 flu vaccine,” said senior and co-corresponding ...
Model for predicting transmission of COVID-19 can help policymakers monitor virus, inform health surveillance systems
2023-03-29
The COVID-19 pandemic presents unprecedented challenges to public health worldwide. Tracking the dynamics of the coronavirus permits governments, organizations, and individuals to make projections in an effort to curb the spread of the pandemic. But while a large amount of data about COVID is collected and publicly available, the information can be unreliable and subject to bias. In a new study, researchers analyzed data from Cali, Colombia, to develop a model that provides a template for tracking data, predicting transmission, and informing health surveillance systems.
The study was conducted by researchers at Carnegie Mellon ...
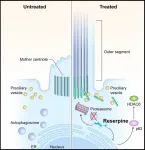
FDA-approved drug shows promise in lab models for blinding childhood disease
2023-03-29
A National Eye Institute-led team has identified a compound already approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration that keeps light-sensitive photoreceptors alive in three models of Leber congenital amaurosis type 10 (LCA 10), an inherited retinal ciliopathy disease that often results in severe visual impairment or blindness in early childhood.
LCA 10 is caused by mutations of the cilia-centrosomal gene (CEP290). Such mutations account for 20% to 25% of all LCA – more than any other gene.
Using a mouse model of LCA10 and two types of lab-created tissues from stem ...
OHIO diabetes researchers discover the potential of CIDEC protein to mitigate obesity-related cardiometabolic disease
2023-03-29
A team of researchers from Ohio University’s Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine recently discovered a novel role of human-CIDEC gene in improving metabolic dysfunction and cardiovascular health. The study, “Endothelial-Specific Expression of CIDEC Improves High-Fat Diet–Induced Vascular and Metabolic Dysfunction,” published in Diabetes focuses on vascular function and its association with metabolic diseases like insulin resistance, Type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
“This is a very impactful study, and we have moved in the right direction to find a way to reduce cardiovascular ...