Low concentration CO2 can be reused in biodegradable plastic precursor using artificial photosynthesis
2023-03-30
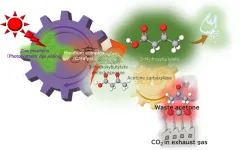
(Press-News.org) Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate—a biodegradable plastic—is a strong water-resistant polyester often used in packaging materials, made from 3-hydroxybutyrate as a precursor. In previous studies, a research team led by Professor Yutaka Amao from the Research Center for Artificial Photosynthesis at Osaka Metropolitan University, found that 3-hydroxybutyrate can be synthesized from CO2 and acetone with high efficiency, but only demonstrated this at higher concentrations of CO2 or sodium bicarbonate.
This new study aimed to reuse waste acetone from permanent marker ink and low concentrations of CO2—equivalent to exhaust gas from power plants, chemical plants, or steel factories. Acetone is a relatively inexpensive and reasonably harmless chemical used in many different laboratory settings, either for reactions or as a cleaning agent, which produces waste acetone. The acetone and CO2 acted as raw materials to synthesize 3-hydroxybutyrate using artificial photosynthesis, powered by light equivalent to sunlight.
“We focused our attention on the importance of using CO2 created by exhaust gas from thermal power plants and other sources to demonstrate the practical application of artificial photosynthesis,” explained Professor Amao.
After 24 hours, more than 60% of acetone had been successfully converted to 3-hydroxybutyrate. Their findings were published in Green Chemistry.
“In the future, we aim to develop artificial photosynthesis technology further, so that it can use acetone from liquid waste and as well as exhaust gas from the laboratory as raw materials,” stated Professor Amao.
###
About OMU
Osaka Metropolitan University is a new public university established by a merger between Osaka City University and Osaka Prefecture University in April 2022. For more science news, see https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/, and follow @OsakaMetUniv_en, or search #OMUScience.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-03-30
A novel drug is showing promise for alleviating heart failure, a common condition associated with sleep apnoea and a reduced lifespan.
The drug, known as AF-130, was tested in an animal model at Waipapa Taumata Rau, the University of Auckland where researchers found it improved the heart’s ability to pump, but, equally important, prevented sleep apnoea, which itself reduces lifespan (see Nature Communications). “This drug does offer benefit for heart failure, but it’s two for the price of one, in that it’s also relieving the apnoea for which ...
2023-03-30
Even for insects, wood is a tough food source as it contains hard substances such as cellulose. To help make wood more palatable, some wood-feeding insects are assisted by symbiotic microorganisms that break down the components of wood into an edible form. A group from Nagoya University in Japan has isolated a symbiotic yeast from adults, larvae, and eggs of the Japanese longicorn beetle and identified specialized organs that store the yeast, allowing the beetles to break down the unpalatable components of wood. Their findings were published in PLOS ONE.
“I have been fascinated with longicorn beetles ...
2023-03-30
Urban honeybees could be used to gain insight into the microbiome of the cities in which they forage, which can potentially provide information on both hive and human health, reports a study published in Environmental Microbiome.
Cities are built for human habitation but are also spaces that host a wide range of living species, and understanding this diverse landscape is important for urban planning and human health. However, sampling the microbial landscape in a manner to cover wide areas of a city can be labour-intensive.
Elizabeth ...
2023-03-30
The standard cosmology can answer almost nothing about how the structure of a galaxy is formed. It expects a supermassive black hole at the center and dark matter in the halo to explain the circulation of stars and its velocity. However, why the visible matters are distributed in such a thin plane by the interaction with the black hole while dark matter results in a spherical distribution is a critical open question for a disc galaxy. The formation process of elliptical, ring, and long–barred galaxies also remains unknown.
The Energy Circulation ...
2023-03-30
A collaboration of Australian and European physicists predict that layered electronic 2D semiconductors can host a curious quantum phase of matter called the supersolid.
The supersolid is a very counterintuitive phase indeed. It is made up of particles that simultaneously form a rigid crystal and yet at the same time flow without friction since all the particles belong to the same single quantum state.
A solid becomes ‘super’ when its quantum properties match the well-known quantum properties of superconductors. A supersolid simultaneously has two orders, solid and super:
solid because of the spatially repeating pattern ...
2023-03-30
Throughout her career, Arizona State University Edson College of Nursing and Health Innovation Associate Professor Kelly Davis has worked to translate her research into action. An expert in alcohol-involved sexual assault, Davis’ studies have been cited in U.S. legislation and have earned her a MERIT Award and now the prestigious Fulbright Scholar Award.
The program will take her to the United Kingdom beginning in early 2024 to collaborate with colleagues at the University ...
2023-03-30
The Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST), in collaboration with Astellas Pharma Inc., has developed a new toolkit that uses small molecules to control the activity of a piece of synthetic RNA, and ultimately regulate gene expression. The technology, which was described in the Journal of the American Chemical Society on March 30, 2023, worked in mammalian cell cultures and in mice.
The ability to precisely control whether a gene is turned on or off is expected to lead to more efficient production of compounds that are made using animal cells, and make gene therapy, cell therapy, and regenerative medicine safer.
For genes to be expressed, cells make many RNA copies of a section ...
2023-03-30
It has been a longstanding assumption that birth mode and associated exposure of newborns to their mothers’ vaginal microbiome during delivery greatly affects the development of babies’ gut microbiome.
To test the scientific validity of this assumption, a team of Canadian researchers has now published a study in Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology in which they examined the effect of maternal vaginal microbiome composition on the development of infants’ stool microbiome at 10 days and three months after birth.
“We show that ...
2023-03-30
The Gairdner Foundation is pleased to announce the 2023 Canada Gairdner Award laureates, recognizing some of the world’s most significant biomedical and global health research and discoveries.
“Congratulations to all the 2023 Canada Gairdner Award recipients! The ground-breaking work of this year’s laureates has resulted in innovative, globally accessible tools to fight diseases and improve our well-being. The work of two Canadian researchers – Dr. Christopher Mushquash and Dr. Gelareh Zadeh especially ...
2023-03-30
Researchers use tiny diamonds to create intracellular sensors
Optically trapped nanodiamonds could be used to measure temperature, magnetic fields and other properties inside living cells
VANCOUVER -- Researchers have developed a new way to study the intricate dynamics within living cells by using optically trapped nanodiamond particles as intracellular sensors. Using custom built optical tweezers, the research team trapped the particles within the cell at low power while the cell was alive. The work represents an important advancement in quantum sensing, which takes advantage of quantum mechanics to analyze changes at the atomic level.
The researchers used optical tweezers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Low concentration CO2 can be reused in biodegradable plastic precursor using artificial photosynthesis