Visible light-induced superoxides production by bacteria accelerates manganese oxidation in the environment
2023-03-31
(Press-News.org)
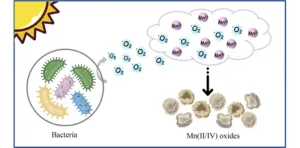
Manganese oxides are natural reactive minerals and widely spread in aquatic and terrestrial environments, affecting the fate of metals (such as As3+ and Cd2+) and organic pollutants (such as phenols and diclofenac) through adsorption and oxidation in sewage treatment. Usually, the manganese (III/IV) oxides in the environment are thought to be formed by the oxidation of dissolved Mn(II) through abiotic or biotic processes. Oxidation of aqueous Mn(II) by dissolved oxygen is thermodynamically favored, but the kinetic is slow due to the high energy barrier of the reaction from dissolved Mn(II) to Mn(III/IV) oxides. The presence of microorganisms accelerates the oxidation rate, which is 4–5 orders of magnitude faster than the rate of abiotic chemical oxidation, therefore is considered as the initial source of manganese oxides in the environment.
Bacteria capable of catalyzing the oxidation of dissolved Mn(II) ions to undissolved Mn(III/IV) oxides are usually called manganese-oxidizing bacteria. The bacterial oxidation of Mn(II) ions are divided into direct and indirect ways, and the process catalyzed by enzymes on the surface of microorganisms is called direct oxidation. For indirect pathways, some bacteria can change their surrounding environmental conditions for Mn(II) oxidation (e.g., the pH and Eh). Roseobacter clade has been demonstrated to oxidize Mn(II) by producing extracellular reactive oxygen species in recent studies. Do other bacteria clades have similar Mn(II) oxidation processes with Roseobacter? Is the Mn(II) oxidation closely relative to the physiological process of bacteria?
To answer these questions, Prof. Feng Zhao from Chinese Academy of Sciences and his team members explored the microbial manganese oxidation process under visible light by using coastal surface seawater microorganisms. The relationship between the transformation of soluble Mn(II) into insoluble Mn(III/IV) oxides by microorganisms and physiological role was analyzed. This study entitled“Visible light induces bacteria to produce superoxide for manganese oxidation”is published online in Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering in 2023.
In this study, the research team found visible light greatly promotes the oxidation rate of Mn(II), and the average rate reaches 64 μmol/(L·d). The generated manganese oxides were then conducive to Mn(II) oxidation, thus the rapid manganese oxidation was the result of the combined action of biotic and abiotic, and biological function accounts for 88 % ± 4 %. Extracellular superoxide produced by microorganisms induced by visible light is the decisive factor for the rapid manganese oxidation in our study. But the production of these superoxides does not require the presence of Mn(II) ions, the Mn(II) oxidation process was more like an unintentional side reaction, which did not affect the growth of microorganisms. More than 70 % of heterotrophic microorganisms in nature are capable of producing superoxide, based on the oxidizing properties of free radicals, all these bacteria can participate in the geochemical cycle of manganese. What’s more, the superoxide oxidation pathway might be a significant natural source of manganese oxide.
This study revealed an essential pathway for bacterial manganese oxidation. Heterotrophic bacteria produce superoxide under visible light irradiation and oxidize Mn(II) ions in the surrounding environment, which is the main source of manganese oxides. The biogenerated Mn(III/IV) oxides can also oxidize Mn(II) ions indirectly through abiotic reactions under light illumination. Many bacteria in the environment that produce superoxide actively or passively may also oxidize Mn(II) in this way, suggesting that the manganese oxidation pathway through superoxide is a common behavior in the environment. In light of the oxidation properties and semiconductor properties of manganese oxides, this research will provide new ideas for the treatment of environmental pollution.
###
About Higher Education Press
Founded in May 1954, Higher Education Press Limited Company (HEP), affiliated with the Ministry of Education, is one of the earliest institutions committed to educational publishing after the establishment of P. R. China in 1949. After striving for six decades, HEP has developed into a major comprehensive publisher, with products in various forms and at different levels. Both for import and export, HEP has been striving to fill in the gap of domestic and foreign markets and meet the demand of global customers by collaborating with more than 200 partners throughout the world and selling products and services in 32 languages globally. Now, HEP ranks among China’s top publishers in terms of copyright export volume and the world’s top 50 largest publishing enterprises in terms of comprehensive strength.
The Frontiers Journals series published by HEP includes 28 English academic journals, covering the largest academic fields in China at present. Among the series, 13 have been indexed by SCI, 6 by EI, 2 by MEDLINE, 1 by A&HCI. HEP’s academic monographs have won about 300 different kinds of publishing funds and awards both at home and abroad.
About Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering
Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering (FESE) is the leading edge forum for peer-reviewed original submissions in English on all main branches of environmental disciplines. FESE welcomes original research papers, review articles, short communications, and views & comments. All the papers will be published within 6 months since they are submitted. The Editors-in-Chief are Prof. Jiuhui Qu from Tsinghua University, and Prof. John C. Crittenden from Georgia Institute of Technology, USA. The journal has been indexed by almost all the authoritative databases such as SCI, Ei, INSPEC, SCOPUS, CSCD, etc.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-03-31
End-of-dry-season CO2 pulses recur each year in the atmosphere above the Australian continent, a discovery made by an international research team led by environmental physicist Prof. Dr André Butz of Heidelberg University. To investigate the carbon fluxes over Australia, the researchers studied atmospheric CO2 measurements. Their analyses show that CO2 emissions spike when heavy rain falls on dried-out soil, thus activating microorganisms in that soil. The findings suggest that dry regions have a greater influence on the variations in the global carbon cycle than previously thought.
The Australian continent is dominated by dry ecosystems and widely varying precipitation patterns. ...
2023-03-31
Ants are pretty much everywhere. There are more than 14,000 different species, spread over every continent except Antarctica, and researchers have estimated that there are more than four quadrillion individual ants on Earth-- that’s 4,000,000,000,000,000. But how ants evolved to take over the world is still a mystery. In a new study in the journal Evolution Letters, scientists used a combination of fossils, DNA, and data on the habitat preferences of modern species to piece together how ants and ...
2023-03-31
Now, Professor Niu serves as deputy director of the National Engineering Research Center of Tree Breeding and Ecological Restoration, deputy secretary general and standing member of the Pine Branch of the Chinese Society of forestry. He was selected as the national young top-notch talent of “Ten Thousand Talents Program”, leading talent of forest and grassland and technology innovation of the National Forestry and Grassland Administration (NFGA), outstanding young scholarship of “Beilin Scholars Program” of Beijing Forestry University, etc. He also served as an evaluation committee member ...
2023-03-31
Burnout is associated with adverse outcomes including medical errors and lower quality of care. While many studies have focused on physician or nurse burnout, the COVID-19 pandemic increased stress across the healthcare workforce, including support staff and healthcare teams who have a crucial role in patient care. A new study of 206 healthcare organizations led by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, identified high levels of burnout, intent to leave the profession, and work overload across all members of the healthcare ...
2023-03-31
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Researchers at Oregon State University have created a means of speeding up and improving the evaluation process for drugs used to combat cervical cancer.
The study led by Kaitlin Fogg, assistant professor of biological engineering in the OSU College of Engineering, is important because the American Cancer Society estimates that nearly 14,000 new cervical cancer cases will be diagnosed in the United States this year and that more than 4,000 women will die from the disease.
Findings were published in the Journal of Biomedical Materials Research.
Fogg and graduate students in the College of Engineering ...
2023-03-31
The kidney plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis within the body by eliminating toxic and superfluous substances in the bloodstream, including waste generated during metabolic processes, through urine. Nevertheless, toxicity can also be induced in the kidney from certain medications. Recently, a research team from POSTECH has engineered an artificial kidney that allows for the early detection of adverse drug reactions.
The POSTECH research team led by Professor Dong-Woo Cho and Professor Jinah Jang (Department ...
2023-03-31
Overview
A research team, led by Professor Yuji Nakamura of the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Toyohashi University of Technology, discovered that the flickering of flames can be freely controlled by moving two flames closer together or further apart. Until now, it had been known that interference between flames separated by a certain distance causes the flames to flicker during in-phase or anti-phase. However, it was not possible to stably express the state of “stopping the flickering of flames” that should occur under critical ...
2023-03-31
□ DGIST Professor Yoonkyu Lee’s research team illuminated intense light on the surface of a copper wire to synthesize graphene, thereby increasing the production rate and lowering the production cost of the high-quality transparent-flexible electrode materials and consequently enabling its mass production. This technology is applicable to various 2D materials[1], and its applicability can be extended to the synthesis of various metal-2D material nanowires.
□ The research team used copper-graphene nanowires to implement high-performance transparent-flexible ...
2023-03-31
□ On February 16 (Thursday), the DGIST held a graduation ceremony for the first half of 2023, that is, those who graduated in February, at the Convention Hall in the Office of the University. A total of 242 students—29 doctoral, 87 master’s, and 126 bachelor’s students—received academic degrees in science and technology fields.
□ Jongho Lee (Minister of Science and ICT), Junghye Noh (the board chairman of DGIST and an honorary professor at SNU), Jonghan Kim (the administrative mayor of Daegu Metropolitan City), ...
2023-03-31
□ The research team led by Professor Minseok Kim from the Department of New Biology at DGIST (President Yang Kuk) has developed a technology that can treat Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease, an incurable hereditary disease, with electric stimulation instead of drug therapy. The core of this technology is electric stimulation that restores the abnormal distribution of peripheral myelin protein 22 (PMP 22)[1], the cause of the disease, to normal. The research team discovered it by conducting a series of electric stimulation experiments using a CMT disease subtype ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Visible light-induced superoxides production by bacteria accelerates manganese oxidation in the environment








