Efficient nanostructuring of glass with elliptically polarized pulses
2023-04-04
(Press-News.org)
The photoexcitation, and especially photoionization, is one of the most important manifestations of the light-matter interaction in nature, ranging from photosynthesis in plants and vision in biology to photography and laser processing of materials. It is generally accepted that the change in a substance is weaker, the less light is absorbed. Here we found that this is not always the case.
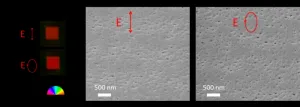
In a new paper published in Light Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by Professor Peter G. Kazansky from Optoelectronics Research Centre, University of Southampton, United Kingdom and co-workers have demonstrated efficient ultrafast laser nanostructuring with elliptical polarization in silica glass. Contrary to intuition, despite the nonlinear absorption being about 2.5 times weaker, elliptically polarized pulses result in about twice the birefringence of linearly polarized light. Anisotropic nanopores with a larger concentration are observed with elliptically polarized pulses. The phenomenon is interpreted in terms of enhanced interaction of circularly polarized light with a network of randomly oriented bonds and hole polarons in silica glass, as well as efficient tunnelling ionization of defects with low excitation potentials by circular polarization.
“It is commonly believed that the multiphoton ionization dominates in ultrafast laser writing in transparent materials, but we revealed that tunneling excitation of laser induced defects, such as self-trapped holes, is a key for nanostructruing in silica glass” the scientists added.
“In 5D optical data storage, information can be recorded by elliptically polarized pulses with lower energy and higher writing speed. Moreover, our demonstration allows production of large area geometric phase optical elements and vector beam converters with ultrahigh transmittance for high power and UV lasers.” they forecast.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-04-04
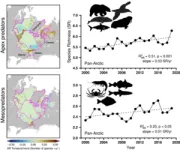
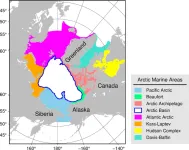
Marine predators have expanded their ranges into the Arctic waters over the last twenty years, driven by climate change and associated increases in productivity.
The seas surrounding the Arctic are important fisheries and ecological regions; they are also among the areas most affected by climate change. The effects of warming waters and loss of sea ice on the biodiversity of these waters, and hence their ecology, is still not fully understood.
An international team of researchers led by Dr. Irene D. Alabia at the Arctic Research Center at Hokkaido University has examined Arctic-wide ...
2023-04-04
Gas emissions are the manifestation of activity occurring beneath the surface of a volcano. Measuring them lets researchers see what can’t be seen from the surface. This knowledge is vital for hazard monitoring and the prediction of future eruptions. Since the mid-2000s, ultraviolet SO2 cameras have become important tools to measure emissions. The measurement campaigns, however, must be accompanied by a user, making SO2 cameras unsuitable for acquiring long-term datasets. Building and operating this type of camera can cost upwards ...
2023-04-04
Personality has become a more important factor than finances when it comes to dating, a new study has found.
Researchers from the University of York and the University of Essex analysed more than a million lonely hearts ads and found that in the USA, France, and Canada, there was a sharp decline in economic factors when choosing a partner. However, finances remained an important issue in India when it came to relationships.
To see how partner preferences changed over time, the researchers analysed lonely hearts ads from various major news outlets from Canada, France, and India. They collected data from publications from 1950 to 1995, the year that most of these ads shifted to being online. ...
2023-04-04
Today (4 April) the British Ecological Society has published the results of a three-year randomised trial comparing double and single-anonymous peer review in the journal Functional Ecology. The findings indicate a reduction in reviewer bias when author identities are anonymised.
The three-year randomised trial in the journal Functional Ecology, provides the most compressive data yet on the effects of anonymising authors during scholarly journal peer review.
Double-anonymous peer review, also referred to as double-blind peer review, is where author identities are not disclosed to reviewers. This differs from single-anonymous peer review where reviewers know ...
2023-04-04
The health and environmental harms of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are well-known, but a new peer-reviewed study calls into question their touted stain-fighting benefits. The study, published today in the AATCC Journal of Research, tested the performance of PFAS finishings on furniture fabrics and found that they had limited to no effectiveness, particularly under real-world conditions.
“It was surprising that these harmful but supposedly indispensable chemicals had no practical benefit,” said lead author Jonas LaPier, a PhD ...
2023-04-04
Scientists have called for a coordinated international effort to fully assess the environmental impacts of tritium ahead of a significant expected rise in its global production.
A radioactive isotope of hydrogen, tritium is a by-product of the nuclear industry and its presence is predicted to grow exponentially with nuclear increasingly seen as being key to the global low carbon economy.
That will result in many nations having to develop long-term strategies to manage tritiated radioactive waste and develop tools to both assess and address its environmental impact.
However, writing in the journal Science of the Total Environment, ...
2023-04-03
A revolutionary investigation that shed vivid light on pioneering female migrants who made their way to Orkney during the Bronze Age has won Research Project of the Year at the prestigious Current Archaeology Awards for 2023.
The project – a collaboration between EASE Archaeology and the University of Huddersfield – focused on human remains excavated at the Links of Noltland, a Bronze Age cemetery on the island of Westray. This work revealed the first concrete evidence of a major influx of non-local people into Orkney during the Bronze Age – and, significantly, it appears that this migration ...
2023-04-03
Roboticists have been using a technique similar to the ancient art of paper folding to develop autonomous machines out of thin, flexible sheets. These lightweight robots are simpler and cheaper to make and more compact for easier storage and transport.
However, the rigid computer chips traditionally needed to enable advanced robot capabilities — sensing, analyzing and responding to the environment — add extra weight to the thin sheet materials and makes them harder to fold. The semiconductor-based components therefore have to be added ...
2023-04-03
FRANKFURT. In millions of years and with a long sequence of small changes, evolution has shaped a particular group of dinosaurs, the theropods, into the birds we watch fly around the planet today. In fact, birds are the only descendants of dinosaurs which survived the catastrophic extinction 66 million years ago that ended the Cretaceous period.
Troodon was such a theropod. The carnivorous dinosaur was about two meters long and populated the vast semi-arid landscapes of North America about 75 million years ago. Like some of its dinosaur relatives, Troodon presented some bird-like ...
2023-04-03
ITHACA, N.Y. - At an academic conference some years ago, Michèle Belot remembers talking with a participant who was convinced she had authored a research paper that wasn’t hers. He’d confused her with another female scholar, an experience she said is familiar to many colleagues.
Such incidents – plus awareness of her own imperfect memory – inspired Belot, a professor in the Department of Economics at Cornell University, to investigate systemic biases in the way we remember people, since this could influence social networks important to career advancement.
In new research focused on academia, Belot ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Efficient nanostructuring of glass with elliptically polarized pulses