Archaeology: Evidence of drug use during Bronze Age ceremonies
2023-04-06
(Press-News.org)
An analysis of strands of human hair from a burial site in Menorca, Spain, indicates that ancient human civilisations used hallucinogenic drugs derived from plants, reports a new paper published in Scientific Reports. These findings are the first direct evidence of ancient drug use in Europe, which may have been used as part of ritualistic ceremonies.
Previous evidence of prehistoric drug use in Europe has been based on indirect evidence such as the detection of opium alkaloids in Bronze Age containers, the finding of remains of drug plants in ritualistic contexts, and the appearance of drug plants in artistic depictions.
Elisa Guerra-Doce and colleagues examined strands of hair from the Es Càrritx cave in Menorca, which was first occupied around 3,600 years ago, and contained a chamber used as a funeral space until around 2,800 years ago. Previous research suggests that around 210 individuals were interred in this chamber. However, strands of hair from only certain individuals were dyed red, placed in wooden and horn containers decorated with concentric circles, and removed to a separate sealed chamber further back in the cave. These hair strands date to approximately 3,000 years ago.
The authors used Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography and High Resolution Mass Spectroscopy to test for the presence of the alkaloids atropine, scopolamine, and ephedrine. Atropine and scopolamine are naturally found in the nightshade plant family, and can induce delirium, hallucinations, and altered sensory perception. Ephedrine is a stimulant derived from certain species of shrubs and pines, which can increase excitement, alertness, and physical activity. The authors detected scopolamine, ephedrine and atropine in three replicated hair samples.
The authors suggest that the presence of these alkaloids may have been due to consumption of some nightshade plants, such as mandrake (Mandragora autumnalis), henbane (Hyoscyamus albus) or thorn apple (Datura stramonium), and joint pine (Ephedra fragilis). The authors suggest that these drug plants may have been used as part of ritual ceremonies performed by a shaman. The concentric circles on the wooden containers may have depicted eyes and could have been a metaphor for inner vision related to a drug-induced altered state of consciousness. Due to cultural changes around 2,800 years ago, the authors speculate that the wooden containers were sealed in the cave chamber in order to preserve these ancient traditions.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-04-06
Analysing changes to DNA in the blood can improve the ability to predict a person’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes within a decade.
Scientists looked at the influence of these changes – known as DNA methylation – alongside other risk factors in almost 15,000 people to predict the likelihood of developing the condition years in advance of any symptoms developing.
The findings could lead to preventative measures being put in place earlier, reducing the economic and health burden caused by type 2 diabetes.
Methylation is a chemical process in the body in which a small molecule called a methyl group is added to DNA.
Current ...
2023-04-06
JOHANNESBURG, SOUTH AFRICA and SHENZHEN, CHINA - 31.03.23
Akili Labs (Pty) Ltd, a pioneer of cost-effective molecular diagnostics and secure genomic data storage solutions, and BGI Genomics Co. Ltd, the world’s leading integrated solutions provider of precision medicine, today announced the signing of a technology transfer agreement that will provide the Southern region of Africa with clinical-grade sequencing solutions.
"Improving the cost and turnaround time of genetic sequencing services will play a major role in the expansion of precision medicine-driven healthcare in Africa," said Charles F.J. Faul, co-founder ...
2023-04-06
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a new way to create dynamic ultrahigh-density 3D holographic projections. By packing more details into a 3D image, this type of hologram could enable realistic representations of the world around us for use in virtual reality and other applications.
“A 3D hologram can present real 3D scenes with continuous and fine features,” said Lei Gong, who led a research team from the University of Science and Technology of China. “For virtual reality, our method could be used with headset-based holographic displays to greatly improve the viewing angles, which would enhance the 3D viewing experience. ...
2023-04-06
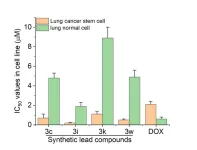
A research team co-led by chemists from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) recently discovered novel, highly effective anticancer agents with tridimensional structures, which have high anticancer activity, low toxicity and the ability to overcome drug resistance in cancer cells. The findings help provide a new direction for anticancer drug development.
Cancer has long been a devastating disease, which affects millions of people worldwide. Despite advances in treatment, current anticancer drugs often have limited effectiveness, lack of cancer ...
2023-04-06
The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology sent recommendations March 30 to the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases on expanding the institute’s diversity, equity, accessibility and inclusivity activities.
The society recommended, broadly, that the NIAID expand the use of diversity and re-entry grant supplements and better support disabled, LGBTQ+ and other underrepresented scientists.
“Because NIAID is one of the largest NIH institutes, they have ...
2023-04-06
Imagine you want to withdraw some cash from an ATM. You expect it to show your account balance correctly and process your request quickly. However, network delays make it hard for the system to meet both of these simple expectations at the same time. If an ATM system tries to achieve high “consistency,” meaning that it displays the latest account balance by checking a remote database, it could make you wait or even prevent you from accessing your accounts during busy times. On the other hand, if an ATM system favors “availability,” it could let you access your accounts fast, but risk showing inaccurate information. To avoid undesired results, ...
2023-04-06
The Science family journals have announced a partnership with the nonprofit data repository Dryad that simplifies the process by which authors deposit data underlying new work – a critical step to facilitating data’s routine reuse. The partnership is yet another step taken by the Science journals to ensure data the scientific community requires to verify, replicate and reanalyze new research is openly available.
“Addressing public access to data at scale is a critical challenge,” said Holden Thorp, Editor-in-Chief of the Science family ...
2023-04-06
A new study from UCLA researchers finds sex-specific brain signals that appear to confirm that different drivers lead men and women to develop obesity. The study, appearing in the peer-reviewed journal Brain Communications, combined data from several modes of MRI with patients’ clinical features and personal histories to identify sex-specific mechanisms in the brain underlying obesity.
“We found differences in several of the brain’s networks associated with early life adversity, mental ...
2023-04-06
Some adults with severe respiratory illness, including women, those with public insurance, and people with fewer financial resources, may be less likely to receive an advanced form of life support known as extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). A research team supported by the National Institutes of Health found that adults who received ECMO appeared to skew toward men, people with private health insurance, and those who came from areas with higher median incomes. ECMO helps patients with life-threatening illness or injury breathe by simulating the function of the heart and/or lungs, while giving those organs a chance to rest.
The study published in the Annals of the American ...
2023-04-06
The number of immune cells in and around kidney tumors, the amount of dead cancer tissue, and mutations to a tumor suppressor gene called PBRM1 form a biomarker signature that can predict — before treatment begins — how well patients with kidney cancer will respond to immunotherapy, according to new research directed by investigators at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and its Bloomberg~Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy.
In reviews of 136 kidney tumor biopsies taken for previous studies, investigators found that patients who had three positive factors — presence of immune cells in and around tumors, known as tumor-infiltrating immune cells, absence ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Archaeology: Evidence of drug use during Bronze Age ceremonies