(Press-News.org) INDIANAPOLIS—For centuries, people have suspected a full moon in the sky to cause mysterious changes in people. Now, psychiatrists at Indiana University School of Medicine have found deaths by suicide increase during the full moon.
“We wanted to analyze the hypothesis that suicides are increased during the period around full moons and determine if high-risk patients should be followed more closely during those times,” said Alexander Niculescu, MD, PhD.
Niculescu and his team looked at data from the Marion County coroner’s office in Indiana about suicides that took place from 2012-2016. They found deaths by suicide significantly increased during the week of the full moon, with people over age 55 showing an even higher increase. They also looked at the time of day and months that suicides took place, finding 3 to- 4 p.m. and the month of September to be peak times for suicides.
The team recently published their findings in Discover Mental Health.
“From a clinical perspective and a public health perspective, we found some important take-home messages in this study,” Niculescu said. “High-risk patients should possibly be followed more closely the week of the full moon, during late afternoons and perhaps the month of September.”
Niculescu and his team previously developed blood biomarker tests for other mental health conditions (anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder) and for pain. Using blood samples previously taken by the coroner from some of the people, the team was able to see which biomarkers were present.
“We tested a list of top blood biomarkers for suicidality that we identified in previous studies,” Niculescu said. “The biomarkers for suicidality that are predictive of death by suicide during full moon, peak hour of day and peak month of the year compared to outside of those periods appear to be genes that regulate the body’s own internal clock, so called ‘circadian clock’. Using the biomarkers, we also found people with alcohol-use disorder or depression may be at higher risk during these time periods.”
Niculescu said the increased light from the full moon could be what leads to the increase in suicides during that period. Ambient light plays a major role on the body’s circadian rhythm, which is the natural 24-hour cycle our bodies follow to regulate when we are asleep and when we are awake. Moonlight could be impacting people at a time when it should be darker.
“The effect of ambient light and body clocks in suicide needs to be studied more closely, along with how people sleep and their exposure to light,” Niculescu said. “Changes in light can affect vulnerable people, in conjunction with other risk factors.”
As for the other two peak periods for suicides, Niculescu said the peak of suicides from 3 to 4 p.m. could be related to stressors throughout the day as well as a decrease in light beginning to occur that day, causing a lower expression of circadian clock genes and cortisol. And in September, many people are experiencing the end of summer vacations, which could cause stress, as well as seasonal affective disorder effects, as daylight decreases during that time of year.
“Our work shows the full moon, fall season and late afternoon are temporal windows of increased risk for suicide, particularly in individuals who suffer from depression or alcohol use disorders,” Niculescu said. In the future, Niculescu hopes to study if exposure to screens at night contributes to increased suicidality in people, especially younger people. “Some people have a full moon in their hand every night,” Niculescu said. “It’s an area we absolutely need to study further.”
About IU School of Medicine
IU School of Medicine is the largest medical school in the U.S. and is annually ranked among the top medical schools in the nation by U.S. News & World Report. The school offers high-quality medical education, access to leading medical research and rich campus life in nine Indiana cities, including rural and urban locations consistently recognized for livability.
END
Deaths by suicide increase significantly during the week of a full moon
2023-04-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How to make electronic noses smell better
2023-04-07
Imagine if you could ask a machine to “smell” something for you with just a click of a button. That’s what electronic noses, or e-noses, are for. They are systems that combine chemical gas sensors, signal processing and machine learning algorithms to mimic the sense of smell. E-noses can be used for many purposes, such as checking food quality, monitoring air pollution, diagnosing diseases and detecting explosives. How do they work? What are the challenges and opportunities in this field? A team led by Jingdong Chen of Northwestern Polytechnical University in Xi’an, China and ...
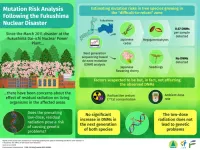
Study assesses risk of mutation due to residual radiation from the Fukushima nuclear disaster
2023-04-07
Ionizing radiation from nuclear disasters are known to be harmful to the natural environment. The Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant meltdown that occurred in 2011 is a prominent example of such a disaster in recent memory. Even a decade after the incident, concerns remain about the long-term effects of the radiation. In particular, it is not clear how the residual low-dose radiation might affect living organisms at the genetic level.
The brunt of the disaster is usually borne by the floras inhabiting the contaminated areas since they cannot move. This, however, makes them ideal for ...
Simple but revolutionary modular organoids
2023-04-07
A team led by Masaya Hagiwara of RIKEN national science institute in Japan has developed an ingenious device, using layers of hydrogels in a cube-like structure, that allows researchers to construct complex 3D organoids without using elaborate techniques. The group also recently demonstrated the ability to use the device to build organoids that faithfully reproduce the asymmetric genetic expression that characterizes the actual development of organisms. The device has the potential to revolutionize the way we test drugs, and could also provide insights into how tissues develop and lead to ...
New book explores possibilities of colonizing planets, moons and beyond
2023-04-07
Dan Răzvan Popoviciu new book New Worlds: Colonizing Planets, Moons and Beyond (published by Bentham Science) explores the possibilities of transforming humanity into a multi-planetary species, while also sounding an alarm about our long-term future. It emphasizes the importance of efficiently using Earth's resources and expanding beyond the planet's borders.
In the book, Popoviciu discusses how various planets, moons, and asteroids in the Solar System can provide important resources and become potential new home worlds for humans. The author goes beyond simple colonization and discusses solutions for terraforming ...
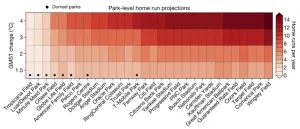
Spike in major league home runs tied to climate change
2023-04-07
In the history of Major League Baseball, first came the low-scoring dead-ball era, followed by the modern live-ball era characterized by power hitters such as Babe Ruth and Henry "Hank" Aaron. Then, regrettably, was the steroid era of the 1990s and early 2000s.
Now, could baseball be on the cusp of a "climate-ball" era where higher temperatures due to global warming increasingly determine the outcome of a game?
A new Dartmouth College study suggests it may be. A report in the Bulletin of the ...
Disease history doubles rate of colorectal cancer screening for family members | BGI Insight
2023-04-07
To uncover attitudes and the biggest challenges facing colorectal cancer (CRC) awareness and screening, BGI Genomics today released its State of Colorectal Cancer Awareness Report, marking the first-ever global survey report on the world's third most common cancer. This report is released on World Health Day, April 07, 2023, in line with achieving Health For All, and seeks to motivate action to tackle the health challenges of today and tomorrow.
This ...
Cedars-Sinai heart experts elected to lead, join prominent medical societies
2023-04-07
Two Smidt Heart Institute experts have been honored for their contributions to medical research by being inducted into select medical societies, while a third expert has been selected for a leadership position.
Cardiologist, echocardiographer and clinician-scientist Susan Cheng, MD, director of Cardiovascular Population Sciences in the Smidt Heart Institute and the Erika J. Glazer Chair in Women’s Cardiovascular Health and Population Science, has been elected to the American Society for Clinical Investigation (ASCI) Council. ASCI is regarded as the most prestigious ...
Internet access must become human right or we risk ever-widening inequality
2023-04-07
People around the globe are so dependent on the internet to exercise socio-economic human rights such as education, healthcare, work, and housing that online access must now be considered a basic human right, a new study reveals.
Particularly in developing countries, internet access can make the difference between people receiving an education, staying healthy, finding a home, and securing employment – or not.
Even if people have offline opportunities, such as accessing social security schemes or finding housing, they are at a comparative ...
Scientists use peroxide to peer into metal oxide reactions
2023-04-07
UPTON, NY— Researchers at Binghamton University led research partnering with the Center for Functional Nanomaterials (CFN)—a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science User Facility at Brookhaven National Laboratory—to get a better look at how peroxides on the surface of copper oxide promote the oxidation of hydrogen but inhibit the oxidation of carbon monoxide, allowing them to steer oxidation reactions. They were able to observe these quick changes with two complimentary spectroscopy ...
Biodiversity auditing key to success of new conservation plans
2023-04-07
New research led by the University of East Anglia (UEA) suggests a way to greatly improve the outcomes of biodiversity conservation efforts globally.
Scientists from UEA, the RSPB and Natural England, propose that biodiversity auditing should be integral to the ongoing development of regionally-targeted conservation plans, such as the Local Nature Recovery Strategies (LNRS) established by the UK Environment Act 2021.
It follows work conducted with two conservation projects in the East of England - one in North Norfolk and another in the Brecks - using this approach to guide conservation locally.
A biodiversity ...