(Press-News.org) Breast cancer is the most common cancer to affect women worldwide. According to the American Cancer Society, about 1 in 8 women in the United States will develop breast cancer in their lifetime. While it is not possible to entirely prevent breast cancer, various medical organizations advise regular screening to detect and treat cases at the early stage. The breast density, defined as the proportion of fibro-glandular tissue within the breast, is often used to assess the risk of developing breast cancer. While various methods are available to estimate this measure, studies have shown that subjective assessments conducted by radiologists based on visual analogue scales are more accurate than any other method.
As expert evaluations of breast density play a crucial role in breast cancer risk assessment, developing image analysis frameworks that can automatically estimate this risk, with the same accuracy as an experienced radiologist, is highly desirable. To this end, researchers led by Prof. Susan M. Astley from the University of Manchester, United Kingdom, recently developed and tested a new deep learning-based model capable of estimating breast density with high precision. Their findings are published in the Journal of Medical Imaging.
“The advantage of the deep learning-based approach is that it enables automatic feature extraction from the data itself,” explains Astley. “This is appealing for breast density estimations since we do not completely understand why subjective expert judgments outperform other methods.”
Typically, training deep learning models for medical image analysis is a challenging task owing to limited datasets. However, the researchers managed to find a solution to this problem: instead of building the model from the ground up, they used two independent deep learning models that were initially trained on ImageNet, a non-medical imaging dataset with over a million images. This approach, known as “transfer learning,” allowed them to train the models more efficiently with fewer medical imaging data.
Using nearly 160,000 full-field digital mammogram images that were assigned density values on a visual analogue scale by experts (radiologists, advanced practitioner radiographers, and breast physicians) from 39,357 women, the researchers developed a procedure for estimating the density score for each mammogram image. The objective was to take in a mammogram image as input and churn out a density score as output.
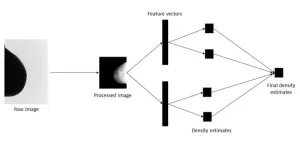
The procedure involved preprocessing the images to make the training process computationally less intensive, extracting features from the processed images with the deep learning models, mapping the features to a set of density scores, and then combining the scores using an ensemble approach to produce a final density estimate.
With this approach, the researchers developed highly accurate models for estimating breast density and its correlation with cancer risk, while conserving the computation time and memory. “The model’s performance is comparable to those of human experts within the bounds of uncertainty,” says Astley. “Moreover, it can be trained much faster and on small datasets or subsets of the large dataset.”
Notably, the deep transfer learning framework is useful not only for estimating breast cancer risk in the absence of a radiologist but also for training other medical imaging models based on its breast tissue density estimations. This, in turn, can enable improved performance in tasks such as cancer risk prediction or image segmentation.
Read the Open Access article by S. Squires et al., “Automatic assessment of mammographic density using a deep transfer learning method,” J. Med. Imaging 10(2) 024502 (2023), doi 10.1117/1.JMI.10.2.024502.
END
Deep learning model estimates cancer risk from breast density
A deep transfer learning framework for making mammographic density estimates based on the visual scores of radiologists
2023-04-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
COVID-19 pandemic increased the frequency of intimate partner violence
2023-04-07
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and queer people who experienced intimate partner violence in their current relationship before COVID-19 had an increase in the frequency of victimization after the pandemic began, according to a Rutgers study.
While national emergencies, crises and pandemics increase the frequency of health risks and intimate partner violence few studies have considered the nuances of social and psychological factors, such as socioeconomic characteristics and mental health, in explaining the increase in intimate partner violence during times of crisis.
“To date, most programs on intimate ...
Scientists discover a way Earth’s atmosphere cleans itself
2023-04-07
Irvine, Calif., April 7, 2023 — Human activities emit many kinds of pollutants into the air, and without a molecule called hydroxide (OH), many of these pollutants would keep aggregating in the atmosphere.
How OH itself forms in the atmosphere was viewed as a complete story, but in new research published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, a research team that includes Sergey Nizkorodov, a University of California, Irvine professor of chemistry, report that a strong electric field that exists at the surface between airborne water droplets and ...
Webb reveals never-before-seen details in Cassiopeia A
2023-04-07
The explosion of a star is a dramatic event, but the remains the star leaves behind can be even more dramatic. A new mid-infrared image from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope provides one stunning example. It shows the supernova remnant Cassiopeia A (Cas A), created by a stellar explosion seen from Earth 340 years ago. Cas A is the youngest known remnant from an exploding, massive star in our galaxy, which makes it a unique opportunity to learn more about how such supernovae occur.
“Cas ...
A new quantum approach to solve electronic structures of complex materials
2023-04-07
If you know the atoms that compose a particular molecule or solid material, the interactions between those atoms can be determined computationally, by solving quantum mechanical equations — at least, if the molecule is small and simple. However, solving these equations, critical for fields from materials engineering to drug design, requires a prohibitively long computational time for complex molecules and materials.
Now, researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory and the University of Chicago’s ...
The social framework
2023-04-07
On January 6, 2021, the public watched in disbelief as the Capitol building was stormed by hundreds of protestors. Most spectators at home didn't know violence at the Capitol building was already circulating through far-right social media channels for months.
Social media, for better or worse, play a large role in how we consume information – as well as spreading misinformation and conspiratorial propaganda.
Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh received $100,000 as part of the Meta Foundational Integrity Research ...
HonorHealth Research Institute joins City of Hope and TGen in creating method for scoring pancreatic cancer patients for surgery
2023-04-07
SCOTTSDALE, Ariz. — April 7, 2023 — A trio of premier Southwest biomedical research centers — HonorHealth Research Institute, City of Hope and the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen), part of City of Hope — have developed a more precise method that may help determine when it is best to surgically remove of pancreatic cancer tumors.
Surgical removal of the tumor can be a key step in helping extend the survival of patients with pancreatic cancer, one of the most aggressive and deadly of all malignancies and the nation’s third leading cause of cancer-related death. Currently, surgery — or surgery plus chemotherapy ...
CHOP-led study identifies two different regulatory T cell populations
2023-04-07
Philadelphia, April 7, 2022—A regulatory class of human T cells descends from two different origins, one that relates to autoimmunity and one that relates to protective immunity, according to a new study led by Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP). The findings, published today in Science Immunology, could pave the way for new treatments for autoimmune diseases that target the immune system selectively.
“When it comes to autoimmunity, the prevailing wisdom has been that the only way to stop inflammation ...
Here’s how a worm’s embryonic cells changed its development potential
2023-04-07
Researchers have spotted how specific proteins within the chromosomes of roundworms enable their offspring to produce specialized cells generations later, a startling finding that upends classical thinking that hereditary information for cell differentiation is mostly ingrained within DNA and other genetic factors.
The Johns Hopkins University team reports for the first time the mechanisms by which a protein known as histone H3 controls when and how worm embryos produce both highly specific cells and pluripotent cells, cells that can turn certain genes on ...
New genetic finding provides clue for personalizing depression treatment
2023-04-07
A team of scientists at the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) has identified a stress-regulated gene that plays a role in the link between long-term stress and a common type of depressive behavior in mice. Specifically, this gene was needed for long-term stress to produce a loss of interest in activities that were once rewarding or pleasurable – often called anhedonia. However, the gene did not play a role in other common depressive-like symptoms, such as social avoidance and increased anxiety-like behavior. The team reported its findings recently in eLife.
The study was led by neuroscientists Makoto Taniguchi, Ph.D., and Christopher Cowan, Ph.D., and also ...
Lonely people’s divergent thought processes may contribute to feeling “alone in a crowded room”
2023-04-07
Common wisdom suggests that a core difference between solitude and loneliness is choice. Whereas a person who appreciates solitude might choose to enjoy a quiet night in or a solo trip abroad, a lonely person may feel disconnected from other people even in a crowded room. New research published in Psychological Science supports this notion, suggesting that lonely people may think differently regardless of the size of their social networks.
“We found that lonely individuals are exceptionally dissimilar to their peers in the way that they process the world around them … ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Deep learning model estimates cancer risk from breast densityA deep transfer learning framework for making mammographic density estimates based on the visual scores of radiologists