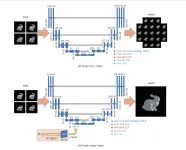
View interpolation networks for reproducing the material appearance of specular objects
2023-04-11
(Press-News.org)
With the spread of Internet shopping nowadays, purchasing products online has become possible and common. However, in many cases, because users are presented with few photographs of products and cannot actually hold the products, they may be unable to perceive the material of the products.
In this study, we proposed view interpolation networks for reproducing material appearances. We implemented U-Net, an existing image transformation network, and a network that used additional information in the middle layer of U-Net. The networks were trained to generate images from the intermediate viewpoints of four cameras placed at the corners of a square on a sphere. As a preliminary step for reproducing complex material appearance, we used relatively simple objects with metallic reflections to verify the effectiveness of the methods.
By comparing the methods and training data formats, we determined that single image output is better for view interpolation than image array output. We also determined that using images from random viewpoints is better than using images from fixed viewpoints as the training data format for the network.Future research should address three major problems.
First, an experiment should be conducted using objects with more complex materials. Only objects with relatively simple materials were used in our experiment. Further experiments using objects with complex optical properties such as transmission, refraction, and internal scattering, are required to reproduce a more general material appearance.
Second, the degrees of freedom of the viewpoint positions and orientations must be extended. In this study, the cameras were placed on a sphere, always facing the center of the sphere, which has two degrees of freedom. If the cameras were shifted back and forth or oriented in another direction, view interpolation with more degrees of freedom would be possible.
Finally, future research should focus on improving the accuracy. The images generated in the experiment looked almost natural; however, the output images fail to reproduce some small details. This study used a simple mean square error as the loss function. The accuracy can be improved using a loss function that is more suitable for the purpose of material appearance reproduction. In addition, the blurring may be reduced using GAN-based networks.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-04-11
Rain streaks of different shapes, sizes, and directions obscure image background scenes, resulting in image degradation, including intensity fluctuation, color distortion, or even content alteration. Such degradation impairs the visual quality of an image and leads to undesirable performance of many outdoor computer vision systems that require high-quality images. Therefore, image deraining must be performed, and effective deraining methods should be developed. In this study, we addressed the problem of single-image rain removal.
We propose a novel unrolling rain-guided detail recovery network ...
2023-04-11
Experts have found that at the start of the COVID-19 outbreak in early 2020, Americans chose not to become pregnant as they grappled with stay-at-home restrictions, anxiety, and economic hardship. Now, a new study led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine shows that some states actually experienced steeper decreases in fertility than others.
The findings revealed that nine months after the pandemic began, there were 18 fewer births a month per 100,000 women of reproductive age across the U.S. compared with the year ...
2023-04-10
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Over the past few years, the Department of Family Medicine and the Department of Psychiatry in UNC’s School of Medicine have been working together to spearhead the development of a new “enhanced primary care” model to provide better primary care for patients who have severe mental illnesses.
A new analysis led by Alex K. Gertner, MD, PhD, psychiatry resident at UNC Hospitals, has added further evidence that the new model is effective. Gertner found that the enhanced primary care model resulted in lower hemoglobin A1c and blood pressure for patients with severe mental illness when compared to other primary care clinics throughout ...
2023-04-10
Adoptive cell therapy (ACT) has become a promising immunotherapy tool to help treat advanced melanoma. The therapy, which harnesses immune cells collected from the patient’s own tumors, could provide a new treatment option to cancer patients, potentially bypassing radiation therapies and harsh chemotherapy drugs.
For the first time, Northwestern University scientists have discovered it is possible to isolate a tumor’s attack cells non-invasively from blood, rather than from tumors. The finding opens the door for ACT to treat harder-to-reach cancer types and makes it a more viable option ...
2023-04-10
Research led by scientists at UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center found that responses to a type of immunotherapy called PD-1 checkpoint blockade in patients with advanced melanoma depended on whether or not they had previously received another immunotherapy – CTLA-4 blockade – as well as other factors.
Their findings, based on analysis of seven data sets generated over the past decade, which included results of tumor biopsies from more than 500 patients, are published in Cancer Cell.
“In our large set of data, features that have been used to predict response ...
2023-04-10
As their plane flew low on its approach to land at the airport on the island of Dominica, researchers from Clemson and Harvard universities looked out the window to see miles of forests with trees that looked like matchsticks.
It was nine months after the island in the West Indies had taken a direct hit from Category 5 Hurricane Maria.
But when the researchers actually got into the forests and examined the trees more closely, they discovered that while 89% of the trees sustained damage — 76% of which had major damage —only 10% were immediately killed. Many of the trees had resprouted.
“These ...
2023-04-10
A Roundtable Discussion was recently held to discuss the importance of community voice in developing 21st century public health systems. Expert panelists emphasized the need to redefine measures, foster new ideas, and work to ensure that historically excluded populations are represented in the data collection process. The Roundtable transcript is now published in the peer-reviewed journal Big Data. Click here to read the transcript.
The discussion was moderated by Michael Crawford, Associate Dean for Strategy, ...
2023-04-10
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — The amount of dissolved oxygen in a river is a matter of life or death for the plants and animals living within it, but this oxygen concentration varies drastically from one river to another, depending on their unique temperature, light and flow. To better understand which factor has the greatest impact on the concentration of dissolved oxygen, researchers at Penn State used a deep learning model to analyze data from hundreds of rivers across the United States.
Oxygen concentration is an important measure of water quality because fish and other aquatic organisms require dissolved oxygen to breathe, according to Wei Zhi, assistant ...
2023-04-10
“[...] the study of immunotherapy for treating triple negative breast cancer might still be at its early stages of development but is full of future promise.”
BUFFALO, NY- April 10, 2023 – A new review paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on March 31, 2023, entitled, “Crosstalk between triple negative breast cancer and microenvironment.”
Although many advances have been made in the treatment of breast cancer, for triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) these therapies have not significantly increased overall survival. Tumor microenvironment (TME) plays an essential role to develop and control TNBC progression. ...
2023-04-10
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A research lab at Penn State will equally share a three-year, $2.55 million grant from the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR) with three other teams at Carnegie Mellon University and the Adolphe Merkle Institute of the University of Fribourg in Switzerland. The multidisciplinary research collaboration aims to develop a framework for the design and production of soft, self-charging, bio-inspired power sources for applications in space.
Joseph Najem, assistant professor of mechanical engineering at Penn State, will lead ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] View interpolation networks for reproducing the material appearance of specular objects