(Press-News.org) Cell secretions like proteins, antibodies, and neurotransmitters play an essential role in immune response, metabolism, and communication between cells. Understanding cell secretions is key for developing disease treatments, but current methods are only able to report the quantity of secretions, without any detail as to when and where they are produced.
Now, researchers in the BIOnanophotonic Systems Laboratory (BIOS) in the School of Engineering and at the University of Geneva have developed a novel optical imaging approach that gives a four-dimensional view of cell secretions in both space and time. By placing individual cells into microscopic wells in a nanostructured gold-plated chip, and then inducing a phenomenon called plasmonic resonance on the chip’s surface, they are able to map secretions as they are being produced, while observing cell shape and movement.
As it provides an unprecedentedly detailed view of how cells function and communicate, the scientists believe their method, recently published in Nature Biomedical Engineering, has “tremendous” potential for pharmaceutical development as well as fundamental research.
“A key aspect of our work is that it allows us to screen cells individually in a high-throughput fashion. Collective measurements of the average response of many cells do not reflect their heterogeneity…and in biology, everything is heterogeneous, from immune responses to cancer cells. This is why cancer is so hard to treat,” says BIOS head Hatice Altug.
A million sensing elements
At the heart of the scientists’ method is a 1 cm2 nanoplasmonic chip composed of millions of tiny holes, and hundreds of chambers for individual cells. The chip is made of a nanostructured gold substrate covered with a thin polymer mesh. Each chamber is filled with a cell medium to keep the cells alive and healthy during imaging.
“Cell secretions are like the words of the cell: they spread out dynamically in time and space to connect with other cells. Our technology captures key heterogeneity in terms of where and how far these ‘words’ travel,” says BIOS PhD student and first author Saeid Ansaryan.
The nanoplasmonics part comes in thanks to a light beam, which causes the gold electrons to oscillate. The nanostructure is engineered so that only certain wavelengths can penetrate it. When something – like protein secretion – occurs on the chip’s surface to alter the light passing through, the spectrum shifts. A CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) image sensor and an LED translate this shift into intensity variations on the CMOS pixels.
“The beauty of our apparatus is that the nanoholes distributed across the entire surface transform every spot into a sensing element. This allows us to observe the spatial patterns of released proteins irrespective of cell position,” says Ansaryan.
The method has allowed the scientists to get a glimpse of two essential cellular processes – cell division and cell death – and to study delicate antibody-secreting human donor B-cells.
“We saw the cell content released during two forms of cell death, apoptosis and necroptosis. In the latter, the content is released in an asymmetric burst, resulting in an image signature or fingerprint. This has never before been shown at the single-cell level,” Altug says.
Screening for cell fitness
Because the method bathes the cells in a nutritious cell medium, and does not require the toxic fluorescent labels used by other imaging technologies, the cells under study can easily be recovered. This gives the method great potential for use in developing pharmaceutical drugs, vaccines, and other treatments; for example, to help researchers understand how cells respond to different therapies at the individual level.
“As the amount and pattern of secretions produced by a cell are a proxy for determining their overall effectiveness, we could also imagine immunotherapy applications where you screen patient immune cells to identify those that are most effective, and then create a colony of those cells,” says Ansaryan.
END
Nanoplasmonic imaging reveals real-time protein secretion
EPFL researchers have used a nanoplasmonics approach to observe the real-time production of cell secretions, including proteins and antibodies; an advancement that could aid in the development of cancer treatments, vaccines, and other therapies.
2023-04-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mutant strains of Salmonella make infection more aggressive in commercial poultry, study shows
2023-04-11
In Brazil, a group of researchers supported by FAPESP created mutant forms of Salmonella to understand the mechanisms that favor colonization of the intestinal tract of chickens by these pathogenic bacteria and find better ways to combat the infection they cause.
An article on the study is published in the journal Scientific Reports. In it, the researchers note that, contrary to expectations, the mutant strains caused more severe infections than wild-type bacteria.
In the mutant strains, the genes ttrA and pduA were deleted. In previous research using mice, both genes had been shown to account for the ability of Salmonella to ...
Financial toxicity of cancer impacts partners’ quality of life
2023-04-11
ANN ARBOR, Michigan — A cancer diagnosis can cause financial strain on patients as they cope with the cost of treatment and lost work. But what about their partners?
A new study from University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center researchers surveyed the partners of colorectal cancer patients and found the financial impact of a loved one’s diagnosis also impacts the partner’s health-related quality of life.
“We know that financial toxicity or hardship is a significant effect of cancer and its treatment ...
Danforth Center research uncovers how plants pass ‘memory’ of high CO2 to their offspring
2023-04-11
ST. LOUIS, MO, April 10, 2023 – New research lead by Keith Slotkin, PhD, member, Donald Danforth Plant Science Center opens the door for scientists to equip plants with the tools they need to adapt to rising levels of carbon dioxide (CO2), high heat, and other stressors associated with climate change. The newly published study in the journal The New Phytologist revealed
that the transgenerational inheritance occurred via DNA methylation, the process by which plants “mark” DNA without changing the code of the DNA itself ...
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai names new chair of microbiology
2023-04-11
Ana Fernandez-Sesma, PhD, has been appointed Chair of the Department of Microbiology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Dr. Fernandez-Sesma will direct all educational and research functions of the Department, while cultivating an academic culture that advances insights into virology, vaccinology, immunology, and microbiology, and encourages innovative approaches to teaching and mentoring.
Dr. Fernandez-Sesma has distinguished herself as an investigator focused on the mechanisms of immune evasion used by viruses, including dengue (DENV), ...
Conspiracy theories cause populism to rise
2023-04-11
Coinciding with the increased support for populist parties that we have witnessed all over the West, the last decade has also seen an increase in the number of populism-related studies, covering topics such as the causes and consequences of voting for parties that support these ideas, or the reasons for and possible consequences of the emergence and increasing presence of the attitudes on which they are based.
The links between conspiracy theories and populism have also aroused a great degree of interest. Carolina Galais, a researcher at the Universitat ...
Breast tomosynthesis improves screening in community settings
2023-04-11
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Researchers have found that digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) has improved breast cancer screening performance in community practice and identifies more invasive cancers, compared to digital mammography. In addition, radiologists’ interpretive performance improved with DBT. The results of the study were published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
“Our study demonstrated that more radiologists in U.S. community practice are meeting recommended performance standards with digital breast tomosynthesis than ...
Key memory receptors are located on interneurons
2023-04-11
A key receptor regulating memory formation has been localized to interneurons, according to a study with implications for drug development. Robert Pearce and colleagues probed the localization of γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors that incorporate α5 subunits (α5-GABAARs). α5-GABAARs are concentrated within the hippocampus, a brain structure that is essential for the formation of episodic memories. The general anesthetic etomidate blocks learning by targeting α5-GABAARs, as do many drugs designed to enhance cognition, intended for use in people with Alzheimer’s disease, ...
Bioprinting technology combined with artificial intelligence allows to obtain high quality in vitro models
2023-04-11
In the process of organoid manufacturing, bioprinting technology can not only facilitate the creation and maintenance of complex biological 3D shapes and structures, but also allow for standardization and quality control during production. And the addition of artificial intelligence, which can validate the product potential in the manufacturing process, allows to provide a more standardized source of cells for the organoid in terms of viability, function, etc. In other words, bioprinting combined with artificial intelligence is expected to perform real-time ...
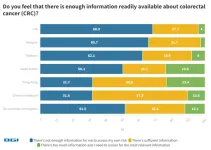
Over 60 percent of Saudi Arabian respondents never took a colorectal cancer test | BGI Insight
2023-04-11
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the most diagnosed cancer among males and third among females in Saudi Arabia, with up to two-thirds diagnosed at an advanced stage, according to the King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre. This report shows Saudi Arabia has a high percentage of respondents (62.7%) who never took CRC tests, far higher than global average of 54.1%. This shows the Kingdom's Early Cancer Detection Program still needs to build greater awareness among the public.
To uncover attitudes and the ...
A protective probiotic blunts the ill effects of alcohol in mice
2023-04-11
Highlights
Excessive alcohol consumption causes short-term and long-term health problems
An enzyme called ADH1B accelerates the breakdown of alcohol in the body
Researchers genetically engineered a probiotic to express ADH1B in mice
Mice treated with the probiotic recovered from alcohol exposure faster than untreated mice, and had fewer resulting health problems
Washington, DC – Excessive alcohol consumption leads to painful hangovers and accompanying headaches, fatigue, and nausea. Drinking alcohol has also been linked to a raft of health problems in the human body, including heart disease, cirrhosis, and immune deficiency. One way to avoid those consequences ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
[Press-News.org] Nanoplasmonic imaging reveals real-time protein secretionEPFL researchers have used a nanoplasmonics approach to observe the real-time production of cell secretions, including proteins and antibodies; an advancement that could aid in the development of cancer treatments, vaccines, and other therapies.