(Press-News.org) The development of biomaterials for artificial organs and tissues is active due to an increase in accidental injuries and chronic diseases, along with the entry into a super-aged society. 3D bioprinting technology, which uses cells and biomaterials to create three-dimensional artificial tissue structures, has recently gained popularity. However, commonly used hydrogel-based bioinks can cause cytotoxicity due to the chemical crosslinking agent and ultraviolet light that connect the molecular structure of photocuring 3D-printed bioink.
Dr. Song Soo-chang's research team at the Center for Biomaterials, Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, President Yoon Seok-jin), revealed the first development of poly(organophosphazene) hydrogel-based temperature-sensitive bioink that stably maintained its physical structure only by temperature control without photocuring, induced tissue regeneration, and then biodegraded in the body after a certain period of time.
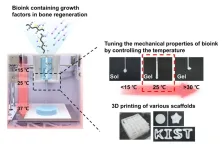
Current hydrogel-based bioinks must go through a photocuring process to enhance the mechanical properties of the 3D scaffold after printing, with a high risk of adverse effects in the human body. In addition, there have been possibility of side effects by transplanting externally cultured cells within bioink to increase the tissue regeneration effect. Accordingly, the research team developed a new bioink material using a temperature-sensitive poly(organophosphazene) hydrogel, which existed in a liquid form at low temperatures and changed to a hard gel at body temperature. This enabled the regeneration of tissues only by temperature control without chemical crosslinking agents or UV irradiation and the manufacture of a three-dimensional scaffold with a physically stable structure, minimizing the possibility of immune adverse effects in the human body.
The developed bioink also had a molecular structure that could interact with growth factors, which were proteins that help in tissue regeneration to preserve growth factors that regulated cell growth, differentiation, and immune responses for a long period of time. The research team was able to maximize the effect of tissue regeneration by creating an environment in which cell differentiation could be autonomously regulated within the 3D scaffold printed with bioink.
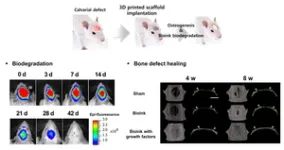
The research team fabricated the 3D scaffold by printing it with a 3D bioprinter using bioink containing transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1) and bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2), which were required for cell infiltration and bone regeneration, and conducted an experiment by implanting it into a damaged bone in a rat. As a result, cells from the surrounding tissue were migrated into the scaffold, and the defected bone was regenerated to a normal tissue level, and the implanted 3D scaffold slowly biodegraded in the body over 42 days.
Dr. Song Soo-Chang of KIST said, "The research team has transferred technology for the thermo-sensitive polyphosphazene hydrogel to NexGel Biotech Co., Ltd. in June 2022, and the development of products such as bone graft materials and cosmetic fillers is underway." "As the bioink developed this time has different physical properties, follow-up research to apply it to the regeneration of other tissues besides bone tissue is being conducted, and we expect to finally be able to commercialize bioink tailored to each tissue and organ," he said.
###
KIST was established in 1966 as the first government-funded research institute in Korea. KIST now strives to solve national and social challenges and secure growth engines through leading and innovative research. For more information, please visit KIST’s website at https://eng.kist.re.kr/
This research was conducted through the KIST Major Projects supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Lee Jong-ho), and the research results were published as the inside back cover in the latest issue of Small (IF: 15.153, top 7.101% in the JCR field), an international academic journal in the field of materials.
END
Safe bioink for artificial organ printing
Development of 3D bioprinting ink that induces tissue regeneration without photocuring, Expected applications including patient-specific regenerative treatment technologies, such as artificial organs
2023-04-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers turn to the power of native aquatic plants to clean coastal waters
2023-04-14
To find a fast, efficient way to clear harmful chemicals along the Gulf of Mexico coastline, researchers are turning to something already familiar with the task – several species of the aquatic grasses and rice that feel very much at home in murky coastal waters.
The research team led by University of Houston’s Venkatesh Balan, associate professor of biotechnology in the Cullen College of Engineering’s Division of Technology, studies the abilities of these water-loving flora to uptake concentrations ...
Rice U. engineering students’ brace puts patients first
2023-04-13
HOUSTON – (April 13, 2023) – Body image can have a significant impact on a person’s life, especially in their youth.
For those suffering from rib flaring associated with congenital deformations of the chest wall that cause it to jut out or cave in, a team of Rice University engineering students has come up with a potential solution.
Pectus carinatum and pectus excavatum are conditions in which a person is born with their breastbone protruding outward or sunken inward, respectively. There ...
PPPL hosts workshop on fusion energy and nonproliferation
2023-04-13
Public and private organizations around the world are developing fusion energy devices that could serve as models for fusion power plants. Scientists are striving to duplicate the fusion power that drives the sun and stars as a source of carbon-free energy to generate electricity without contributing to climate change.
While fusion plants could help meet global energy demands without emitting greenhouse gases and producing long-lived radioactive waste, they could also have risks — many of which were discussed at a two-day workshop hosted by the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory ...
Nurses trained via virtual reality performed better than those trained by inpatient clinical training
2023-04-13
In search of novel tactics to accommodate a larger student body and fulfill workforce demands, nursing schools are developing new approaches to optimize learning, engage learners, and provide methods to ensure competency in future nursing graduates.
A recent study by Bethany Cieslowski, associate professor of Nursing, and colleagues found that immersive virtual reality (VR) training has been shown to be as effective as inpatient training for students learning to provide care for acute care pediatric ...
Hallmarks to improving pancreatic cancer therapy identified by UC Irvine researchers
2023-04-13
Irvine, Calif., April 13, 2023 — Scientists from the University of California, Irvine, the University of Michigan and the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have made a significant contribution to the field of pancreatic cancer research. Their new study presents several crucial themes in the biology of pancreatic cancer that can serve as hallmarks for pancreatic cancer therapy. These themes include genomic alterations, metabolism, the tumor microenvironment, immunotherapy and innovative clinical trial design. The study appears in the journal Cell.
(Link to study: https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(23)00142-3)
Pancreatic ...
Four major Illinois research institutions form a collaboration to improve urban forest drought resilience
2023-04-13
Scientists at four leading Illinois research institutions, three in the Chicago region, are forming a new collaboration to study the effects of drought on urban trees and develop more effective drought response strategies nationwide through a grant from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
The project is being led by researchers at The Morton Arboretum in conjunction with the U.S. Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory, the University of Chicago and the Illinois State Water Survey at the Prairie Research ...
Good news! Only a modest reduction in added sugars consumption is needed to achieve the Healthy People 2030 target
2023-04-13
Ann Arbor, April 13, 2023 – Reducing caloric intake from added sugars is a Leading Health Indicator in Healthy People 2030, a national public health initiative led by the US Department of Health and Human Services that sets data-driven national objectives to improve health and wellbeing over the next decade. Although many Americans consume too much sugar, investigators found that only a modest reduction in added sugars intake is needed to reach a population mean of 11.5% of calories from added sugars by 2030. Prioritizing reducing added sugars intake among people not meeting recommendations could help those most at risk for chronic disease related to added sugars consumption. They report ...
T-cell vaccine for COVID-19 may last longer than current vaccines
2023-04-13
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — The current COVID-19 vaccines are designed to trigger an antibody response to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, which is vulnerable to mutations that could make the vaccine less effective over time. Focusing on the T-cell instead, Penn State researchers partnered with Evaxion Biotech on a study that was the first to demonstrate the effectiveness of an artificial intelligence-generated vaccine in a live viral challenge model. Such a vaccine may provide long-lasting immunity against future emerging variants and could be used as a model for other seasonal viral diseases ...
Rice U. students engineer socks for on-the-go neuropathy treatment
2023-04-13
HOUSTON – (April 13, 2023) – Need a little spring — or buzz — in your step? A wearable electrical-stimulation and vibration-therapy system designed by Rice University engineering students might be just what the doctor ordered for people experiencing foot pain and balance loss due to diabetic neuropathy.
Rice engineering students in the StimuSock team — Abby Dowse, Yannie Guo, Andrei Mitrofan, Sarah Park and Kelly Xu — designed a sock with a smart insole that can deliver both transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) and vibration therapy that block pain signals to the brain and ...
UC Davis study finds tweets can amplify, disrupt, unite and divide
2023-04-13
Social media connects people and amplifies different aspects of humanity in good and bad ways. But the effects of social media appear neither universally good nor bad, but rather present an oscillating, dynamic system that can be divisive but also uniting, a new University of California, Davis, study suggests.
Department of Communication researchers said their findings both in an observational study and simulation speak to the ongoing debate about social media’s contributions to political polarization, misinformation and echo chambers. To conduct their research, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
[Press-News.org] Safe bioink for artificial organ printingDevelopment of 3D bioprinting ink that induces tissue regeneration without photocuring, Expected applications including patient-specific regenerative treatment technologies, such as artificial organs