(Press-News.org) A new study of worldwide polling data suggests that a person’s income rank relative to their peers is linked to their experience of physical pain, with a lower income rank linked to a higher likelihood of experiencing pain. It is the first time such a relationship has been shown.
The study found the link to persist, to the same degree, irrespective of whether the person lives in a rich country or a poor country.
Income rank is the position of an individual’s absolute personal income amount in a list of those amounts ordered from lowest to highest. The higher the position in the list, the higher the income rank.
The study, authored by Dr Lucía Macchia, Lecturer in Psychology at City, University of London, also suggests that people in poor countries fare no better than those living in rich countries when it comes to the effect of the absolute amount of personal income they earn on the likelihood of them experiencing pain. This was an unexpected finding and requires further investigation, as the prediction was that those in poorer countries would be more strongly affected, assuming that an increase in absolute income would allow them to obtain more resources to support their wellbeing that are more readily available in rich countries.
Overall, the study findings suggest that an overriding factor affecting a person’s pain levels based on their personal income could be negative emotions related to their appraisal of their income ranking compared to their peers. Whether that be related to their perception of their own levels of deprivation relative to their peers (in keeping with Relative Deprivation Theory) or their standing in a society and a feeling of a lack of social mobility (Social Comparison theory).
In the study, analyses were made of data from the annual World Gallup Poll (GWP), across the years 2009-18, and consisting of responses from approximately 1.3 million adult survey respondents from across 146 countries. Respondents were asked what their total monthly household income was before taxes, which was divided by the number of people in their household to derive the respondent’s personal income amount. Respondents were also asked whether they experienced physical pain the day before being surveyed to which they could respond ‘yes’ or ‘no’. In the analyses, linear regression models were created from these data in addition to further ancillary information.
This study refers to pain as the feeling that people experience when their body hurts regardless of the presence of physical damage.
Physical pain is one of the main reasons people visit the accident and emergency room in the UK. Approximately nine million people live with chronic pain in the UK and musculoskeletal pain alone accounts for 30 per cent of the country’s medical consultations.
Physical pain has been increasing dramatically in the last decades, becoming a priority for global public health. Pain affects leisure and productivity at work, increases health care costs, and represents a major challenge for healthcare systems. Pain plays a key role in suicide and in drug and alcohol misuse. In light of these circumstances, understanding the context of pain is crucial to addressing its consequences.
Study author, Dr Lucía Macchia, said:
“This is the first study that shows that income rank and pain are linked around the world. It suggests that psychological factors related to the well-known phenomenon of social comparison may influence people’s physical pain.”
The study is published online in the journal, Social Psychological and Personality Science.
ENDS
Notes to Editors
To speak to Dr Lucía Macchia, contact Dr Shamim Quadir, Senior Communications Officer, School of Health & Psychological Sciences, City, University of London. Tel: +44(0) 207 040 8782 Email: shamim.quadir@city.ac.uk.
To read a copy of the embargoed manuscript for the study article (to be published 00.01 ET Monday 17 April, 2023):
‘Having less than others is physically painful: Income rank and pain around the world’ in the journal, Social Psychological and Personality Science
please request it from Dr Shamim Quadir, Senior Communications Officer, School of Health & Psychological Sciences.
City, University of London
City, University of London is a global higher education institution committed to academic excellence, with a focus on business and the professions and an enviable central London location.
City’s academic range is broadly-based with world-leading strengths in business; law; health sciences; mathematics; computer science; engineering; social sciences; and the arts including journalism and music.
City has around 20,000 students (46% at postgraduate level) from more than 160 countries and staff from over 75 countries.
In the last REF, City doubled the proportion of its total academic staff producing world-leading or internationally excellent research.
More than 140,000 former students from over 180 countries are members of the City Alumni Network.
The University’s history dates from 1894, with the foundation of the Northampton Institute on what is now the main part of City’s campus. In 1966, City was granted University status by Royal Charter and the Lord Mayor of London became its Chancellor. In September 2016, City joined the University of London and HRH the Princess Royal became City’s Chancellor. END
Income rank linked to experience of physical pain, irrespective of whether in a rich or poor country, study suggests
New study suggests that comparing one’s earnings relative to peers may induce negative emotions that lead to physical pain
2023-04-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Treatment with immunotherapy alone produces ‘exceptional’ response rates in some melanoma patients
2023-04-16
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Data from a national clinical trial shows that a striking 89% of patients with desmoplastic melanoma responded to immunotherapy (pembrolizumab) alone, suggesting that many patients could avoid the risk for toxicity from combination therapies and achieve cancer control with this approach to treatment.
Desmoplastic melanoma is a subset of melanoma skin cancer that is caused by high levels of ultraviolet (UV) radiation damage and, therefore, a high number of tumor mutations that all contribute to aggressive ...
SWOG S1512 trial sees high response rate to pembrolizumab in patients with unresectable desmoplastic melanoma
2023-04-16
Close to 90 percent of patients with unresectable (inoperable) desmoplastic melanoma, a rare form of skin cancer, saw their cancer improve after treatment with the immunotherapy drug pembrolizumab in a recent clinical trial.
These results from the S1512 trial conducted by the SWOG Cancer Research Network, a group funded by the National Cancer Institute (NCI), are being delivered in an oral presentation at the clinical trials plenary session of the 2023 annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) in Orlando, Florida, on April 16th.
The S1512 ...
AACR: YAP/TEAD inhibitor VT3989 is well tolerated and shows antitumor activity in advanced mesothelioma and NF2-mutant cancers
2023-04-16
ABSTRACT: CT006
ORLANDO, Fla. ― The first-in-class YAP/TEAD inhibitor VT3989 was well tolerated with durable antitumor responses in patients with advanced malignant mesothelioma and other tumors with NF2 mutations, according to results of a Phase I trial led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. The first-in-human study was presented today at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2023.
Seven of 69 patients had radiological partial responses that persisted up to at least 21 months, indicating tumor shrinkage, while 34 had stable disease. Patient benefit was observed in patients with both mesothelioma ...
AACR: Penn Medicine preclinical study identifies new target for recurrent ovarian cancer
2023-04-16
ORLANDO – Despite recent advances, ovarian cancer remains the fifth leading cause of cancer-related deaths among women, and there’s a critical need for new treatment options, especially for advanced cancers that grow back after standard of care treatment. Results from a preclinical study, led by researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, verified a new target for drug-resistant ovarian cancer and provided data to support a treatment approach that is already making its way into clinical trials.
Sarah Gitto, PhD, an instructor of Pathology and Laboratory ...
Adding new vaccine type to leading immunotherapy dramatically reduced melanoma recurrence
2023-04-16
VIDEO OF RESEARCHER AND PATIENT COMMENTARY IS AVAILABLE AT:
https://bcove.video/3mxxASq
The combination of an experimental mRNA vaccine with an immunotherapy reduced the likelihood of melanoma recurring or causing death by 44% when compared to immunotherapy alone, a new clinical trial shows.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone Health and its Perlmutter Cancer Center, the randomized phase 2b trial involved men and women who had surgery to remove melanoma from lymph nodes or other organs and were at high risk of the disease returning in sites distant from the original cancer. ...
AACR: Lung cancer outcomes significantly improved with immunotherapy-based treatment given before and after surgery
2023-04-16
ABSTRACT: CT005
ORLANDO, Fla. ― A regimen of pre-surgical immunotherapy and chemotherapy followed by post-surgical immunotherapy significantly improved event-free survival (EFS) and pathologic complete response (pCR) rates compared to chemotherapy alone for patients with operable non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), according to Phase III trial results presented today by researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2023.
The ...
A new breakthrough in Alzheimer disease research - visualizing reactive astrocyte-neuron interaction
2023-04-16
Recently, a team of South Korean scientists led by Director C. Justin LEE of the Center for Cognition and Sociality within the Institute for Basic Science made a new discovery that can revolutionize both the diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. The group demonstrated a mechanism where the astrocytes in the brain uptake elevated levels of acetates, which turns them into hazardous reactive astrocytes. They then went on further to develop a new imaging technique that takes advantage of this mechanism to directly observe the astrocyte-neuron interactions.
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), one of ...
Statin use is associated with lower risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation
2023-04-16
Barcelona, Spain – 16 April 2023: A region-wide study in more than 50,000 patients with atrial fibrillation has found reduced risks of stroke and transient ischaemic attack in those who started statins within a year of diagnosis compared with those who did not. The findings are presented at EHRA 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
“Our study indicates that taking statins for many years was even more protective against stroke than short-term use,” said study author Ms. Jiayi Huang, a PhD student at the University of Hong Kong, China.
Atrial fibrillation is the most common ...
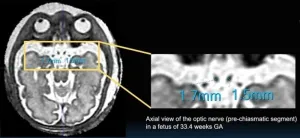
ARRS Annual Meeting: 3D SVR MRI helps delineate fetal optic nerve pathway
2023-04-16
Honolulu, HI | April 16, 2023—An award-winning Scientific Online Poster presented during the 2023 ARRS Annual Meeting on the island of Oahu explained how the novel technique of three-dimensional (3D) slice-to-volume (SVR) MRI allows for precise delineation and measurement of the fetal optic pathway (FOP).
Noting the limited fetal presentation and low reproducibility of ultrasound-based techniques, as well as conventional MRI’s inconsistencies in FOP visualization due to low resolution (i.e., large slice thickness), “our preliminary results nevertheless demonstrate the promises and utility of this technique,” said Eric Juang, MS, of Creighton University ...
Erik Paulson gaveled in as president of American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS)
2023-04-16
Honolulu, HI | April 16, 2023—Erik K. Paulson, MD, chair of the radiology department at Duke University, has been named the 123rd President of the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) during the opening ceremony of the 2023 ARRS Annual Meeting in Honolulu, HI.
“I am absolutely honored and delighted to serve as the President of our country’s oldest radiology society, a society whose sweet spot is member education,” Dr. Paulson said in his ARRS Annual Meeting opening remarks at ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
[Press-News.org] Income rank linked to experience of physical pain, irrespective of whether in a rich or poor country, study suggestsNew study suggests that comparing one’s earnings relative to peers may induce negative emotions that lead to physical pain