(Press-News.org) McMaster University researchers have developed a rapid and inexpensive test for Salmonella contamination in chicken and other food – one that’s easier to use than a home COVID test.
The test, described in a new paper in the journal Angewandte Chemie, could improve food safety, reduce the cost of processing fresh poultry and other foods, and help to limit broad recalls to batches that have specifically been identified as contaminated.
The researchers have shown that the test provides accurate results in an hour or less without the need for accessories or a power source, compared to today’s monitoring through lab cultures, which require at least a full day to produce results.
Once scaled up and made available commercially, the new test could be a significant boon to poultry processors, for whom Salmonella is among the most significant contamination risks. The test would also be beneficial for ensuring the safe processing of other foods that are particularly vulnerable to Salmonella, such as eggs, dairy products and ground beef.
A single major poultry processor performs tens of thousands of Salmonella lab tests each year. Reducing or even eliminating the need for overnight lab cultures would represent significant savings and make it easier to identify contamination earlier in the process.
“Anyone can use it right in the setting where food is being prepared, processed or sold,” says co-author Yingfu Li, a professor of Biochemistry and Chemical Biology who leads McMaster’s Functional Nucleic Acids Research Group. “There’s a balance between cost, convenience and need. If it’s cheap, reliable and easy, why not use it?”
Protecting the public from Salmonella is a high priority for food producers, retailers and regulators alike, since Salmonella is one of the most common and serious forms of food-borne infection, causing 155,000 deaths globally every year.
What makes the test work is a new synthetic nucleic acid molecule, developed at McMaster. For the test, the molecule is sandwiched between microscopic particles such as gold.
The test platform lines the inside of the tip of a pipette and begins to work when a liquefied sample of the food being tested is drawn inside the tube.
If Salmonella bacteria are present, they cut through the particles, allowing the molecule to escape.
When the solution is dropped onto a paper test strip, the presence of Salmonella shows as a visible shade of red, thanks to a new form of biosensor, also created by the McMaster team. The greater the concentration of Salmonella, the brighter the colour appears.
“Using these tests is easier than using a COVID test, which so many people are already doing,” says co-author Carlos Filipe, chair of McMaster’s Department of Chemical Engineering. “For this to be as effective and useful as possible, it has to be easy to use.”
The new technology has been developed with support from the non-profit research organization Mitacs, and Toyota Tsusho Canada Inc., an indirect subsidiary of Toyota Tsusho Corporation in Japan, which plans to develop the innovation for commercial use.
The research is part of an ongoing, broader effort to establish McMaster and its Global Nexus for Pandemics and Biological Threats as a centre for the development of real-time sensors, pathogen-repellent materials and other products that improve food safety.
“This is very important to us in the development of our food-testing program,” says co-author Tohid Didar, an associate professor of Mechanical Engineering and Canada Research Chair in Nano-biomaterials. “Being able to create a test that is both easy to use and which produces a readily visible color within an hour is significant.”
Li, Didar and Filipe authored the paper with postdoctoral research fellow Jiuxing Li, PhD student and Vanier Scholar Shadman Khan, and research associate Jimmy Gu.
Reducing illness and food waste aligns with Toyota Tsusho Canada’s values, explained Toyota Tsusho Canada Inc. President Grant Town.
“Our goal is to help bring proven research from the lab to the marketplace, where it can benefit society,” Town says. “Reducing the risk of illness while also cutting food waste will benefit everyone, and Toyota Tsusho Canada sees this as a great opportunity.”
END
Salmonella solution
Researchers develop rapid food-contamination test to improve safety, reduce waste and lower costs
2023-04-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New genetic target for male contraception identified
2023-04-17
PULLMAN, Wash. – Discovery of a gene in multiple mammalian species could pave the way for a highly effective, reversible and non-hormonal male contraceptive for humans and animals.
Washington State University researchers identified expression of the gene, Arrdc5, in the testicular tissue of mice, pigs, cattle and humans. When they knocked out the gene in mice, it created infertility only in the males, impacting their sperm count, movement and shape. The researchers detailed their findings in the journal Nature Communications.
“The study identifies this gene for the first time as being expressed ...
The annual report on antisemitism worldwide – 2022: Haredi Jews – The main target of antisemitic assaults
2023-04-17
Embargoed until Monday, April 17th at 11AM (Israel time)
On the eve of Holocaust Remembrance Day
Tel Aviv University in cooperation with the Anti-Defamation League (ADL) presents
The Annual Report on Antisemitism Worldwide – 2022:
Haredi Jews – The Main Target of Antisemitic Assaults
2002 saw another sharp increase in the number of antisemitic incidents in the United States and other Western countries, alongside a decline in several other countries, including France, Germany, and the United Kingdom.
The report found that Haredi Jews are the main victims of antisemitic assaults in the West. Physical attacks, which ...
8.8 million euros for accelerated drug repurposing for rare neurological disorders
2023-04-17
The SIMPATHIC Consortium, led by the Radboud University Medical Center and Amsterdam UMC, has developed a new approach to expedite the use of existing drugs for groups of patients with rare neurological disorders. The consortium has been awarded an 8.8-million-euro grant from the Horizon Europe program to further develop this innovative method.
Traditionally, drugs are developed one disease at a time, which is costly and time-consuming. It often takes a long time before patients can use a new drug. The international ...
Does depression affect the care and survival of patients with breast cancer?
2023-04-17
Study’s findings suggest that detecting and treating depression are critical to patient health.
In a recent study, having depression before or after a breast cancer diagnosis was associated with a lower likelihood of survival. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
For the study, Bin Huang, DrPH, of the University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center, and his colleagues analyzed data from the Kentucky Cancer Registry to identify adult women diagnosed with primary invasive breast cancer in 2007–2011. Utilizing the health claims–linked cancer registry data, the ...
Teen jobs: Some parents cautious about negative impact on grades, sleep and social life
2023-04-17
For many teens, that first formal job as a fast-food cashier, barista or lifeguard is a rite of passage.
And while some families tout the positives of job experiences, such as improving their teen’s money management skills and self-esteem, others worry about the potential to negatively impact sleep, schedules and grades, according to the University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health.
But finding a job that meets logistical considerations – with schedules and transportation topping the list ...
ARRS Annual Meeting: 4D flow MRI, 3D phantoms benefit atrial fibrillation patients
2023-04-17
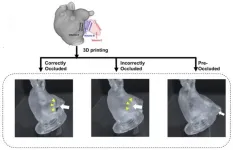
Honolulu, HI | April 17, 2023—Findings from an award-winning Scientific Online Poster presented during the 2023 ARRS Annual Meeting at the Hawaiian Convention Center suggest that correctly occluded left atrial appendages (LAAs) could present maximal reduction in left atrial (LA) flow stasis and thrombogenicity, offering a clinical goal for the procedure in patients with atrial fibrillation.
Pointing out the paucity of knowledge in atrial fibrillation (AF) populations regarding the actual flow dynamic changes before and after percutaneous left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO), “we aimed to evaluate LA flow dynamics for pre-occluded, correctly occluded, and incorrectly ...
American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) Global Partners honor Jeong Min Lee, Korean Society of Radiology (KSR) President, with ARRS membership
2023-04-17
Honolulu, HI | April 17, 2023—The Global Partner Society Program of the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) is proud to announce that Jeong Min Lee, President of the Korean Society of Radiology (KSR) and professor of radiology at South Korea’s Seoul National University Hospital, will receive Honorary Membership in ARRS during the opening ceremony of the 2023 ARRS Annual Meeting in Honolulu, HI.
As per Section 6 of the ARRS bylaws, honorary members of the ARRS shall be those who have rendered valuable service ...
Over 1 million lives saved across Europe by COVID-19 vaccines since the end of 2020
2023-04-17
**Note: the release below is from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
COVID-19 vaccination directly saved at least 1,004,927 lives across Europe between December 2020 and March 2023, according to new research being presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) in Copenhagen, Denmark (15-18 April).
The new estimates by WHO/Europe and presented at the conference by Dr Margaux Meslé, Epidemiologist at WHO/Europe highlight the striking ...
Long COVID incidence and severity no worse than post viral syndrome following seasonal influenza, study suggests
2023-04-17
**Note: the release below is from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
In the highly vaccinated population of Queensland exposed to the Omicron variant, long COVID appears to manifest as a post-viral syndrome of no greater incidence or severity than seasonal influenza, according to new research being presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) in Copenhagen, Denmark (15-18 April).
The study by Queensland Health researchers suggests that despite the similarity of clinical outcomes ...
Metagenomic sequencing outperforms conventional tests to identify antimicrobial resistance in bloodstream infections
2023-04-17
Metagenomic sequencing can provide rapid and actionable antimicrobial resistance predictions to treat bloodstream infections much faster than conventional laboratory tests, and has the potential to save lives and better manage the use of antibiotics, according to new research being presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) in Copenhagen, Denmark (15-18 April).
The study led by Dr Kumeren Govender from the John Radcliffe Hospital, University of Oxford, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
[Press-News.org] Salmonella solutionResearchers develop rapid food-contamination test to improve safety, reduce waste and lower costs