(Press-News.org) LA JOLLA, CA—La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) Instructor Estefania Quesada Masachs, M.D., Ph.D., has won the 2023 Young Investigator of the Year Award from the Network for Pancreatic Organ donors with Diabetes (nPOD). This prestigious award recognizes Quesada Masachs' groundbreaking research in type 1 diabetes.
Quesada Masachs says she was "happily surprised" to receive the award from nPOD at their 2023 conference. The organization provides pancreatic tissue samples to researchers, opening the door for in-depth research into type 1 diabetes, an autoimmune disease where the body's own immune cells target the pancreas. "This is an organization made up of scientists who really care about finding a cure for type 1 diabetes," says Quesada Masachs.
Mark Atkinson, Ph.D., Founder and Executive Director of nPOD, says the nomination committee was unanimous in selecting Quesada Masachs for the 2023 award. “The primary mission of nPOD is to increase our understanding of how and why type 1 diabetes develops," says Atkinson. “At nPOD, we believe Dr. Quesada Masachs' work brings us one step closer toward that goal. We take pride in her receiving this well-deserved award."
Type 1 diabetes affects more than 1.45 million people in the United States. Although type 1 diabetes can be managed with careful monitoring, the disease has no cure. Part of the problem in finding a cure is the lack of understanding around what actually triggers immune cells to damage the pancreas.
Quesada Masachs' background makes her an excellent person to investigate why some people develop type 1 diabetes while others do not. She studied medicine and worked as a pediatric rheumatologist before joining LJI as a postdoctoral fellow in 2018.
Her research delves into the behavior of T cells, the immune cells that can mistakenly kill insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas and cause type 1 diabetes. She also studies the local pancreatic environment and the behavior of insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells. "These cells have the ability to express inflammatory proteins, and this can call the attention of the surrounding immune system, contributing to their own demise," says Quesada Masachs. She has also shed light on how potentially destructive "autoantibodies" may add to a person's risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
This research hinges on getting access to quality samples of human pancreatic tissues. Fortunately, Quesada Masachs has established a strong collaboration with nPOD. "Good quality pancreatic tissue sections are difficult to get, but nPOD standardizes everything to get at the issue that is of the highest quality—and tissue that is absolutely suitable for research," says Quesada Masachs.
Going forward, Quesada Masachs is eager to study pancreatic tissue samples in more detail than ever before. She's currently working with the LJI Microscopy and Histology Core to harness the Institute's RareCyte Orion Slide Scanner to examine up to 18 different proteins in each tissue sample. By spotting patterns in these samples from nPOD, Quesada Masachs can get even closer to understanding the origins of type 1 diabetes.
"nPOD doesn't just provide tissues," adds Quesada Masachs. "They bring scientists together and contribute to the development of new technologies so researchers can ask new questions and get to new discoveries. With every new discovery, you are one step closer to finding a cure or therapy for type 1 diabetes."
About La Jolla Institute
The La Jolla Institute for Immunology is dedicated to understanding the intricacies and power of the immune system so that we may apply that knowledge to promote human health and prevent a wide range of diseases. Since its founding in 1988 as an independent, nonprofit research organization, the Institute has made numerous advances leading toward its goal: life without disease. Visit lji.org for more information.
END
nPOD honors Estefania Quesada Masachs for type 1 diabetes discoveries
LJI researcher delves into what triggers type 1 diabetes
2023-04-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
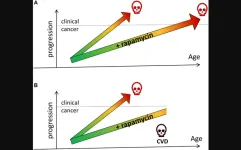
Cancer prevention with rapamycin
2023-04-17
“[...] long-term treatment with rapamycin slows down aging, a major risk factor for cancer [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- April 17, 2023 – A new research perspective was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on April 14, 2023, entitled, “Cancer prevention with rapamycin.”
The mTOR (Target of Rapamycin) pathway is involved in both cancer and aging. Furthermore, common cancers are age-related diseases, and their incidence increases exponentially with age. In his new research perspective, Mikhail V. Blagosklonny, M.D., Ph.D., from Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center discusses rapamycin and other rapalogs and their ...
Temperature, drought influencing movement of Plains bison
2023-04-17
It epitomizes the Great Plains in spirit and in form: a 2,000-pound tank on hooves, cloaked in shaggy winter-tested coat, capped by horns acting as warning and weapon.
Even its scientific name, Bison bison bison, seems to conjure an echo worthy of its majesty. Still, the implacable profile of the Plains bison — the national mammal of the United States and largest on the continent — belies the vulnerability in its history, which saw its legions decimated from tens of millions to just a few hundred in the span of a few colonial centuries.
Conservation efforts have pushed its number back to roughly 20,000, and its status from endangered ...
Oregon State researchers make breakthrough in understanding the chemistry of wildfire smoke in wine
2023-04-17
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Oregon State University researchers have discovered a new class of compounds that contributes to the ashy or smokey flavors in wine made with grapes exposed to wildfire smoke.
This development is significant for winemakers who have struggled to combat the impact of smoke on grapes at a time when climate change is leading to an increase in the number and severity of wildfires, the researchers said.
“These findings provide new avenues for research to understand and prevent smoke taint in grapes,” said Elizabeth Tomasino, an associate professor of enology ...
Coastal species persist on high seas on floating plastic debris
2023-04-17
The high seas have been colonized by a surprising number of coastal marine invertebrate species, which can now survive and reproduce in the open ocean, contributing strongly to the floating community composition. This finding was published today in Nature Ecology and Evolution by a team of researchers led by the Smithsonian Environmental Research Center (SERC) and the University of Hawai‘i (UH) at Mānoa.
The researchers found coastal species, representing diverse taxonomic groups and life history traits, in the eastern North Pacific Subtropical Gyre on over 70 percent of the plastic debris ...
UCF researchers create digital map of sympathetic nervous system
2023-04-17
UCF Researchers Create Digital Map of Sympathetic Nervous System
A team of UCF College of Medicine researchers has created a digital topographical map of the cardiac sympathetic neural network, the region that controls the body’s heart rate and its “fight-or-flight” response. They hope this map will eventually serve as a guide to treat cardiovascular conditions using bioelectronic devices.
The study, led by Dr. Zixi Jack Cheng, a neuro-cardiovascular scientist, was published in the Scientific Reports journal ...
UCF scientist publishes book on emergence of new pathogens
2023-04-17
Climate change may be linked to an increase in the emergence of new pandemics, according to a new book published by an internationally recognized College of Medicine microbiologist.
Dr. Salvador Almagro-Moreno has teamed with fellow molecular biologist Dr. Stefan Pukatzki of City University New York – CUNY, to author the book titled Vibro spp. Infections, recently published by Springer Nature and includes the latest scientific research articles in this field from experts worldwide.
The book examines the factors associated with ...
Prime editing shows proof of concept for treating sickle cell disease
2023-04-17
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – April 17, 2023) Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a serious blood disorder affecting millions of people, primarily those of African descent. A mutation in the gene that encodes a subunit of the oxygen-carrying molecule, hemoglobin, causes the disease. Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard showed a precise genome editing approach, prime editing, can change mutated hemoglobin genes back to their normal form in SCD patient cells, which restores ...
JNM publishes appropriate use criteria for lymphoscintigraphy in sentinel node mapping and lymphedema/lipedema
2023-04-17
Reston, VA—The Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) and 10 other professional societies have issued new appropriate use criteria (AUC) for lymphoscintigraphy in sentinel node mapping and lymphedema/lipedema. The criteria, summarized in the April issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine (JNM), include a list of relevant clinical scenarios, a systematic review of evidence in the literature, and a systematic analysis of available evidence, followed by grading each of the clinical scenarios.
Sentinel lymph nodes ...
Father of the photonic bandgap to speak at Utah State University
2023-04-17
Renowned physicist, engineer and entrepreneur Eli Yablonovitch will visit Utah State University on April 25 for two lectures about his work in the electrical and computer engineering field.
Yablonovitch, who is currently a professor emeritus at the University of California Berkeley, will present lectures on controlling carbon intake as a solution to climate change and on physics and optimization in the engineering world. The lectures will take place on April 25, at 1 pm and 3 pm respectively. An RSVP form can be found on this webpage. All are encouraged to attend.
“Having Dr. Yablonovitch travel to speak to us is a great honor and a great opportunity for us ...
Scientists discover pristine deep-sea coral reefs in the Galápagos Marine Reserve
2023-04-17
17 April 2023 - Galápagos, Ecuador – Scientists have discovered extensive, ancient deep-sea coral reefs within the Galápagos Marine Reserve (GMR) – the first of their kind ever to be documented inside the marine protected area (MPA) since it was established in 1998. The first reef observed was found at 400-600m (1,310-1,970 feet) depth at the summit of a previously unmapped seamount in the central part of the archipelago and supports a breathtaking mix of deep marine life.
Cresting the ridge of a submerged volcano, and stretching over several kilometers, the impressive reef structure was first recorded by Dr. Michelle ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
[Press-News.org] nPOD honors Estefania Quesada Masachs for type 1 diabetes discoveriesLJI researcher delves into what triggers type 1 diabetes