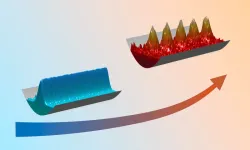
(Press-News.org) Supersolids are a relatively new and exciting area of research. They exhibit both solid and superfluid properties simultaneously. In 2019, three research groups were able to demonstrate this state for the first time beyond doubt in ultracold quantum gases, among them the research group led by Francesca Ferlaino from the Department of Experimental Physics at the University of Innsbruck and the ÖAW Institute for Quantum Optics and Quantum Information (IQOQI) in Innsbruck.
In 2021, Francesca Ferlaino's team studied in detail the life cycle of supersolid states in a dipolar gas of dysprosium atoms. They observed something unexpected: “Our data suggested that an increase in temperature promotes the formation of supersolid structures,” recounts Claudia Politi of Francesca Ferlaino's team. “This surprising behaviour was an important boost to theory, which had previously paid little attention to thermal fluctuations in this context.”
The Innsbruck scientists joined the force with the danish theoretical group led by Thomas Pohl to explore the effect of thermal fluctuation. They developed and published in Nature Communications a theoretical model that can explain the experimental results and underlines the thesis that heating the quantum liquid can lead to the formation of a quantum crystal. The theoretical model shows that as the temperature rises, these structures can form more easily.
“With the new model, we now have a phase diagram for the first time that shows the formation of a supersolid state as a function of temperature,” Francesca Ferlaino is delighted to say. “The surprising behavior, which contradicts our everyday observation, arises from the anisotropic nature of the dipole-dipole interaction of the strongly magnetic atoms of dysprosium.”
The research is an important step towards a better understanding of supersolid states of matter and was funded by the Austrian Science Fund FWF, the European Research Council ERC and the European Union, among others.
Publication: Heating a quantum dipolar fluid into a solid. J. Sanchez-Baena, Claudia Politi, F. Maucher, Francesca Ferlaino, and T. Pohl. Nature Communications 14, 1868 (2023) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-37207-3
END
Quantum liquid becomes solid when heated
First phase diagram for a supersolid at finite temperature
2023-04-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers ID gene that shapes heart attack, aneurysm risk
2023-04-18
University of School of Medicine researchers have identified a gene that plays a crucial role in determining our risk for heart attacks, deadly aneurysms, coronary artery disease and other dangerous vascular conditions.
The discovery advances our understanding of the underlying causes of a wide range of serious health conditions, including atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), and moves us closer to new treatments and preventive measures that could help people live longer, healthier lives.
“The first step towards translating the knowledge of population risk for vascular disease is disentangling the fundamental cellular ...
Extreme poverty a key driver for relapse in kids with ALL
2023-04-18
(WASHINGTON, DC, April 18, 2023) – Children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) who live in extreme poverty and were undergoing maintenance therapy faced an almost two-fold greater risk of relapse compared with kids who weren’t as poor, according to a study published in today’s issue of Blood. Moreover, a higher proportion of these children had difficulty adhering to treatment, though researchers said this only partially explains the link between poverty and the risk of relapse.
“ALL is a curable disease, so while we observed relatively few relapses in total, children living in extreme poverty – those whose families were really stretched thin and not able ...
Study: vitamin D may play a role in prostate cancer disparities
2023-04-18
Vitamin D deficiency could be the reason African American men experience more aggressive prostate cancer at a younger age compared with European American men, new research from Cedars-Sinai Cancer suggests. The multi-institutional study, published today in Cancer Research Communications, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR), could pave the way for revised nutritional guidelines.
While previous research has investigated vitamin D in the context of health disparities, this is the first study to look at its functions in a genome-wide manner in African American versus European American ...
Announcing inaugural Hevolution/AFAR New Investigator Awards in Aging Biology and Geroscience
2023-04-18
New York, New York — The American Federation for Aging Research (AFAR) and Hevolution Foundation are pleased to announce the inaugural Hevolution/AFAR New Investigator Awards in Aging Biology and Geroscience Research recipients. Eighteen three-year awards of US $375,000 each have been granted to support research projects in basic biology of aging or geroscience — a research paradigm based on addressing the biology of ...
Teasing strange matter from the ordinary
2023-04-18
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – In a unique analysis of experimental data, nuclear physicists have made the first-ever observations of how lambda particles, so-called “strange matter,” are produced by a specific process called semi-inclusive deep inelastic scattering (SIDIS). What’s more, these data hint that the building blocks of protons, quarks and gluons, are capable of marching through the atomic nucleus in pairs called diquarks, at least part of the time. These results come from an experiment conducted at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility.
It’s a result that has been ...
Study provides evidence that peer-support groups can be beneficial in reducing healthcare worker stress and burnout
2023-04-18
INDIANAPOLIS – Serving on the front lines in the arduous battle against the coronavirus, emergency department (ED) physicians are among the true heroes of the pandemic, working long, stressful hours at great personal risk, especially in the many months before vaccines became available. A pilot study examining the feasibility, receptivity and preliminary effectiveness of peer-support groups for ED doctors during COVID-19 found this support provided potential benefit in terms of reduction of mental health stresses involved in emergency care during this time.
The researchers assessed change in symptoms of distress, depression and burnout before and after participating ...
Narrative risk messaging and vaccine hesitancy
2023-04-18
Public health messages that focus on protecting others are more effective at increasing vaccination rates than messages focused on protecting oneself, according to a study. Vaccine hesitancy is a challenge for public health workers and others concerned with reducing the deleterious effects of infectious diseases. Elizabeth Shanahan and colleagues tested three visual policy narrative messages promoting COVID-19 vaccination that emphasized protecting oneself, one’s circle of friends and family, or one’s community. A non-narrative control message simply urged participants to “get the vaccine” with an accompanying image of a syringe. ...
A neural coordination strategy for attachment and detachment of a climbing robot inspired by gecko locomotion
2023-04-18
A research article by scientists at the Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics developed a neural control algorithm to coordinate the adhesive toes and limbs of the climbing robot. The new research article, published in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, provided a novel hybrid-driven climbing robot and introduced a neural control method based on CPG (Central Pattern Generator) for coordinating between adhesion and motion.
“Currently, the movement speed and stability of climbing robots have not yet reached the level of biological organisms. Animals have flexible climbing abilities on various slopes and roughness, ...
Children with COVID-19 treated safely at home, helping to take burden off hospitals
2023-04-18
Children with COVID-19 can be treated safely at home, helping to take the burden off the hospital system, according to a new study.
The research, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute and published in Archives of Disease in Childhood, found COVID-positive children with moderate symptoms or pre-existing high-risk conditions could be treated effectively via a Hospital-in-the-Home (HITH) program. Additionally, many more sick children without COVID-19 were treated at home during the pandemic.
Murdoch Children’s Dr Laila Ibrahim said the program took pressure off paediatric emergency departments ...
Increasing skeletal muscle mitochondrial efficiency after weight loss as a novel mechanism for lower energy expenditure
2023-04-18
Weight regains is a common problem for weight loss individuals. A number of studies have shown that weight loss in overweight people results in a reduction in whole-body energy expenditure. This reduction in energy expenditure is disproportionate across tissues, known as energetic mismatch which primarily originates from lean tissue, thus increasing weight regain risk. Although this phenomenon has long been identified and has been suggested that weight loss may alter skeletal muscle mitochondrial respiration, the mechanisms ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] Quantum liquid becomes solid when heatedFirst phase diagram for a supersolid at finite temperature