(Press-News.org) Using talking therapies to effectively treat depression in adults over the age of 45 may be linked with reduced rates of future cardiovascular disease, finds a new analysis of health data led by UCL researchers.
In the first-of-its-kind study, published in the European Health Journal, researchers assessed whether evidence-based psychological therapies, such as cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT), used to treat depression could play a role in reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease later in life.
Cardiovascular diseases, such as stroke and heart disease, are the leading cause of death worldwide. They represent 32% of all deaths, with 18.6 million people having died from this cause in 2019 globally. Previous studies have also shown that people who experience depression are approximately 72% more likely to develop cardiovascular disease in their lifetime, compared to people who do not.
The new research analyses data from 636,955 people over the age of 45 who accessed treatment via England’s national Improving Access to Psychological Therapies (IAPT) service, between 2012 and 2020 (soon to be called “NHS Talking Therapies for anxiety and depression”).
IAPT is a free service and offers CBT, counselling and guided self-help, with sessions delivered either face-to-face individually or in groups online.
Depressive symptoms were measured using the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9), which considers factors such as a lack of interest in doing things, issues with sleep and feelings of low mood.
Researchers then linked the IAPT outcomes (depression scores) with patients’ healthcare records to look for new incidence of cardiovascular events.
The team found that people whose depression symptoms reliably improved after psychological treatment were less likely to develop cardiovascular disease over an average of three years of follow-up, compared to those who did not.
Reliable improvement from depression (compared to no reliable improvement) was associated with a 12% decrease in future cardiovascular disease at any given time, with similar results observed for coronary heart disease, stroke and death.
The association was stronger in people below 60 years old, who had a 15% decreased risk of cardiovascular disease and 22% decreased risk of death from all causes respectively.
Meanwhile, those over the age of 60 had a 5% decreased risk of developing cardiovascular disease and 14% decreased risk of death from all other causes.
Lead author, PhD candidate Celine El Baou (UCL Psychology & Language Sciences) said: “This study is the first to establish a link between psychological therapy outcomes and future risk of cardiovascular disease.
“The findings are important as they suggest that the benefits of psychological therapy may extend beyond mental health outcomes and have long-term physical health. They stress the importance of increasing access to psychological therapy to under-represented groups, for example minority ethnic groups who may be more at risk of experiencing cardiovascular disease.”
The dataset used in this study was funded by Alzheimer’s Society.
Study limitations
Further research is needed to establish whether this link between improvement over therapy and cardiovascular disease is indeed causal, and what mechanisms would be involved. For example, the researchers had little information about lifestyle behaviours, such as exercise or smoking habits.
Another explanation for the results could be that those who respond to psychological therapy had lifestyle behaviours that were more protective of cardiovascular disease in the first place.
END
Talking therapies could reduce future risk of cardiovascular disease
Peer reviewed | Observational study | People
2023-04-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Investigating the growth of snow algal blooms on Mount Gassan, Japan
2023-04-19
Rising temperatures have led to the growth of algal blooms in water bodies, mountainous areas, and coastal regions as far as the Arctic. Recently, pigmented snow algae have been spotted on Japan’s Mount Gassan after the winter season. The presence of such algal blooms is concerning because they reduce the reflectivity of snow-covered surfaces, resulting in faster snow melting. Additionally, the algal blooms can have unforeseen impacts on the surrounding wildlife and vegetation. The growth and color of snow algae in mountainous areas appear to differ depending on the season, elevation, ...
Vesicles produced by intestinal bacteria cause a malignant cycle in patients with cirrhosis
2023-04-19
Niigata, Japan - Researchers from Niigata University and Kyoto Prefectural University have revealed that small vesicles, around 100 nm in size, released by intestinal bacteria induce immune activation and progression of liver cirrhosis, as well as reduction of serum albumin level, subsequently leading to edema and ascites.
The global prevalence of cirrhosis is high and it can be fatal upon progressing to end-stages. The progression of cirrhosis results in various symptoms including jaundice, ascites, rupture of varices, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Often, even if root causes, such as hepatitis virus, alcohol, and lifestyle factors, ...
77% of Americans have used addictive behaviors or unhealthy coping mechanisms to manage their mental health, according to Myriad Genetics nationwide survey
2023-04-19
From restricted or binge eating to excessive gambling to extreme social media use, 77% of Americans surveyed say they have used at least one addictive behavior and/or unhealthy coping mechanism to manage their mental health issues, according to the GeneSight® Mental Health Monitor, a nationwide survey from Myriad Genetics, Inc. (NASDAQ: MYGN).
Nearly all Americans (94%) surveyed agree that substance and behavioral addictions often mask underlying mental health issues. Though they may view these behaviors as addictive or as unhealthy coping mechanisms (or both), many ...
New open access journal series offers a fast and supported author experience
2023-04-19
Researchers looking to share their work openly and at pace have an exciting new publishing option that delivers on reach and impact. Launched by Taylor & Francis, the Elevate Series of broad-scope open access journals offers a fast, streamlined experience and full support in navigating the publication process.
Authors will experience the editorial excellence and high ethical standards of Taylor & Francis journals, along with personalized support at every step, allowing them to efficiently publish their work and comply ...
Time of day and a patient’s sex may alter the effectiveness of blood pressure medication
2023-04-19
New research from a team based at the University of Waterloo suggests that the time of day and a patient's sex may alter the effectiveness of certain blood pressure medications.
Biological sex and the body's circadian clock are critical factors in managing blood pressure. The circadian clock is a natural, internal process that regulates things like the sleep-wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. Among its many other functions, the circadian clock also regulates kidney function. The kidneys play ...
Young adults with cancer at greater risk for HPV-related cancers
2023-04-19
A team of researchers at Huntsman Cancer Institute and the University of Utah (the U) found that human papillomavirus-related cancer diagnoses are more common in adolescent and young adults (AYAs) who have previously had cancer. The team is led by Anne Kirchhoff, PhD, MPH, investigator in the Cancer Control and Population Sciences Research Program and associate professor of pediatrics at the U.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a very common infection spread through sexual contact. ...
Could this copycat black hole be a new type of star?
2023-04-18
It looks like a black hole and bends light like a black hole, but it could actually be a new type of star.
Though the mysterious object is a hypothetical mathematical construction, new simulations by Johns Hopkins researchers suggest there could be other celestial bodies in space hiding from even the best telescopes on Earth. The findings are set to publish in Physical Review D.
“We were very surprised,” said Pierre Heidmann, a Johns Hopkins University physicist who led the study. “The object looks identical to a black hole, but there’s light coming out from its ...
Exercise boosts brain health with chemical signals
2023-04-18
Physical activity is frequently cited as a means of improving physical and mental health. Researchers at the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology have shown that it may also improve brain health more directly. They studied how the chemical signals released by exercising muscles promote neuronal development in the brain.
Their work appears in the journal Neuroscience.
When muscles contract during exercise, like a bicep working to lift a heavy weight, they release a variety of compounds into the bloodstream. These compounds can travel to different parts of the body, including the brain. The researchers were particularly interested in how exercise could ...
Who goes to the ICU and why?
2023-04-18
More is not always better when it comes to hospital care. The same interventions that could save one patient’s life could lead to no benefit, higher hospital bills and even injury for another.
A University of Michigan led study published in the journal Intensive Care Medicine interviewed almost 90 clinicians and hospital staff and performed onsite observations across eight unaffiliated hospitals in Michigan to understand why different hospitals used the intensive care unit more than others.
“You would ...
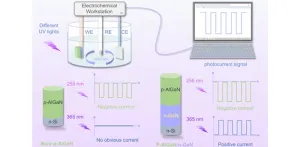
New self-powered ultraviolet photodetector
2023-04-18
Ultraviolet (UV) light detection can revolutionize industries such as civil engineering, military defense, aerospace exploration, and medical research. The future of electronics relies heavily on energy-efficient devices that can function independently, which makes the development of photoelectric UV detectors critical. These detectors come in two main types: photoconductive and photovoltaic, each with unique advantages and applications.
Photoconductive detectors rely on the changes in the conductivity ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Concrete sensor manufacturer Wavelogix receives $500,000 grant from National Science Foundation
California communities’ recovery time between wildfire smoke events is shrinking
Augmented reality job coaching boosts performance by 79% for people with disabilities
Medical debt associated with deferring dental, medical, and mental health care
AAI appoints Anand Balasubramani as Chief Scientific Programs Officer
Prior authorization may hinder access to lifesaving heart failure medications
Scholars propose transparency, credit and accountability as key principles in scientific authorship guidelines
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop DDINet for accurate and scalable drug-drug interaction prediction
IEEE researchers achieve 20x signal boost in cerebral blood flow monitoring with next-generation interferometric diffusing wave spectroscopy
IEEE researchers achieve low-power ultrashort mid-IR pulse compression
Deep-sea natural compound targets cancer cells through a dual mechanism
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
Study: Electrical stimulation can restore ability to move limbs, receive sensory feedback after spinal cord injury
Rice scientists unveil new tool to watch quantum behavior in action
Gene-based therapies poised for major upgrade thanks to Oregon State University research
Extreme heat has extreme effects r—but some like it hot
Blood marker for Alzheimer’s may also be useful in heart and kidney diseases
Climate extremes hinder early development in young birds
Climate policies: The swing voters that determine their fate
Building protection against infectious diseases with nanostructured vaccines
Oval orbit casts new light on black hole - neutron star mergers
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
[Press-News.org] Talking therapies could reduce future risk of cardiovascular diseasePeer reviewed | Observational study | People