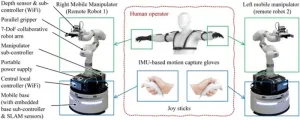
(Press-News.org) Imagine lying on a bed, you just have to move your fingers to guide a mobile robot to bring you a cup of water, open the door to fetch some deliveries, or even do some laundry. If you are interested, you may want to learn more about a new remotely operated robotic system based on two mobile manipulators. This system was developed by roboticists from Osaka University. They published a research paper describing this robotic system on Feb. 10 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems.
Back in the year of 2013, Fukushima nuclear power plant witnessed a catastrophic radioactive leakage and contamination, which makes the surrounding area extremely dangerous for humans to stay and perform emergency tasks. Under this circumstance, many robots were deployed and controlled remotely, which greatly reduced the risks and harm to rescuers. Since then, remotely operated robotic systems have been a hot research topic.
“More than being used in radiation-exposed areas, there were also many field robots developed for collecting data at distant damaged sites caused by earthquakes or other man-made and natural disasters, medical sites without expert doctors, and outer space, etc.” said the study authors.
“The research interest in remote control has been further signified in the past 2 years as the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic restricted people’s movement. A series of robots were developed and remotely deployed at the Wuhan hospitals to assist doctors and patients” said Weiwei Wan, the corresponding author of this study, from the Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University.
Compared with former research, which tends to contain one mobile base and one or two robotic arms mounted on this base, this study features two separate mobile bases. Each base is mounted with a manipulator. Each manipulator-mounted base is controlled by one hand. In particular, the human teleoperator’s poses of each hand were recorded by a motion capture system to control the poses of the respective robotic arm. In addition, the operator can move the two mobile bases using two joysticks. Therefore, these two mobile manipulators can work in a cooperative manner, like how we use our hands.
“The proposed idea of incorporating two independently movable manipulators for motion-tracking-based teleoperation is intriguing. However, there are some inherent issues to be addressed.” Said Wan, “First of all, how to map the postures of the human teleoperator’s two arms to the corresponding manipulator’s poses. In addition, how to avoid it when under some circumstances, the manipulator may collide with itself. Moreover, how to remotely monitor the two manipulators with the large operating range.” They believe they have addressed these issues by applying special routines and hand-mounted cameras.
They demonstrate this robotic system by picking up a coffee mug and handing over it using only one mobile manipulator. More importantly, the two mobile manipulators can work in a cooperative manner to pick up and place long sticks. “Since there are two mobile manipulators, the presented system could keep the advantages of having two arms while extending the human body functions.” said Wan, “The results demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed system, resulting in extending the human body to a large space while keeping the benefits of having two limbs.”
In the future, they will focus on addressing several remaining problems including a) developing an automatic calibration method to match the direction of the human teleoperator’s arms and the manipulators; b) using a joystick with built-in IMU sensor to allow the teleoperator more flexibly control the joystick; c) minimizing the coordination errors between two manipulators; d) providing a feedback interface for teleoperation in a distant and unseen workspace.
The authors of the paper include Yusuke Hirao, Weiwei Wan, Dimitrios Kanoulas, and Kensuke Harada.
The research is funded by the UKRI Future Leaders Fellowship (RoboHike) and the UCL-Osaka University Strategic Partner Fund 2021.
The paper, “Body Extension by Using Two Mobile Manipulators,” was published in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems on Feburary 10, 2023, at DOI: https://doi.org/10.34133/cbsystems.0014
Reference
Authors: Yusuke Hirao1, Weiwei Wan1, Dimitrios Kanoulas2, and Kensuke Harada1
Title of original paper: Body Extension by Using Two Mobile Manipulators
Journal: Cyborg and Bionic Systems
DOI: 10.34133/cbsystems.0014
Affiliations:
1Graduate School of Engineering Science, Osaka University, Osaka, Japan.
2Department of Computer Science, University College London, London, UK.
END
Body extension by using two mobile manipulators
2023-04-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Advance care planning produces trend toward less aggressive and more comfort- focused care for patients with cancer
2023-04-20
INDIANAPOLIS – A meta-analysis of studies involving 33,541 cancer patients evaluates the relationship between advance care planning and aggressive vs. comfort-focused end-of-life care. The study, led by Kristin Levoy, PhD, MSN, RN, of the Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of Nursing, found a general trend toward less aggressive and more comfort-focused end-of-life care among cancer patients who had engaged in advance care planning, compared to those who did not do so.
Advance care planning is a dynamic process to help prepare people for future decision-making with the goal of ensuring that individuals receive care at the end-of-life that is consistent ...
Ground reaction force and moment estimation through EMG sensing using long short-term memory network during posture coordination
2023-04-20
Imagine by only attaching a number of electromyography (EMG) sensors to your legs, your motion in the future several seconds can be predicted. Such a way of predicting motion via muscle states is an alternative to the mainstream visual cue-based motion prediction, which heavily relies on multi-view cameras to construct time-series posture. However, there is still a gap between muscle states and future movements.
Muscles act upon the ground, which induces ground reaction force. Together with muscle states and ground reaction force, body movements are produced. Therefore, estimating ...
ASBMB cautions against sacrificing science funds to make debt-ceiling deal
2023-04-20
The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology released a statement this week calling on policymakers participating in debt-ceiling negotiations to preserve funding to major scientific agencies such as the National Institutes of Health, National Science Foundation and the Department of Energy.
In January, the United States reached its debt limit of $31.4 trillion. House Republicans are resisting raising the debt ceiling unless federal spending levels are reduced to fiscal year 2022 levels, which would reduce discretionary funding ...
Important role of intestinal immune cells in iron deficiency identified for the first time
2023-04-20
Iron deficiency is one of the five main causes of impaired health. It affects 30 percent of the world's population, particularly women. Why iron deficiency can occur, even if enough iron is supplied through the diet, has not yet been sufficiently clarified in scientific research. For the first time, a research team from MedUni Vienna has discovered that certain immune cells in the intestine play an important role in iron absorption in the body. The study results may provide a new approach for possible therapeutic measures and were recently published in the journal "Blood".
Approximately one to two milligrams of ...
Versatile, high-speed, and efficient crystal actuation with photothermally resonated natural vibrations
2023-04-20
Every material possesses a unique natural vibration frequency such that when an external periodic force is applied to this material close to this frequency, the vibrations are greatly amplified. In the parlance of physics, this phenomenon is known as “resonance.” Resonance is ubiquitous in our daily life, and, depending on the context, could be deemed desirable or undesirable. For instance, musical instruments like the guitar relies on resonance for sound amplification. On the other hand, buildings and bridges are more likely to collapse under an earthquake if the ground vibration frequency matches their natural frequency.
Interestingly, natural vibration has not received ...
Children’s language development doesn’t just happen through words
2023-04-20
Children learn to understand language and to speak largely independently of cognitive functions like spatial awareness, working (short-term) memory and perception (interpreting and organizing sensory impressions), according to established theory and tradition within linguistics.
Professor Mila Vulchanova at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) heads the university's language laboratory and studies language learning. Her findings over several years have challenged this linguistic assumption and demonstrated ...
Researchers identify a potential new therapeutic target in Parkinson’s disease
2023-04-20
TORONTO - In a study published in Nature Communications, a team led by Krembil Brain Institute Senior Scientists, Drs. Lorraine Kalia and Suneil Kalia, and University of Toronto (U of T) Professor, Dr. Philip M. Kim, identified a protein-protein interaction that contributes to Parkinson’s disease.
In the disease, a protein called α-synuclein (a-syn) accumulates in the brain and leads to cell death. Much research is currently focused on clearing a-syn with antibodies or using small molecules to prevent a-syn from aggregating. In this study, the researchers took an alternate approach by looking for protein-protein interactions that may be promoting ...
Dr. Natalya Chernichenko named site chief of otolaryngology at NewYork-Presbyterian Brooklyn Methodist Hospital
2023-04-20
Dr. Natalya Chernichenko, a leading otolaryngologist who specializes in tumors of the head and neck, has been named site chief of otolaryngology at NewYork-Presbyterian Brooklyn Methodist Hospital, effective May 1. Dr. Chernichenko was also recruited to Weill Cornell Medicine as an assistant professor of clinical otolaryngology and vice chair in the Department of Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery.
In her new role, Dr. Chernichenko will lead a skilled team of specialists and surgeons providing comprehensive otolaryngology care, also known as ear, nose and throat, or ENT care, and further develop the hospital’s head and neck surgical oncology ...
FAU gets $6 million to increase mental health counselors in Florida schools
2023-04-20
Youth mental and emotional health is a matter of high priority in Florida. A 2019 Florida Department of Health survey showed that 12.7 percent of Florida high schoolers (grades 9 to 12) had carried a weapon; 21.2 percent were involved in a physical altercation; 24.2 percent reported having been teased about their size, weight or physical appearance; and 11.3 percent and 14.9 percent were bullied electronically or on school property, respectively.
In this same survey, 15.6 percent of Florida high school students reported they had seriously considered attempting suicide, and 33.7 percent acknowledged feeling sad or hopeless for two or more weeks in a row. Alarmingly, the 2019 survey ...
University of Cincinnati research examines the impact of maternal stress during pregnancy on child’s health
2023-04-20
New research out of the University of Cincinnati examines the impact that maternal stress during pregnancy has on the neurodevelopment of babies.
The study was published in the journal Molecular Psychiatry.
Prenatal maternal stress life events are associated with adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes in offspring. Biological mechanisms underlying these associations are largely unknown, but a chemical reaction in the body in which a small molecule known as a methyl group gets added to DNA, called DNA methylation, likely plays a role, according to researchers. These findings could provide new insights into how the fetal environment potentially influences ...