(Press-News.org) About The Study: The results of this study suggest that the COVID-19 crisis exacerbated pre-existing inequities in food insecurity and difficulty paying rent according to race and ethnicity and maternal nativity and that equity-focused policy changes are needed to ensure that all children and their families in the U.S. can afford basic needs for optimal health.
Authors: Stephanie Ettinger de Cuba, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the Boston University School of Public Health, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.0508)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama-health-forum/fullarticle/10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.0508?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=042123
About JAMA Health Forum: JAMA Health Forum is an international, peer-reviewed, online, open access journal that addresses health policy and strategies affecting medicine, health and health care. The journal publishes original research, evidence-based reports and opinion about national and global health policy; innovative approaches to health care delivery; and health care economics, access, quality, safety, equity and reform. Its distribution will be solely digital and all content will be freely available for anyone to read.
END
Association of hardship among families with young children with federal relief program participation
JAMA Health Forum
2023-04-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Social media data provides first glimpse at increased popularity of air conditioning worldwide
2023-04-21
With temperatures rising worldwide, more and more people globally consider air-conditioning an essential element of living with climate change. However, air-conditioning units are also rather power-hungry and are likely to increase energy consumption in areas where they are used often. To limit the impact of air-conditioners on our energy grids and our climate, we need data to better understand where they're sold globally. That's quite a struggle in regions where that data is not available. However, through social media advertising ...
Study shows most children recover from Lyme disease within six months of treatment
2023-04-21
WHAT:
A majority of parents of children diagnosed with Lyme disease reported that their kids recovered within six months of completing antibiotic treatment, according to a new joint study from Children’s National Research Institute and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, published in Pediatric Research. The findings, based on Lyme disease treatment outcome data from 102 children in the United States, also revealed that a notably small percentage of children took longer than six months to recover ...
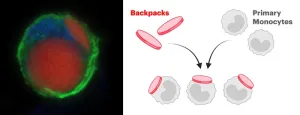
A backpack full of multiple sclerosis therapy
2023-04-21
A backpack full of multiple sclerosis therapy
A cell therapy using myeloid cells bound to drug delivery microparticles reduces disease burden in a preclinical multiple sclerosis model.
By Benjamin Boettner
(BOSTON) — Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a devastating autoimmune disease that destroys the protective myelin covering around nerves, disrupting communication between the brain and body, and causing patients’ ability to move and function to progressively decline. The MS atlas reported in 2020 that someone is diagnosed with MS every five minutes around the world, adding ...
USTC realizes light-driven programmable colloidal self-assembly
2023-04-21
Prof. PENG Chenhui's team from the School of Physics, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), realized the collective transfer and reconfigurable self-assembly of colloidal particles by combining the light-driven molecular motors with liquid crystal (LC) molecules in the nematic phase whose orientations are programmed with topological patterns and disclination networks. The work was published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America on April 11th. Through light irradiation, the cooperative reorganizations of nanomotors induce collective dynamics of the disclination networks. The morphology ...
Tiny plastic particles also find their way into the brain
2023-04-21
The study was carried out in an animal model with oral administration of MNPs, in this case polystyrene, a widely-used plastic which is also found in food packaging. Led by Lukas Kenner (Department of Pathology at MedUni Vienna and Department of Laboratory Animal Pathology at Vetmeduni) and Oldamur Hollóczki (Department of Physical Chemistry, University of Debrecen, Hungary) the research team was able to determine that tiny polystyrene particles could be detected in the brain just two hours after ingestion. The mechanism that enabled them to breach the blood-brain barrier ...
On-demand preparation of organosilicon reagents
2023-04-21
National University of Singapore (NUS) scientists have demonstrated that stepwise customised functionalisation of multihydrosilanes to access fully substituted silicon compounds can be realised using neutral eosin Y, an inexpensive dye molecule.
The development of a unified catalytic platform for stepwise and programmable functionalisation of multihydrosilanes is highly challenging. However, having this platform will facilitate the rational design of organosilanes with predictable functions, in which bespoke silane molecules are required. Three specific requirements ...
Green living environment in early childhood does not protect against eczema
2023-04-21
According to a new Finnish study, greenness around the home in early childhood does not seem to protect children from atopic eczema. Instead, the proximity of coniferous, mixed forests and agricultural areas was associated with elevated risk of eczema. The effect was seen especially in children who were born in the spring.
“General greenness around the home did not protect children against eczema, which was contrary to our expectations and to the hypothesised allergy protective effect of nature contacts. Eczema is, however, only one of the allergic diseases in children, albeit generally the first to emerge,” says MD Minna Lukkarinen, a paediatric specialist from the ...
Finnish population-based study: Vulnerable groups were the least likely to uptake COVID-19 vaccination
2023-04-21
A large-scale registry study in Finland has identified several factors associated with uptake of the first dose of COVID-19 vaccination. In particular, persons with low or no labor income and persons with mental health or substance abuse issues were less likely to vaccinate.
The study, carried out in collaboration between the University of Helsinki and the Finnish Institute of Health and Welfare, tested the association of nearly 3000 health, demographic and socio-economic variables with the uptake of the first COVID-19 vaccination dose across the entire Finnish population.
This work, just published in the Nature Human Behavior, is the largest study ...
Best practices in new product development: what separates the Best from the Rest?
2023-04-21
No single one practice is sufficient for greater innovation performance, say the researchers, overviewing the results of the most recent PDMA's 2021 global survey. The Best companies, according to the results, are better at employing multiple types of innovation, but the spend more time on radical innovation, are oriented towards risk-taking, and employ long-term strategies. The results were drawn from responses from 651 companies in 37 countries, the most extensive PDMA survey so far.
“I believe, we should fundamentally look ...
New study: No evidence that shielding reduced COVID-19 infections in Wales
2023-04-21
A research team from Swansea University have been examining data from the year after the policy was introduced in March 2020, concluding that a “lack of clear impact on infection rates raises questions about the success of shielding.”
Shielding was introduced to protect those thought to be at highest risk of serious harm should they catch COVID-19, for example because of preconditions such as cancer or medications that they were taking. Key to protecting vulnerable people was to reduce their risk of contracting COVID-19.
The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Association of hardship among families with young children with federal relief program participationJAMA Health Forum