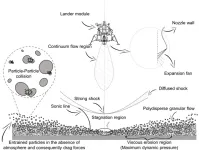
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, April 25, 2023 – When a lander descends toward the moon – or a rocky planet, asteroid, or comet – the exhaust plume of the rocket interacts with the surface, causing erosion and kicking up regolith particles. The resulting blanket of dusty debris can create a dangerous brownout effect, limiting visibility and potentially damaging the spacecraft or nearby equipment.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Chungnam National University, the University of Edinburgh, Gyeongsang National University, and the Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information developed a model to describe the interaction between a rocket plume and the surface of a planetary body in near-vacuum conditions. The results can be used to evaluate the safety and feasibility of a proposed landing site and to optimize the design of spacecraft and rocket engines for planetary landings.
“Understanding the interaction between the rocket plume and the surface is important for the safety and success of space missions in terms of contamination and erosion, landing accuracy, planetary protection, and engineering design, as well as for scientific understanding and future exploration,” said author Byoung Jae Kim of Chungnam National University.
The computational framework takes in information about the rocket, its engines, and the surface composition and topography, as well as the atmospheric conditions and gravitational forces at the landing site.
By considering the interaction of the gas with solid particles as a system of equations, the simulation estimates the shape and size of the plume, the temperature and pressure of the plume and surface, and the amount of material eroded or displaced. It does so in a way that is more computationally efficient than previous methods.
“Our tool can simulate the plume surface interaction problem at the fundamental level (e.g., scour pattern formation and development of erosion models) and for practical engineering applications (e.g., predicting particle trajectories to avoid damage to the lander and previously established sites and planning descend/ascend scenarios),” said Kim.
In the model, small regolith particles reached high altitudes and caused severe brownout effects during ascent and descent. In contrast, larger particles with increased bed height led to a more favorable brownout status.
“The insights gained from this study of the effects of different parameters on plume-surface interaction can inform the development of more effective and efficient landing technologies,” said Kim. “The study also sheds light on the festooned scour patterns that can be observed on planetary surfaces, which can provide valuable information for future scientific investigations of planetary bodies.”
The researchers plan to improve the capabilities of the framework to include more complex physics, such as chemical reactions and solid particle collisions. They believe the model can be applied to other physics scenarios including needle-free drug delivery systems.
###
The article “Full continuum approach for simulating plume-surface interaction in planetary landings” is authored by Omid Ejtehadi, Rho Shin Myong, Ilyoup Sohn, and Byoung Jae Kim. It will appear in Physics of Fluids on April 25, 2023 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0143398). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0143398.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Physics of Fluids is devoted to the publication of original theoretical, computational, and experimental contributions to the dynamics of gases, liquids, and complex fluids. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/phf.
###
END
How to land on a planet safely
Simulations capture the interaction between a rocket plume and the surface and find ways to make planetary descents and ascents safer.
2023-04-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
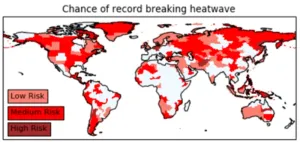
Global research reveals countries where record-breaking heatwaves are likely to cause most harm
2023-04-25
A new study has highlighted under-prepared regions across the world most at risk of the devastating effects of scorching temperatures.
The University of Bristol-led research, published today in Nature Communications, shows that unprecedented heat extremes combined with socioeconomic vulnerability puts certain regions, such as Afghanistan, Papua New Guinea, and Central America, most in peril.
Countries yet to experience the most intense heatwaves are often especially susceptible, as adaptation measures are often only introduced after the event. A high chance of record-breaking ...
Using artificial intelligence to create a tsunami early warning system
2023-04-25
Cardiff University media release/Datganiad i’r wasg gan Brifysgol Caerdydd
Under embargo until 16:00 BST/11:00 EST on Tuesday 25 April 2023/O dan embargo tan 16:00 BST/11:00 EST ddydd Mawrth 25 Ebrill 2023
Using artificial intelligence to create a tsunami early warning system
Real-time classification of underwater earthquakes enables earlier and more reliable tsunami alerts
An early warning system that quickly classifies submarine earthquakes and determines the risk of tsunami events has been developed by scientists at Cardiff ...
Researchers at Albert Einstein College of Medicine discover how long-lasting memories form in the brain
2023-04-25
April 25, 2023—(BRONX NY)—Helping your mother make pancakes when you were three…riding your bike without training wheels…your first romantic kiss: How do we retain vivid memories of long-ago events? As described in a paper published online on April 25 in Neuron, researchers at Albert Einstein College of Medicine have found the explanation.
“The ability to learn new information and store it for long periods is one of the brain’s most remarkable features,” said Robert H. Singer, Ph.D., ...
Researchers find rhythmic brain activity helps to maintain temporary memories
2023-04-25
New research shows that rhythmic brain activity is key to temporarily maintaining important information in memory. Researchers at the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience at the University of Rochester published these findings today in Current Biology that found brain rhythms—or patterns of neuronal activity—organize the bursts of activity in the brain that maintain short-term connections.
“The thought has been that the temporary storage of important information is linked to neurons in the brain that just fire away, retaining that information until it is no longer needed. Recent research has shown that it might not be such persistent ...
Near-universal T cell immunity towards a broad range of bacteria
2023-04-25
Typically T cells of the immune system respond to a specific feature (antigen) of a microbe, thereby generating protective immunity. As reported in the journal Immunity, an international team of scientists have discovered an exception to this rule. Namely, a group of divergent bacterial pathogens, including pneumococci, all share a small highly conserved protein sequence, which is both presented and recognized by human T cells in a conserved population-wide manner.
The study set out to understand immune mechanisms that protect against pneumococcus, a bacterial pathobiont that can reside harmlessly in the upper respiratory mucosae but can also cause infectious ...
Novel living yeast-based dual biosensor for detecting peptide variants
2023-04-25
Biosensors—sensors that can detect biological samples—are powerful tools for understanding the function, composition, and structure of biochemical molecules. Biosensors are often applied for the detection of proteins and their subunits, called peptides, yielding a wide range of biomedical applications. In 2017, researchers from Columbia University in USA engineered a living yeast biosensor by rewiring pheromone-related signaling pathways used by yeast for mating. In the presence of the pheromone peptide, the G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) could detect the peptide, triggering a cascade that would eventually activate a ...
Sizing them up! An algorithm to accurately quantify rapeseed silique morphology
2023-04-25
Rapeseed or oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) is an important crop cultivated worldwide for its oil-rich seeds. The rapeseed silique is an organ that plays a role in photosynthesis, sends developmental signals to maturing seeds, and provides a capsule that harbors the seeds. High-yield rapeseed varieties have both a high number and optimal morphology–the form and structure–of siliques. In this regard, rapeseed genotype and cultivation method directly influence the number of siliques that a plant produces. Thus, accurately quantifying silique development parameters is critical for predicting ...
Columbia University launches Center for Precision Psychiatry & Mental Health with $75 million grant from the Stavros Niarchos Foundation
2023-04-25
NEW YORK, April 24, 2023—Columbia University today announced the establishment of the Stavros Niarchos Foundation (SNF) Center for Precision Psychiatry & Mental Health at Columbia University. The center will catalyze the scientific innovation and clinical implementation of precision medicine to advance the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of mental illness. The center is being established with a $75 million grant from the Stavros Niarchos Foundation (SNF), an international philanthropic organization, as part of SNF’s Global Health Initiative (GHI).
The SNF Center is a joint effort of the Department of Psychiatry at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians ...
Research links common insecticide to neurodevelopmental disorders
2023-04-25
A new study from The University of Toledo suggests early exposure to a common class of insecticides called pyrethroids may increase the risk of autism and other developmental disorders, even at levels currently recognized as safe by federal regulators.
The findings, which come from a study of mice, were published today in the peer-reviewed journal PNAS Nexus.
Pyrethroids are some of the most widely used insecticides in the country, appearing in both consumer products and industrial preparations.
“If ...
New research sheds light on how to choose quality eHealth tools
2023-04-25
With so many eHealth tools available, it can be challenging to select the best one for a specific health need. A recent study published in JMIR Human Factors provides valuable insights on how to choose quality eHealth tools in an evolving landscape of digital health technology. This study titled “Assessing the Quality and Impact of eHealth Tools: Systematic Literature Review and Narrative Synthesis” comprehensively examined how the quality and impact of eHealth tools are currently assessed.
Led by Dr Christine Jacob, a health tech researcher at the University of Applied Sciences and Arts Northwestern ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Minimally invasive procedure effectively treats small kidney cancers
SwRI earns CMMC Level 2 cybersecurity certification
Doctors and nurses believe their own substance use affects patients
Life forms can planet hop on asteroid debris – and survive
Sylvia Hurtado voted AERA President-Elect; key members elected to AERA Council
Mount Sinai and King Saud University Medical City forge a three-year collaboration to advance precision medicine in familial inflammatory bowel disease
AI biases can influence people’s perception of history
Prenatal opioid exposure and well-being through adolescence
Big and small dogs both impact indoor air quality, just differently
Wearing a weighted vest to strengthen bones? Make sure you’re moving
Microbe survives the pressures of impact-induced ejection from Mars
Asteroid samples offer new insights into conditions when the solar system formed
Fecal transplants from older mice significantly improve ovarian function and fertility in younger mice
Delight for diastereomer production: A novel strategy for organic chemistry
Permafrost is key to carbon storage. That makes northern wildfires even more dangerous
Hairdressers could be a secret weapon in tackling climate change, new research finds
Genetic risk for mental illness is far less disorder-specific than clinicians have assumed, massive Swedish study reveals
A therapeutic target that would curb the spread of coronaviruses has been identified
Modern twist on wildfire management methods found also to have a bonus feature that protects water supplies
AI enables defect-aware prediction of metal 3D-printed part quality
Miniscule fossil discovery reveals fresh clues into the evolution of the earliest-known relative of all primates
World Water Day 2026: Applied Microbiology International to hold Gender Equality and Water webinar
The unprecedented transformation in energy: The Third Energy Revolution toward carbon neutrality
Building on the far side: AI analysis suggests sturdier foundation for future lunar bases
Far-field superresolution imaging via k-space superoscillation
10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
[Press-News.org] How to land on a planet safelySimulations capture the interaction between a rocket plume and the surface and find ways to make planetary descents and ascents safer.